Mutualism Drawing
Mutualism Drawing - In this case, pollinators land on the milkweed flower and stand on “landing. Examples of mutualisms cleaning mutualisms. In exchange, they get a free ride and a meal from. Web this page titled 8.4: Web the three relationships — mutualism commensalisms, and parasitism — are the type of organism that exhibits symbiosis. Mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, and competition. In this video, you will see some great examples of how different species benefit each other. Mutualism is a close, symbiotic relationship that mutually benefits two different species present in an ecosystem. This resource addresses the following standards: Other types of symbiotic relationships include parasitism (where one species benefits and the other is. To learn about these relationships, let's imagine diving deep into the ocean. Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship in which two species benefit each other.; Mutualism is the interspecies symbiotic relationship wherein both species benefit from their mutual. Parasitism is a relationship between two species in which one benefits and the other is. Mutualism is found ubiquitously throughout all ecosystems. Here, you might spot a group of clownfish swimming in a bed of sea anemones. Mutually beneficial interactions, in contrast, may become so interdependent that each organism requires the other for survival. Imagine you are diving in the pacific ocean. This resource addresses the following standards: Web evolution of mutualisms. This resource addresses the following standards: Web mutualism is a term used to describe a symbiotic relationship between two or more different species. Mutualism ecology match symbiotic relationships symbiosis symbiosis worksheet. There are hundreds of examples of mutualism between a heterotroph and an alga. Mutually beneficial interactions, in contrast, may become so interdependent that each organism requires the other for. Symbiotic relationships in which each species benefits are mutualistic. There four main symbiotic relationships: Amenalism is a relationship where one species is harmed and the other is unaffected.; Web millions of species roam planet earth, and they have to figure out how to share resources such as food and shelter. In this video, you will see some great examples of. Mutualism, association between organisms of two different species in which each benefits. Web mutualistic interactions are mutually beneficial species interactions. Depending upon the types of relationships in nature, organisms may be classified into the above three classes. Web there are four main types of symbiosis: Mutualism is the interspecies symbiotic relationship wherein both species benefit from their mutual. Predatory interactions may reduce the number of organisms or eliminate whole populations of organisms. An interaction in which both types of organisms benefit symbiosis: Web mutualism describes a type of mutually beneficial relationship between organisms of different species. Mutualistic interactions are common but sometimes rather complicated. Examples of mutualisms cleaning mutualisms. Mutualism, association between organisms of two different species in which each benefits. In this video, you will see some great examples of how different species benefit each other. Imagine you are diving in the pacific ocean. Here, you might spot a group of clownfish swimming in a bed of sea anemones. Web there are four main types of symbiosis: Web evolution of mutualisms. They also scream when predators approach. Commensalism occurs when one species benefits, and the other is unharmed. There four main symbiotic relationships: The paramecium certainly benefits from the food synthesized by the alga. It is a symbiotic relationship in which two different species interact with and in some cases, totally rely on one another for survival. Examples of mutualisms cleaning mutualisms. Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship in which two species benefit each other.; Mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, and competition. Web millions of species roam planet earth, and they have to figure out how to. Web it is widely believed that mutualisms, interspecific interactions that benefit both species, have been grossly neglected relative to their true importance in nature. Web competition, predation, and mutualism. In this video, you will see some great examples of how different species benefit each other. Imagine you are diving in the pacific ocean. Mutualistic arrangements are most likely to develop. The termite benefits from the. Mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, and competition. An interaction in which one organism is consumed by another For example, termites have a mutualistic relationship with protists that live in the insect’s gut (figure 17.2.2 17.2. Web a mutualism (or mutualistic symbiosis) is a relationship between two or more organisms, where each partner benefits from living with the other. I have reviewed the recent primary literature in order to assess quentitatively the frequency of studies of mutualism, the types of questions they address, and their general scientific approach. Creatures interact with one other in a variety of ways, and these relationships are known all together as symbiosis. Mutualism is found ubiquitously throughout all ecosystems. Web it is widely believed that mutualisms, interspecific interactions that benefit both species, have been grossly neglected relative to their true importance in nature. Web millions of species roam planet earth, and they have to figure out how to share resources such as food and shelter. Web this page titled 8.4: Web mutualism is a type of relationship between organisms where both animals benefit. Web evolution of mutualisms. It thus is a type of association where all the partners work together, with each partner benefiting from the relationship. There four main symbiotic relationships: Other types of symbiotic relationships include parasitism (where one species benefits and the other is.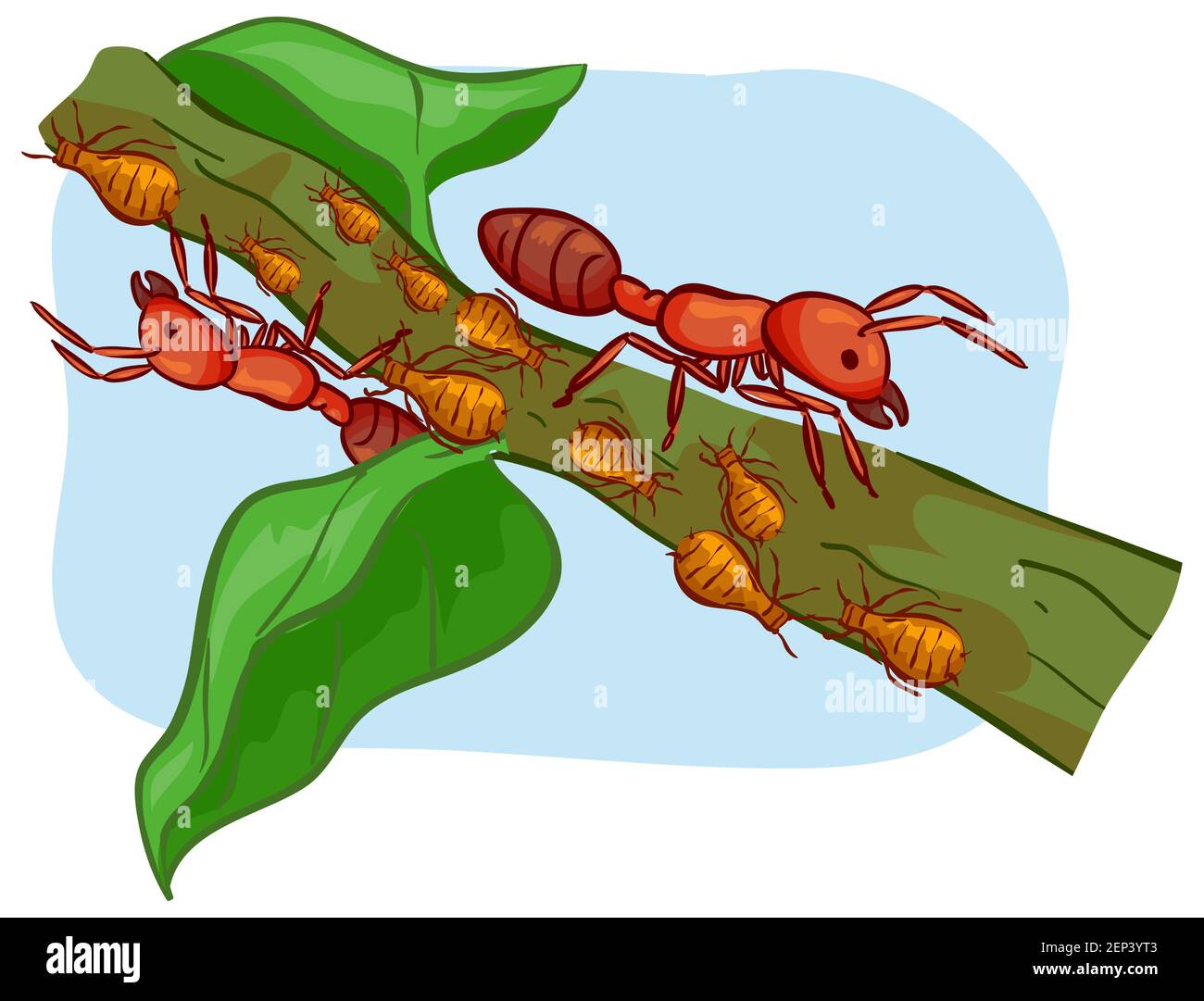
Illustration of Ants and Aphids Crawling on a Branch, Symbiotic

Mutualism Examples Drawing

15 Mutualism Examples Fauna Facts

Mutualism — Definition & Examples Expii
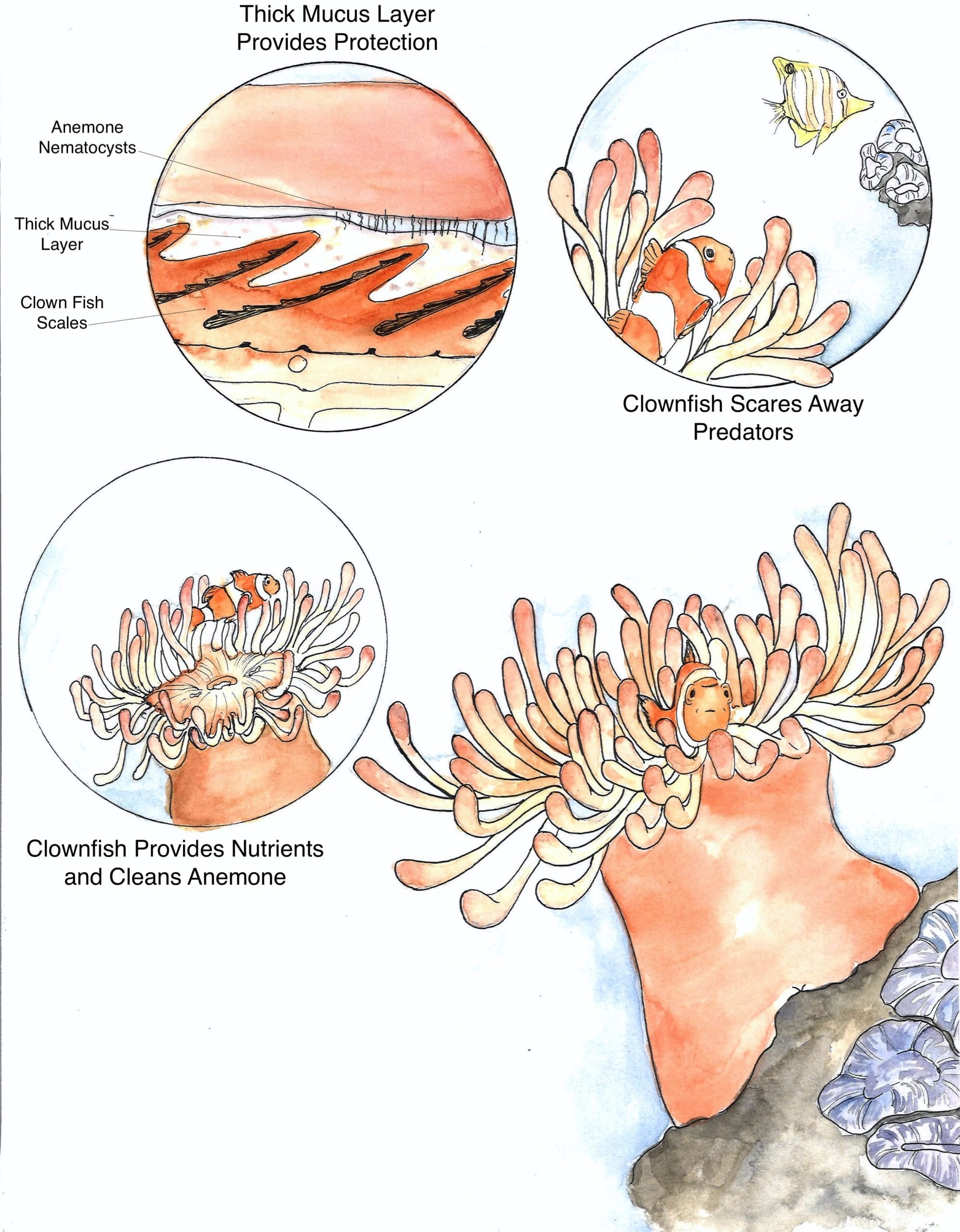
The sea anemone and the clownfish have a mutually beneficial

Learn to Draw Mutualism Ghost Pipes and Tube Worms Sierra Club BC

Mutualism Definition and Examples in Biology

20_2018_Mutualism Art+Science

Learn to Draw Mutualism Ghost Pipes and Tube Worms Sierra Club BC

Biology Classroom, Biology Teacher, Teaching Biology, Science Biology
Web Competition, Predation, And Mutualism.
Mutualisms, Interactions Between Two Species That Benefit Both Of Them, Have Long Captured The Public Imagination.
This Means Helping The Poor Help Themselves By.
It Is A Form Of Symbiosis That Organisms Develop For Any Of A Number Of Reasons, Including A Need For Protection, Nutrition, Shelter, Or Reproduction.
Related Post: