Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart
Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart - Web the impact of tidal volume (v t) on outcomes in mechanically ventilated children with pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (pards) remains unclear. All simulated trials displayed consistency in measured and monitored values. Web ltvv is an approach that targets tidal volume between 6 and 8 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome or ards, and 4 to 6 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for those with ards. Web there are four major factors to consider when interpreting the measured tidal volumes that are reported by the ventilator: Web target tidal volume ranges from 6 to 8 ml/kg ibw, where: No target tidal volume range has consistently been associated with outcomes, and compliance with delivering specific tidal volume ranges has been poor. A good understanding of the design of mechanical ventilators can improve clinical care. These technical advancements have impact on clinical decisions in pediatric intensive care units (picus). Web remember to set appropriate respiratory rate for age and tidal volume for size. Web low tidal volume ventilation has been generally accepted for pediatric patients, even in the absence of supporting evidence. The mean age of the pediatric patients was 8.7±5.6 years (median: 2.8 months), and the mean weight was 4.6±3.3 kg (median: Web this project will inform a future project that will prospectively calculate, in children mechanically ventilated, tidal volumes based on different weight measurement techniques (actual, ideal body weight [ibw]): No target tidal volume range has consistently been associated with. All simulated trials displayed consistency in measured and monitored values. Web low tidal volume ventilation has been generally accepted for pediatric patients, even in the absence of supporting evidence. 5.7 years) with a mean weight of 27.9±22.9 kg (median: To date, observational investigations have failed to calculate v. This will be done by using the ml/kg value documented in the. On average, the displayed v t was inaccurate and was 27% more than the measured volumes. This will be done by using the ml/kg value documented in the patient’s medical chart. Web respiratory rate (titrate for ventilation) average patient on ventilator requires 120ml/kg/min for eucapnia. Just as in adult patients, the. Web this project will inform a future project that. No target tidal volume range has consistently been associated with outcomes, and compliance with delivering specific tidal volume ranges has been poor. 5.7 years) with a mean weight of 27.9±22.9 kg (median: (2) the site of tidal volume measurement within the Web there are four major factors to consider when interpreting the measured tidal volumes that are reported by the. Web low tidal volume ventilation has been generally accepted for pediatric patients, even in the absence of supporting evidence. 4 subsequent studies support the recommendation for similar tidal volumes to prevent. All simulated trials displayed consistency in measured and monitored values. Web ltvv is an approach that targets tidal volume between 6 and 8 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body. Web the mean age of the infant population was 2.8±2.3 months (median: Web this project will inform a future project that will prospectively calculate, in children mechanically ventilated, tidal volumes based on different weight measurement techniques (actual, ideal body weight [ibw]): The calculated v t was on average more precise, within 5% of the measured volumes. (2) the site of. 5.7 years) with a mean weight of 27.9±22.9 kg (median: The mean age of the pediatric patients was 8.7±5.6 years (median: On average, the displayed v t was inaccurate and was 27% more than the measured volumes. All simulated trials displayed consistency in measured and monitored values. Web the pediatric anesthetist needs to make individual decisions regarding the patient's treatment,. Web we aimed to compare 4 methods of ibw calculation and determine level of agreement between methods and impact of measurement variance on tidal volumes (tv) prescribed in mechanically ventilated pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (pards). Web in the case of a 5kg baby, the targeted tidal volume may be 40ml (8ml/kg). Web the impact of tidal volume (v t). Web the pediatric anesthetist needs to make individual decisions regarding the patient's treatment, taking into account the wide range of physiological characteristics of the respiratory system, changing from birth through adolescence, including information obtained from the anesthesia workstation (aws). Web we aimed to compare 4 methods of ibw calculation and determine level of agreement between methods and impact of measurement. Web remember to set appropriate respiratory rate for age and tidal volume for size. 2.8 months), and the mean weight was 4.6±3.3 kg (median: Web the pediatric anesthetist needs to make individual decisions regarding the patient's treatment, taking into account the wide range of physiological characteristics of the respiratory system, changing from birth through adolescence, including information obtained from the. Just as in adult patients, the. No target tidal volume range has consistently been associated with outcomes, and compliance with delivering specific tidal volume ranges has been poor. Web we aimed to compare 4 methods of ibw calculation and determine level of agreement between methods and impact of measurement variance on tidal volumes (tv) prescribed in mechanically ventilated pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (pards). (2) the site of tidal volume measurement within the Web remember to set appropriate respiratory rate for age and tidal volume for size. To date, observational investigations have failed to calculate v. Web low tidal volume ventilation has been generally accepted for pediatric patients, even in the absence of supporting evidence. A good understanding of the design of mechanical ventilators can improve clinical care. 5.7 years) with a mean weight of 27.9±22.9 kg (median: 4 subsequent studies support the recommendation for similar tidal volumes to prevent. Web ltvv is an approach that targets tidal volume between 6 and 8 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome or ards, and 4 to 6 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for those with ards. Web target tidal volume ranges from 6 to 8 ml/kg ibw, where: Web the mean age of the infant population was 2.8±2.3 months (median: 2.8 months), and the mean weight was 4.6±3.3 kg (median: Web there are four major factors to consider when interpreting the measured tidal volumes that are reported by the ventilator: Web respiratory rate (titrate for ventilation) average patient on ventilator requires 120ml/kg/min for eucapnia.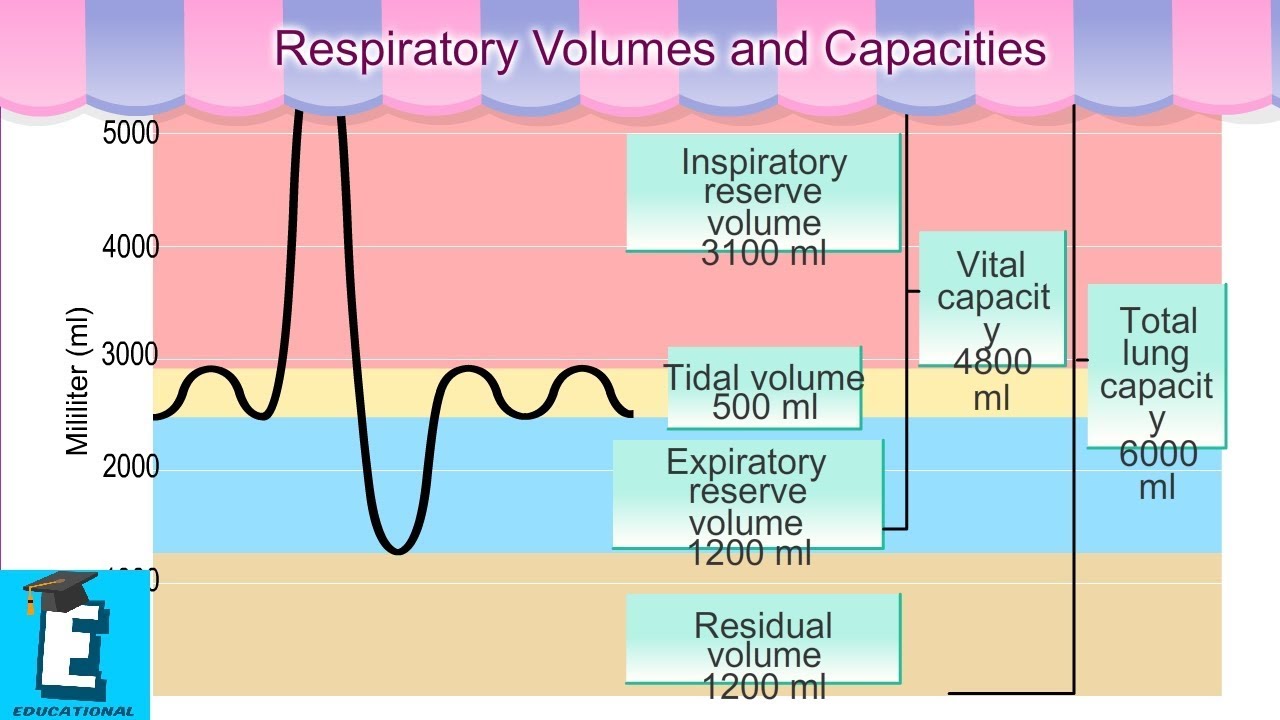
Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart

Tidal breathing measurements. Tidal volumes, BPM, and IE ratios were

a) Tidal volume versus weight for term and preterm infants. The black

Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart

Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart

Neonatal Tidal Volume Chart

Ards Tidal Volume Chart
Tidal Volumes Cheat Sheet

34+ tidal volume calculator pediatric JasveerMonica

Ibw Tidal Volume Chart
On Average, The Displayed V T Was Inaccurate And Was 27% More Than The Measured Volumes.
Web Low Tidal Volume Ventilation Has Been Generally Accepted For Pediatric Patients, Even In The Absence Of Supporting Evidence.
Web The Impact Of Tidal Volume (V T) On Outcomes In Mechanically Ventilated Children With Pediatric Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Pards) Remains Unclear.
This Will Be Done By Using The Ml/Kg Value Documented In The Patient’s Medical Chart.
Related Post:
