Oxygen At Elevation Chart
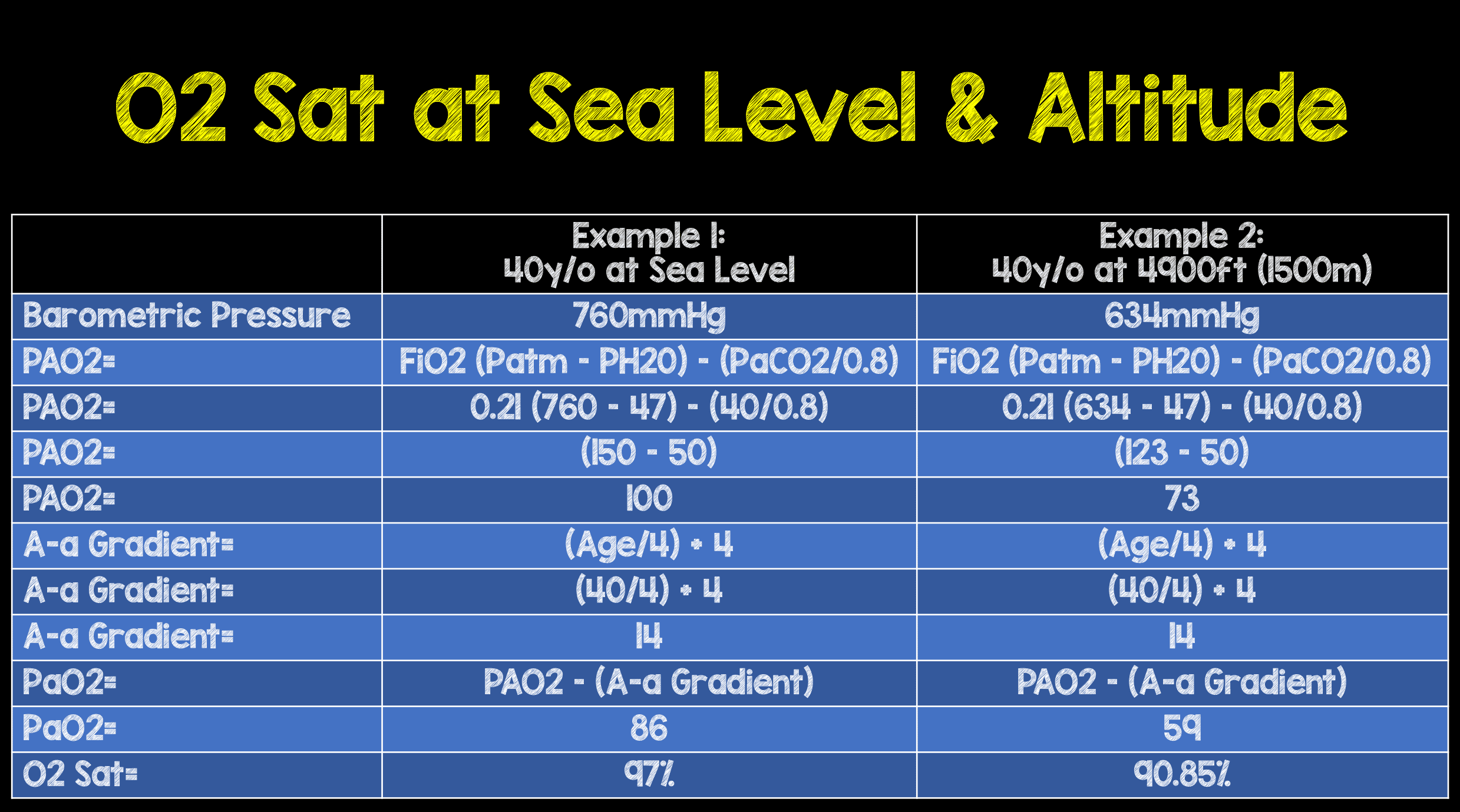
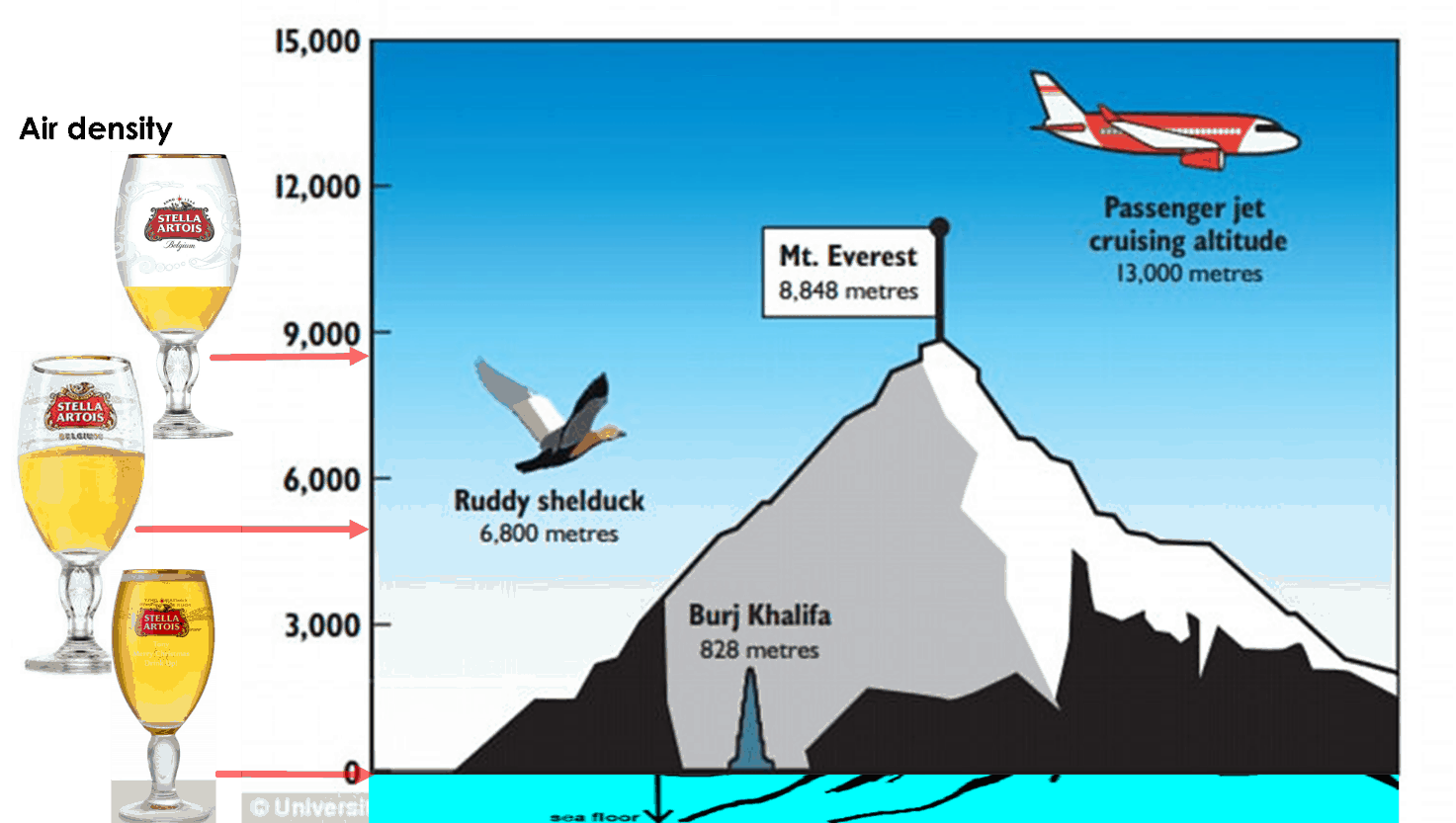
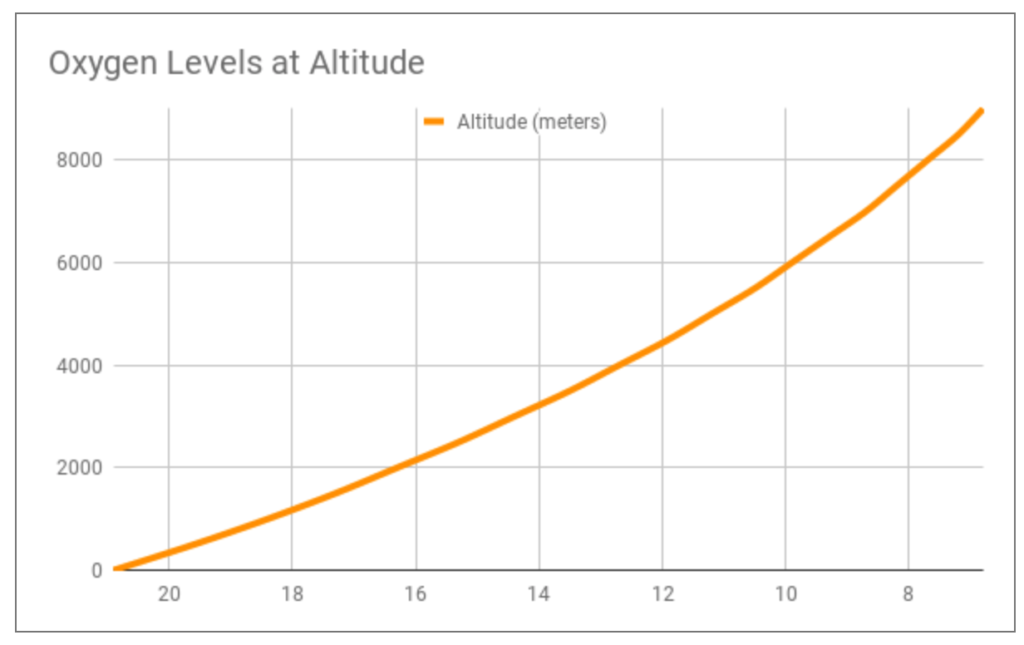
Oxygen At Elevation Chart - Web a healthy blood oxygen level, according to abg test results, ranges between 75 and 100 mm hg. Web below is an altitude oxygen chart that extrapolates oxygen percentages to real altitude, which you can use in conjunction with hypoxico systems. This measures the amount of oxygen in the blood. Learn how to use normobaric hypoxia to simulate high altitude and acclimatize to altitude sickness. Hyperoxemia is defined as blood oxygen levels above 120 mmhg. Web rather than relying on scientifically valid projections of expected oxygen saturations and optimistically applying those numbers to our high altitude centers we can consider data from a prospective validation of the perc rule performed at altitude (5280 ft) that used an oxygen saturation cutoff of 90% instead of 95%. Web • 10,000 ft ( 3048 m) — 5 weeks. Web values between 75 and 100 mm hg are considered normal for an abg test. When we breathe in air, our lungs transmit oxygen into tiny blood vessels called capillaries. Another value reported by the abg test is oxygen. At real altitude, the barometric pressure of the atmosphere is significantly lower than that of sea level. Web although the oxygen levels (percent of oxygen in the atmosphere) is the same, the “thinner air” means there is less oxygen to breathe. Acclimatization happens when oxygen saturation (spo2) levels in the blood have to adjust to high altitude, where the percentage. The test usually includes the following measurements: Altitude (feet) altitude (meters) o2 monitor reading. Web hypoxico altitude to oxygen chart. When values fall below 75 mm hg, you’re considered to have hypoxemia. Hyperoxemia is defined as blood oxygen levels above 120 mmhg. When values fall below 75 mm hg, you’re considered to have hypoxemia. Web above 120 mmhg: What does a low blood. Web • 10,000 ft ( 3048 m) — 5 weeks. Web find out the effective oxygen percentages at different altitudes with this chart. This chart will help you find oxygen levels at altitudes you are interested in, starting with the oxygen content of. • 14,000 ft ( 4267 m) — 7 weeks. This measures the amount of hemoglobin in your blood. Web • 10,000 ft ( 3048 m) — 5 weeks. What does a low blood. Web find the oxygen levels by elevation for many common altitudes with this chart. Altitude (feet) altitude (meters) o2 monitor reading. Atmospheric pressure and inspired oxygen pressure fall roughly linearly with altitude to be 50% of the sea level value at 5500 m and only 30% of the sea level value at 8900 m (the height of the summit of. This range indicates no abnormalities in a person’s blood oxygen level. This measures the amount of oxygen in the blood. When values fall below 75 mm hg, you’re considered to have hypoxemia. Web as oxygen is 21% of dry air, the inspired oxygen pressure is 0.21×(100−6.3)=19.6 kpa at sea level. • 14,000 ft ( 4267 m) — 7 weeks. This measures the amount of oxygen in the blood. • 14,000 ft ( 4267 m) — 7 weeks. Another value reported by the abg test is oxygen. Compared to measurements at sea level, measurement of oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry (spo 2) at altitude differs fundamentally because of the cyclical course of spo 2, caused by periodic breathing. Or use. Atmospheric pressure and inspired oxygen pressure fall roughly linearly with altitude to be 50% of the sea level value at 5500 m and only 30% of the sea level value at 8900 m (the height of the summit of everest). Therefore, the determination of a representative spo 2 value is difficult. Another value reported by the abg test is oxygen.. What does a low blood. At real altitude, the barometric pressure of the atmosphere is significantly lower than that of sea level. Or use the altitude oxygen graph (below) to see how much less oxygen is available at any altitude. • 14,000 ft ( 4267 m) — 7 weeks. Hyperoxemia is defined as blood oxygen levels above 120 mmhg. Web • 10,000 ft ( 3048 m) — 5 weeks. Web below is an altitude oxygen chart that extrapolates oxygen percentages to real altitude, which you can use in conjunction with hypoxico systems. Altitude (feet) altitude (meters) effective oxygen % altitude category example 0 0 20.9 low boston, ma 1000 305 20.1 low 2000 610 19.4 low 3000 914 18.6. Compared to measurements at sea level, measurement of oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry (spo 2) at altitude differs fundamentally because of the cyclical course of spo 2, caused by periodic breathing. Web as oxygen is 21% of dry air, the inspired oxygen pressure is 0.21×(100−6.3)=19.6 kpa at sea level. This handy 'altitude to oxygen %' table extrapolates the effective amount of oxygen to real altitude. Altitude (feet) altitude (meters) o2 monitor reading. Web find out the effective oxygen percentages at different altitudes with this chart. Learn how to use normobaric hypoxia to simulate high altitude and acclimatize to altitude sickness. This chart will help you find oxygen levels at altitudes you are interested in, starting with the oxygen content of. Web find the oxygen levels by elevation for many common altitudes with this chart. Hyperoxemia is mostly seen in hospitals when patients are exposed to high pressures of supplemental oxygen for prolonged periods (3 to more than 10 hours). When we breathe in air, our lungs transmit oxygen into tiny blood vessels called capillaries. This measures the amount of oxygen in the blood. Web the effective amount of oxygen at different altitudes. The test usually includes the following measurements: Web basically, pulse oximetry is a painless, noninvasive method of measuring the saturation of oxygen in a person’s blood. What does a low blood. Another value reported by the abg test is oxygen.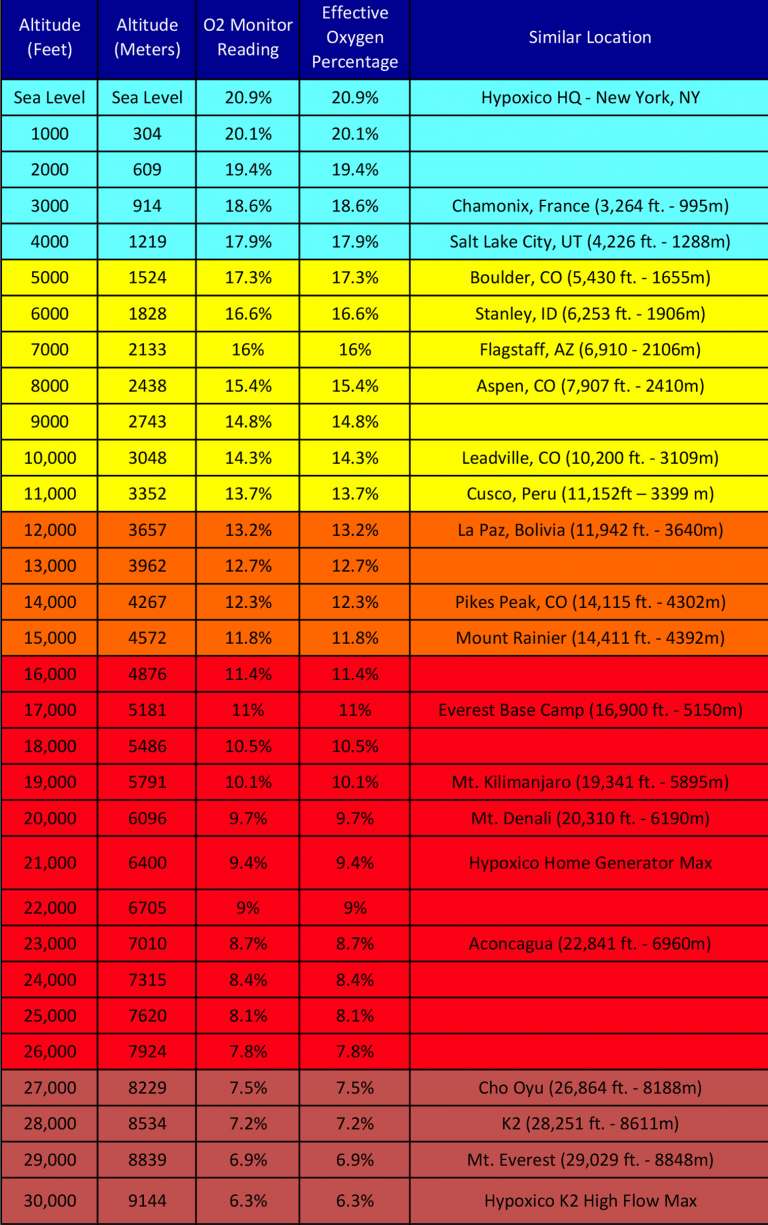
Oxygen At Altitude Chart

Oxygen Levels Altitude Chart
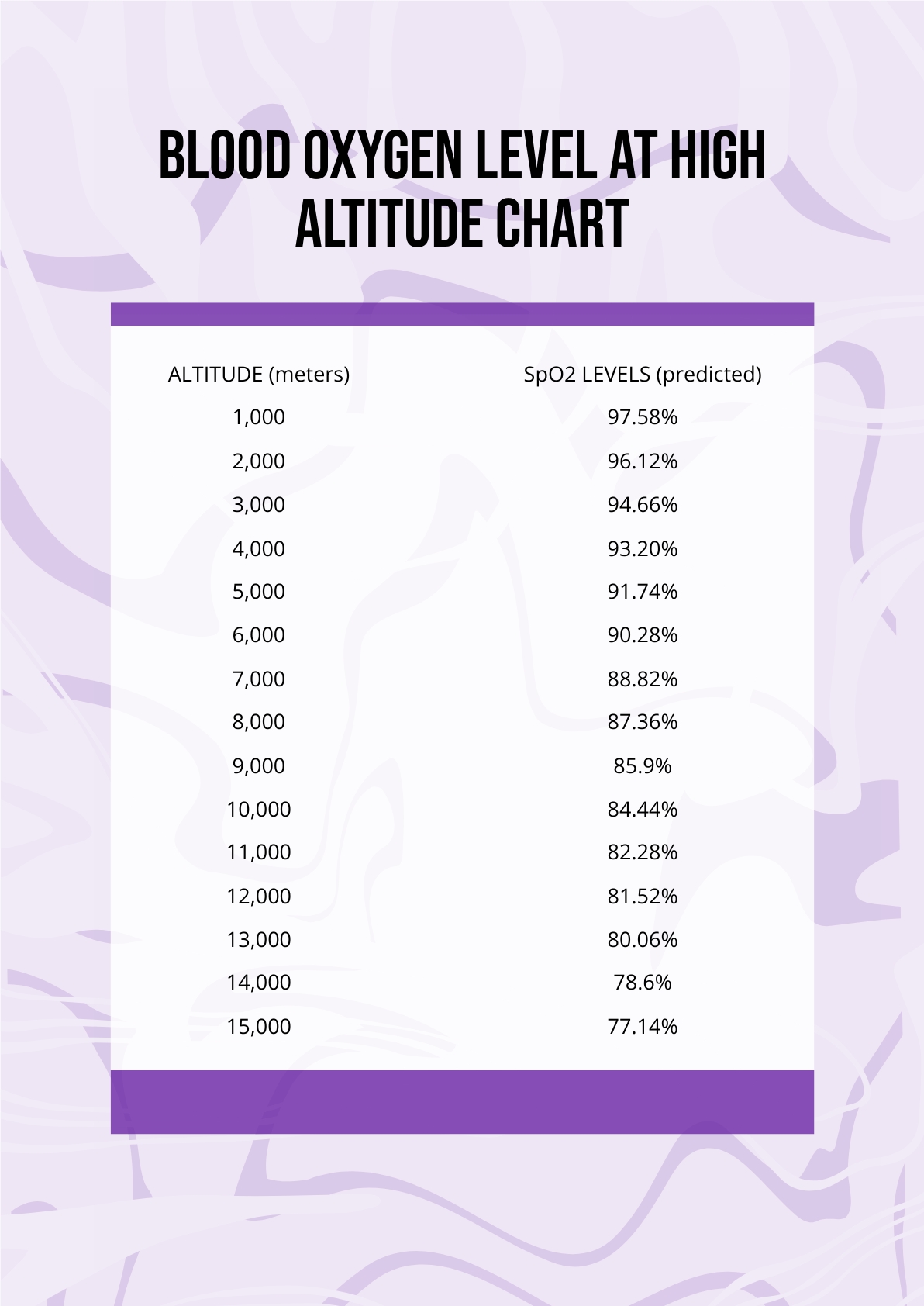
Blood Oxygen Level At High Altitude Chart in PDF Download

Oxygen at high altitude The BMJ

Oxygen at high altitude The BMJ
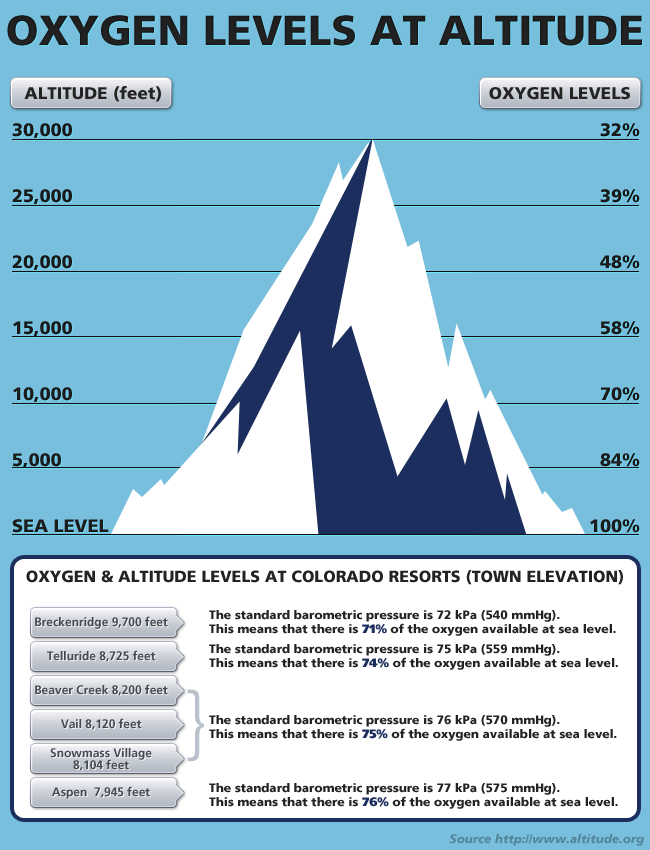
Oxygen Elevation Chart
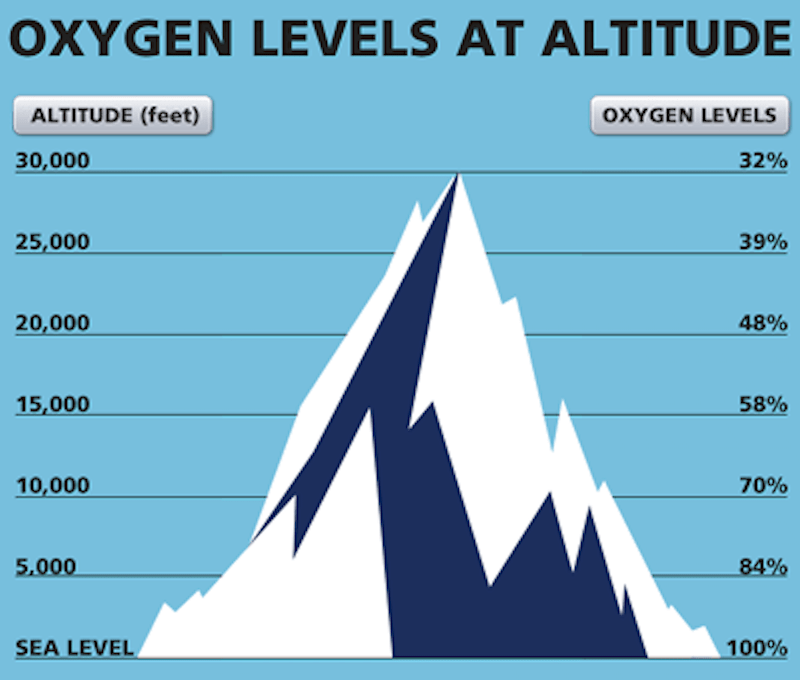
Former Gurkha Close to Being First Ever to Climb the 14 Tallest
Oxygen Elevation Chart
Oxygen At Altitude Chart
At What Altitude Do You Need Oxygen When Hiking? OutdoorYak
Web A Healthy Blood Oxygen Level, According To Abg Test Results, Ranges Between 75 And 100 Mm Hg.
Atmospheric Pressure And Inspired Oxygen Pressure Fall Roughly Linearly With Altitude To Be 50% Of The Sea Level Value At 5500 M And Only 30% Of The Sea Level Value At 8900 M (The Height Of The Summit Of Everest).
Acclimatization Happens When Oxygen Saturation (Spo2) Levels In The Blood Have To Adjust To High Altitude, Where The Percentage Of Oxygen Is Less.
• 12,000 Ft ( 3658 M) — 6 Weeks.
Related Post: