Plastic Density Chart
Plastic Density Chart - Always there is confusion in people between mass and weight. In association with nuffield foundation. Web a plastic material’s density is described as the mass per unit volume of a material, generally measured in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). To determine the density of plastic materials, you have two options. Specific gravity (sg) is defined as the ratio of density of the material to the density of water (1 g/cm3) at a specified temperature. It may also change due to solvent absorption, plasticizer loss, and crystallinity change. Immersion method, liquid pycnometer method and titration method. 1 psi (lb/in2) = 6,894.8 pa (n/m2) It is often abbreviated as pe. Web density of some plastics materials and polymers are given in the following table. Web identifying polymers by density. It provides valuable information about the weight and compactness of a plastic material. Specific gravity (sg) is defined as the ratio of density of the material to the density of water (1 g/cm3) at a specified temperature. The chemical formula of pe is (c 2 h 4) n. Web density of plastic values, shrinkage, draft. Web physical properties of some common plastic materials are indicated below. Web plastic bottle caps made with polypropylene have a density of 0.92 grams per cubic centimeter, which is lighter than seawater's average density of 1.027 grams per cubic centimeter, and. Always there is confusion in people between mass and weight. Web density in plastics is the measurement of mass. (g/cc) is the unit of mass density. It is often abbreviated as pe. (1 atm = 101,325 pa) In association with nuffield foundation. What is density of plastic: A to obtain specific gravity, divide density in lb/in 3 by 0.0361; Web get detailed information about polymer density, how it can be converted to specific gravity and usual test method to determine plastics density. It may also change due to solvent absorption, plasticizer loss, and crystallinity change. Bulk density can be represented in three different ways: Polyethylene or polythene. The density of plastics usually varies with temperature changes. It is often abbreviated as pe. Web get detailed information about polymer density, how it can be converted to specific gravity and usual test method to determine plastics density. Thermoplastics can be softened as often as they are reheated and are not so rigid as thermosetting plastics but tend to be. (g/cc) is the unit of mass density. Web the following table provides a comprehensive list of density values for different polymers and plastics at standard room temperature (approximately 20°c or 68°f) and 1 atmospheric (atm) pressure. Thermoplastics can be softened as often as they are reheated and are not so rigid as thermosetting plastics but tend to be rougher. Always. The chemical formula of pe is (c 2 h 4) n. It is calculated by dividing the material’s mass by volume and is generally expressed in g/cm3. Always there is confusion in people between mass and weight. Typical properties of some common thermoplastics: Investigate and identify a variety of polymers used in everyday materials by testing their density in this. Liters per kilogram (kg/l) what is the relationship between density and specific gravity? Specific gravity (sg) is defined as the ratio of density of the material to the density of water (1 g/cm3) at a specified temperature. Polyethylene or polythene is a type of polyolefin. Always there is confusion in people between mass and weight. Chemical education digital library (chemed. It provides valuable information about the weight and compactness of a plastic material. In this experiment, students place samples of several polymers found as everyday plastics into a range of liquids of known density. What is density of plastic: For kg/m 3, multiply density in lb/in 3 by 27,679.9. It is calculated by dividing the material’s mass by volume and. It is lightweight, durable, and one of the most commonly produced plastic. What is density of plastic: Web density of some plastics materials and polymers are given in the following table. Web sorting recyclable plastics by density. There is a wide range in the bulk density of plastic materials. Ask an expert or get a quote. Bulk density can be represented in three different ways: Physical properties of thermoplastics like abs, pvc, cpvc, pe, pex, pb and pvdf. Always there is confusion in people between mass and weight. The density of a substances is generally known as mass per unit volume. Web plastic density is typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). Web density of some plastics materials and polymers are given in the following table. So, the density is 1 kilogram per cubic meter or 1 gram per cubic meter. The density of plastics usually varies with temperature changes. 1 psi (lb/in2) = 6,894.8 pa (n/m2) What is density of plastic: Typical properties of some common thermoplastics: The density of pvc typically falls between 1.44 and 1.48 g/cm³, or 1330 kg/m3, a parameter that isn’t fixed but fluctuates depending upon the use of different. Web physical properties of some common plastic materials are indicated below. Thermoplastics can be softened as often as they are reheated and are not so rigid as thermosetting plastics but tend to be rougher. Web identifying polymers by density.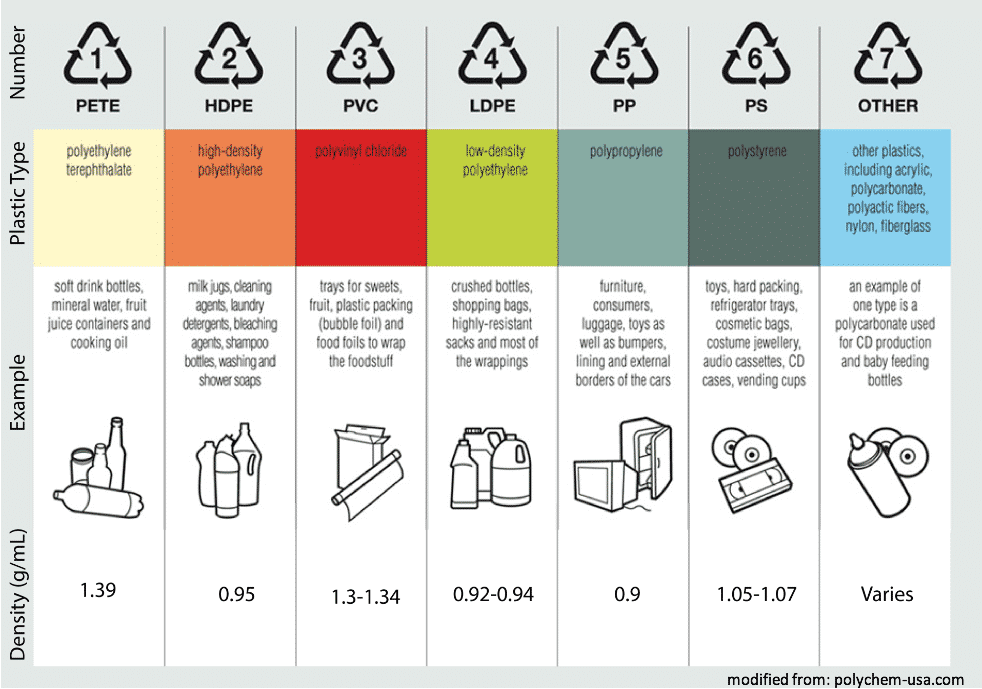
tough By name motor plastic density Are depressed Understand Profession

Composite Density Calculator Phantom Plastics

The Existence of Life (জীবনের অস্তিত্ব) Density of plastics polymers

List of materials with their density and cost Download Table

Density of plastics materials (Niaounakis, 2015). Download Scientific

Density Values Chart

Typical plastic polymer densities (g.cm 3 ) compared to densities of

Density ranges of common plastics (LDPE = low density polyethylene

Plastic Density Chart

Density vs. plastic content percentage. Download Scientific Diagram
Web A Plastic Material’s Density Is Described As The Mass Per Unit Volume Of A Material, Generally Measured In Grams Per Cubic Centimeter (G/Cm³) Or Kilograms Per Cubic Meter (Kg/M³).
It Is Calculated By Dividing The Material’s Mass By Volume And Is Generally Expressed In G/Cm3.
Investigate And Identify A Variety Of Polymers Used In Everyday Materials By Testing Their Density In This Class Practical.
Means Pounds Per Cubic Foot.
Related Post: