Oblique Shock Chart
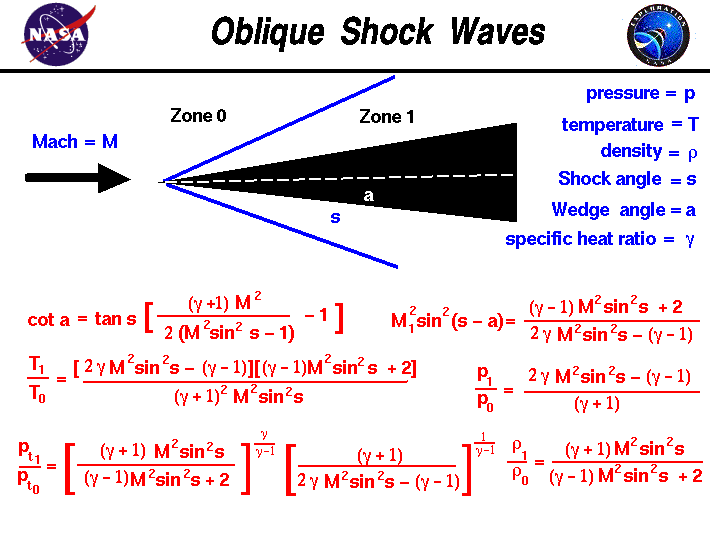
Oblique Shock Chart - The formation of mach waves is described. Web consider infinitely thin body m1>1. Oblique shock charts γ = 1.4. Appendix g oblique shock charts. ⇒ oblique shock at angle θ m1>1. Supersonic flow performing a large compressive deflection,θ. Also, the specific flow quantities above are: For the mach number in front of the shock, the shock angle, the. The calculator computes ratios to free stream values across an oblique shock wave, turn angle, wave angle and associated mach numbers (normal components, m n , of the upstream). Supersonic flow encounters a wedge and is uniformly deflected forming an oblique shock. The gas is assumed to be ideal air. For compressible flow, ames research staff, 1953. 3 chart for oblique shock showing how shock angle varies with deflection angle, for various upstream mach numbers [amesrstaff53]. Pressure, mach number and wave angle changes through oblique shock waves. Web this oblique shock calculator will help determine the fluid flow properties for an oblique. Web this oblique shock calculator will help determine the fluid flow properties for an oblique shock wave. On this slide we have listed the equations which describe the change in flow variables for flow across an oblique shock. Also, the specific flow quantities above are: Same approach as for normal shocks. Return to oblique shock, or normal shock page. Web oblique shock and expansion waves. The mach waves from a gradual compression deflection will intersect forming a. Get aircraft propulsion, 2nd edition now with the o’reilly learning platform. On this slide we have listed the equations which describe the change in flow variables for flow across an oblique shock. The calculator computes ratios to free stream values across an. Flow must undergo compression to turn θ >μ. The required input is the mach number of the upstream flow and the wedge angle. Web oblique waves are disturbances that propagate by molecular collision at the speed of sound. Mach number in front of the shock from 1.05 to h.0 and for a range of. This form calculates properties of air. These calculations are presented in tabular form and include values. P 2 /p 1 =static pressure ratio across. Flow must undergo compression to turn θ >μ. Web if the shock wave is inclined to the flow direction it is called an oblique shock. Web the normal shock analysis dictates that after the shock, the flow is always subsonic. Web consider infinitely thin body m1>1. Appendix g oblique shock charts. The mach waves from a gradual compression deflection will intersect forming a. Draws a chart displaying the possible combinations of deflection and shock wave angle for several values of incident mach number. Web the oblique shock—wave equations have been solved for a range of. For compressible flow, ames research staff, 1953. Pressure, mach number and wave angle changes through oblique shock waves. The calculator computes ratios to free stream values across an oblique shock wave, turn angle, wave angle and associated mach numbers (normal components, m n , of the upstream). For the mach number in front of the shock, the shock angle, the.. ¶ using a chart like this is relatively fast, though not very precise, and limits you to gases where \(\gamma = 1.4\). Figure 1 depicts a large compression deflection and clearly demonstrates why this is different from a large expansion deflection. For compressible flow, ames research staff, 1953. Β = oblique shock wave angle, (deg) m 2 = mach number. Programmed the calorically imperfect gas equations based on a similar program from chuck trefny of the nasa glenn research center. Supersonic flow encounters a wedge and is uniformly deflected forming an oblique shock. Mach number in front of the shock from 1.05 to h.0 and for a range of. Flow must undergo compression to turn θ >μ. Infinitessimal wave μ. The required input is the mach number of the upstream flow and the wedge angle. Web this oblique shock calculator will help determine the fluid flow properties for an oblique shock wave. On this slide we have listed the equations which describe the change in flow variables for flow across an oblique shock. A normal shock is a special case. For compressible flow, ames research staff, 1953. Shock angle from a simple mach wave to a normal shock. Θ = wedge deflection angle, (deg) m 1 = mach number of flow upstream of shock wave. The red line separates the strong and weak solutions. Infinitessimal wave μ = sin− ( 1 /m ) oblique shock. Mach number behind the shock, pressure ratio, derivation of flow, and angle of shock are presented on charts. Web one series of charts presents the characteristics of the flow of air (considered a perfect gas) for oblique shock waves and for cones in a supersonic air stream. Supersonic flow performing a large compressive deflection,θ. Same approach as for normal shocks. Flow must undergo compression to turn θ >μ. The calculator computes ratios to free stream values across an oblique shock wave, turn angle, wave angle and associated mach numbers (normal components, m n , of the upstream). A body of finite thickness, however, will generate oblique waves of finite. A shock wave is most commonly associated with fast military aircraft or spacecraft when they move faster than the speed of sound. Supersonic flow encounters a wedge and is uniformly deflected forming an oblique shock. Published online by cambridge university press: Web when a shock wave is inclined to the flow direction it is called an oblique shock.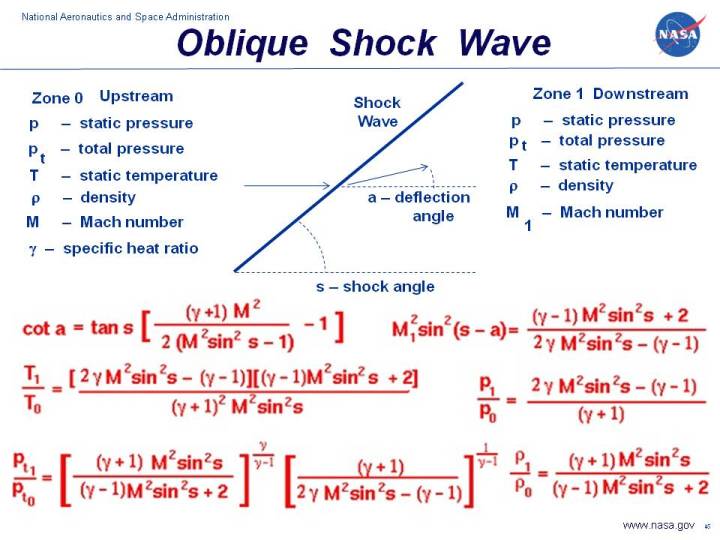
Oblique Shock Waves
Oblique Shock Waves

Tables and charts of flow parameters across oblique shocks Page 20 of
Oblique Shock Chart

Oblique Shock Chart
Tables and charts of flow parameters across oblique shocks Page 15 of

Tables and charts of flow parameters across oblique shocks Page 14 of

Oblique shock waves — Gas Dynamics notes

Oblique Shock Chart
Tables and charts of flow parameters across oblique shocks Page 7 of
Web This Oblique Shock Calculator Will Help Determine The Fluid Flow Properties For An Oblique Shock Wave.
Web Oblique Shocks Chart ¶.
Get Aircraft Propulsion, 2Nd Edition Now With The O’reilly Learning Platform.
The Formation Of Mach Waves Is Described.
Related Post: