Pacemaker Settings Chart
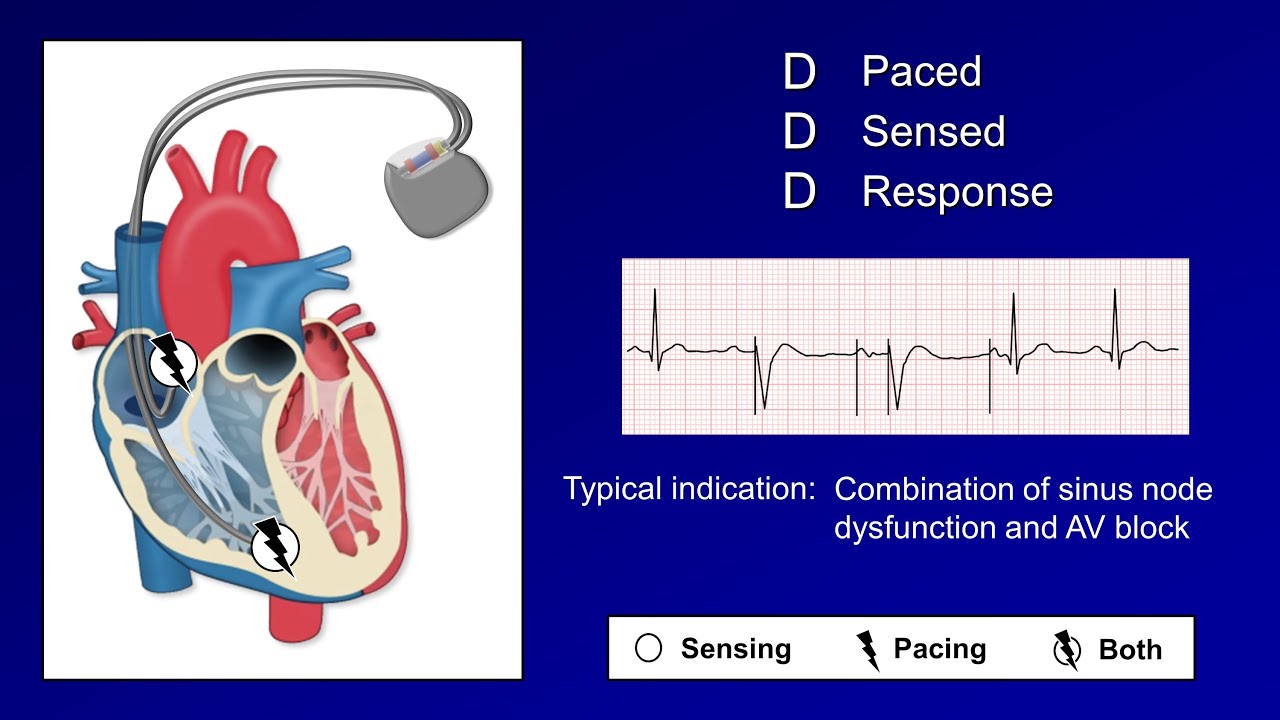
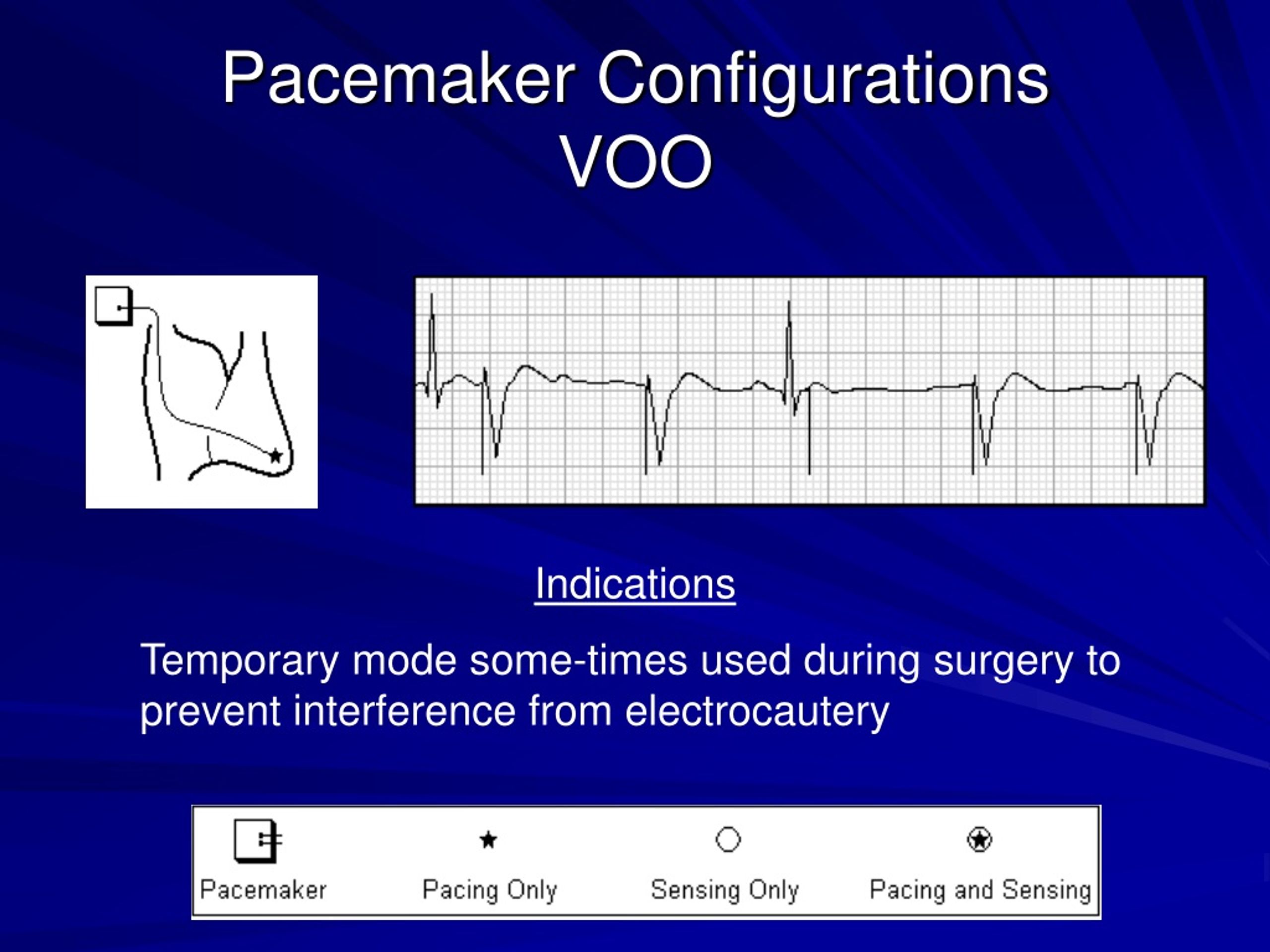
Pacemaker Settings Chart - Make sure you understand your pacemaker’s programmed lower and upper heart rate. You need surgery to get a pacemaker. Reed switch (magnet activated switch) lead (s) single or multiple. Web early pacemakers sent an electrical signal to one heart chamber at a set interval regardless of whether the patient had an intrinsic cardiac rhythm or not. Your pacemaker at a glance A pacemaker generates electrical impulses that help your heart beat at a normal rate, rhythm, or both. • a pacemaker monitors the heart’s rate (how fast it beats) and rhythm (the pattern in which it beats) and provides electrical stimulation when the heart does not beat or beats too slowly. They can stabilize abnormal heart rhythms and prevent problems that can disrupt or endanger your life. Traditional pacemakers have three parts: Most pacemakers are small machines with two parts: It produces electrical impulses to help control abnormal heartbeats. A pacemaker generates electrical impulses that help your heart beat at a normal rate, rhythm, or both. If electrical impulse sensed then pacing inhibited. Web you'll also receive a card with information about your pacemaker, when it was placed, its settings, your health care professional and the hospital. They can stabilize. Permanent pacemaker type and placement examples. Most pacemakers are small machines with two parts: A pacemaker checks your heart rhythm all the time. Contemporary pacemakers are versatile and capable of the most commonly used pacing modes and basic functions (ie, mode switching and rate responsiveness). How does a pacemaker work? Reed switch (magnet activated switch) lead (s) single or multiple. Estimated number of pacemakers implanted worldwide each year1. Web this topic review will discuss pacemakers, when they may be necessary or appropriate, the types of pacemakers that are available, and the precautions patients need to take after having a pacemaker placed. When a pacemaker makes sense. There are different types. A pacemaker checks your heart rhythm all the time. It produces electrical impulses to help control abnormal heartbeats. A pacemaker is a small electrical device which is used to treat some abnormal heart rhythms which can cause your heart to beat too slowly or miss beats. A pacemaker generates electrical impulses that help your heart beat at a normal rate,. • a pacemaker monitors the heart’s rate (how fast it beats) and rhythm (the pattern in which it beats) and provides electrical stimulation when the heart does not beat or beats too slowly. You need surgery to get a pacemaker. Permanent pacemaker type and placement examples. The heart is powered by a complex, natural electrical system that helps it maintain. Web when walton lillehei and earl bakken pioneered the use of pacemakers for heart block following cardiac surgery, they reasoned that the programmed lower rate limit (lrl) should be set to a heart rate (hr) that the patient would be expected to have if conduction disease was not present. Contemporary pacemakers are versatile and capable of the most commonly used. Web a discussion of pacemaker modes (e.g. It produces electrical impulses to help control abnormal heartbeats. You should also do your part to help your pacemaker control your heart rate. • a pacemaker monitors the heart’s rate (how fast it beats) and rhythm (the pattern in which it beats) and provides electrical stimulation when the heart does not beat or. You need surgery to get a pacemaker. Pacemakers are devices that can be placed in your body, usually by surgery, to support the electrical system in your heart. You should always carry this card with you. Make sure you understand your pacemaker’s programmed lower and upper heart rate. Estimated number of pacemakers implanted worldwide each year1. Contemporary pacemakers are versatile and capable of the most commonly used pacing modes and basic functions (ie, mode switching and rate responsiveness). A cardiac pacemaker is a small device implanted in a person’s chest that provides an electrical pulse to the heart, as needed, to regulate a slow heart rate. Vvi, ddd, etc.) and settings (timing cycles, sensitivity, output, mode. A pacemaker also is called a cardiac pacing device. Web you'll also receive a card with information about your pacemaker, when it was placed, its settings, your health care professional and the hospital. Below, we’ll cover more about pacemakers, including: Web this topic review will discuss pacemakers, when they may be necessary or appropriate, the types of pacemakers that are. Web early pacemakers sent an electrical signal to one heart chamber at a set interval regardless of whether the patient had an intrinsic cardiac rhythm or not. Wires (leads/electrodes) that are implanted in your heart and connected to the computer. Up to 50% of the current drain from the battery is used for pacing, whereas the other half is used for sensing and housekeeping functions. Some newer pacemakers are wireless. Web you'll also receive a card with information about your pacemaker, when it was placed, its settings, your health care professional and the hospital. A pacemaker checks your heart rhythm all the time. Make sure you understand your pacemaker’s programmed lower and upper heart rate. Vvi, ddd, etc.) and settings (timing cycles, sensitivity, output, mode switching). Web this is an arrhythmia. There are different types of pacemakers. The heart is powered by a complex, natural electrical system that helps it maintain a healthy rhythm, while pumping blood throughout the body. Web when walton lillehei and earl bakken pioneered the use of pacemakers for heart block following cardiac surgery, they reasoned that the programmed lower rate limit (lrl) should be set to a heart rate (hr) that the patient would be expected to have if conduction disease was not present. Some pacemakers can also help the chambers of your heart beat in time. Your pacemaker at a glance A generator, wires (leads) and sensors (electrodes). Below, we’ll cover more about pacemakers, including:
Basic cardiac pacing, pacemaker functions and settings ECG & ECHO

Dr. Smith's ECG Blog Extreme Bradycardia a CaseBased Lesson in Pacing

Pacemaker Essentials What we need to know in the ED CanadiEM

PPT CARDIAC PACING AND DEFIBRILLATION PowerPoint Presentation, free
Pacemaker Modes and Settings YouTube
PPT Pacemakers PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID231622

Pacemaker Codes and Modes Explained YouTube

Components and construction of a pacemaker Cardiovascular Education

Basic cardiac pacing, pacemaker functions and settings (2023)

The Basics of Paced Rhythms ECG Medical Training
A Pacemaker Is A Small Electrical Device Which Is Used To Treat Some Abnormal Heart Rhythms Which Can Cause Your Heart To Beat Too Slowly Or Miss Beats.
• A Pacemaker Monitors The Heart’s Rate (How Fast It Beats) And Rhythm (The Pattern In Which It Beats) And Provides Electrical Stimulation When The Heart Does Not Beat Or Beats Too Slowly.
Traditional Pacemakers Have Three Parts:
When A Pacemaker Makes Sense.
Related Post: