Polymer And Monomer Chart
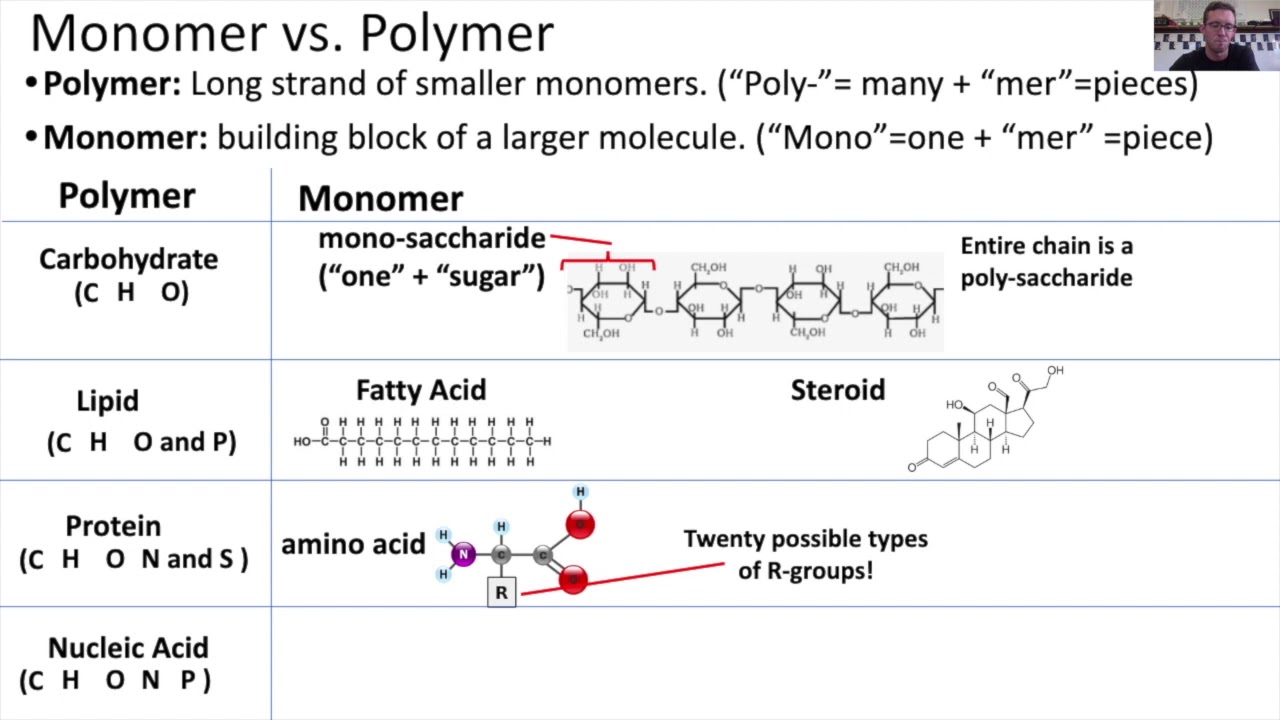
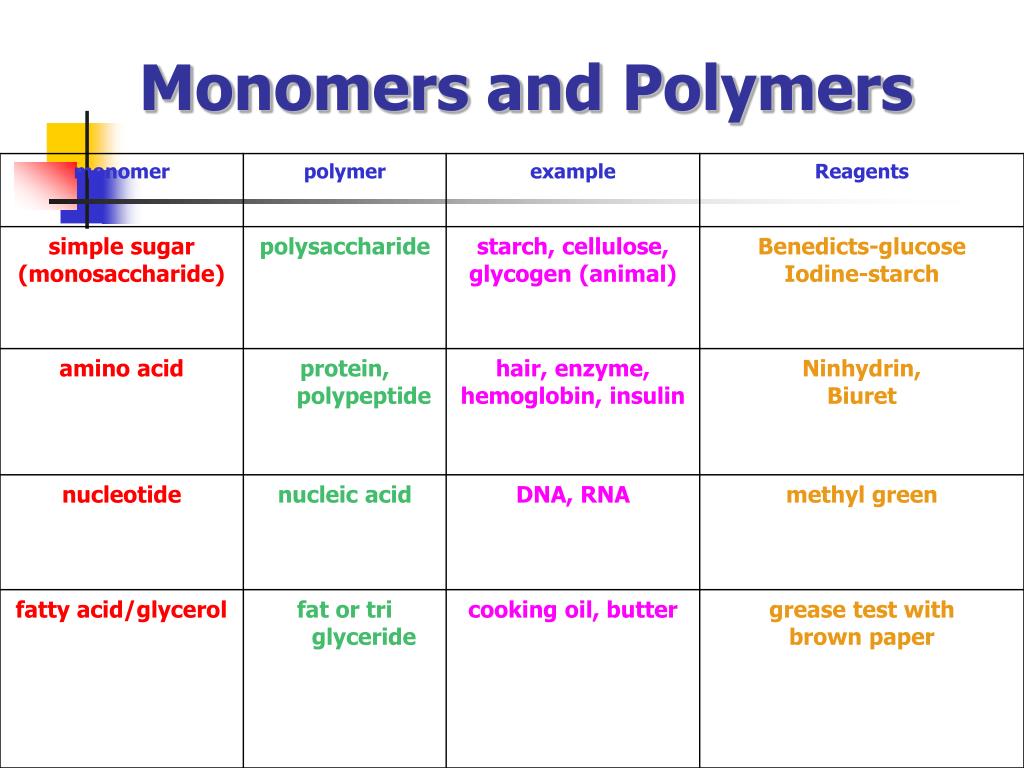
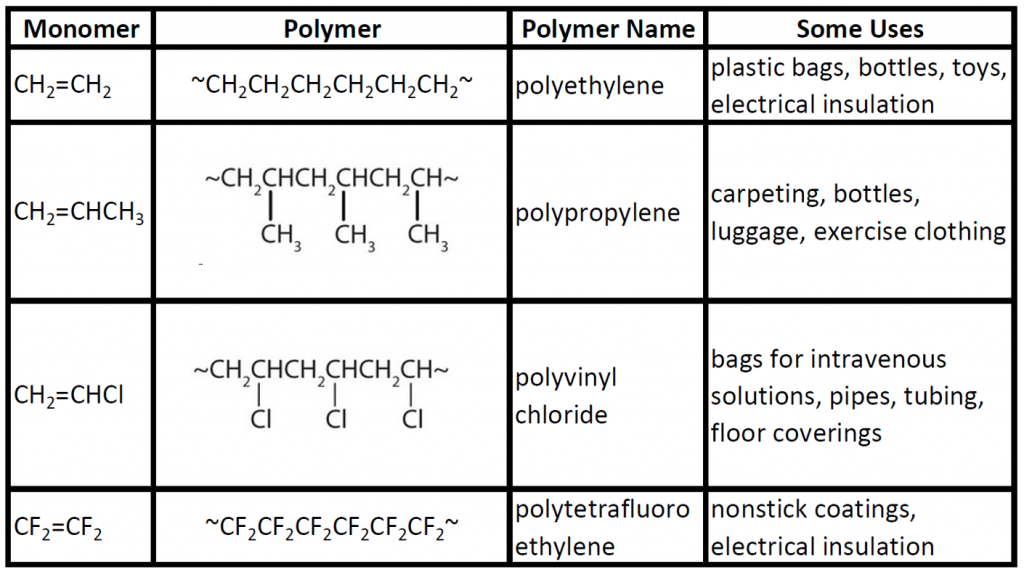
Polymer And Monomer Chart - Web polymers are very large molecules made from smaller ones. *one of the most important biomolecules. Increased crystallinity is associated with an increase in rigidity, tensile strength and opacity (due to light scattering). Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. What are monomers and polymers? Monosaccharides such as glucose make up polysaccharides like starches. A polymer is made by polymerization of monomers in regular and repeating fashion. Web definition of macromolecules. Web polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called monomers. Most large biological molecules are polymers, long chains made up of repeating molecular subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. If you think of a monomer as being like a bead, then you can think of a polymer as being like a necklace, a series of beads strung together. Web a large, organic molecule such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. A monomer is a type of molecule that has the ability to chemically. *one of the most important biomolecules. In biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. Ethylene molecules are joined together in long chains. Web definition of macromolecules. The monomer is a small molecule, which can undergo polymerization, thereby contributing constitutional units to. In addition polymerization, the monomers add to one another in such a way that the polymer contains all the atoms of the starting monomers. Increased crystallinity is associated with an increase in rigidity, tensile strength and opacity (due to light scattering). How those smaller units are arranged within the polymer is an issue we haven't addressed very closely yet. What. Web a large, organic molecule such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web there are two general types of polymerization reactions: Web polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called monomers. Monomers are small molecules that can combine to form larger molecules. The definition of a macromolecule differs somewhat between biochemistry and biology: The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. *one of the most important biomolecules. Polymers make up many of the materials in living organisms, including, for example, proteins, cellulose, and nucleic acids. Web the physical and chemical properties of polymers vary. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Monomers are small molecules that can combine to form larger molecules called polymers. Web definition of macromolecules. A relatively small molecule that can form covalent bonds with other molecules of this type to form a polymer. A molecule from which a polymer is made is called a monomer. If you think of a monomer as being like a bead, then you can think of a polymer as being like a necklace, a series of beads strung together. Web polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. What are monomers and polymers? A polymer is a chain of an unspecified number of. If you think of a monomer as being like a bead, then you can think of a polymer as being like a necklace, a series of beads strung together. Essentially, monomers are the building blocks of polymers, which are more complex type of molecules. Monomers are small molecules that can combine to form larger molecules called polymers. Addition polymerization and. How those smaller units are arranged within the polymer is an issue we haven't addressed very closely yet. *control rate of chemical reactions through enzymes. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. A polymer is a chain of an unspecified number of monomers. In biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called. Web definition of macromolecules. The definition of a macromolecule differs somewhat between biochemistry and biology: Web polymers are very large molecules made from smaller ones. Web there are two general types of polymerization reactions: What are monomers and polymers? Web in the diagram on the right, crystalline domains are colored blue. Increased crystallinity is associated with an increase in rigidity, tensile strength and opacity (due to light scattering). The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Web a large, organic molecule such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web polymers are very large molecules made from smaller ones. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. A relatively small molecule that can form covalent bonds with other molecules of this type to form a polymer. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. Web the physical and chemical properties of polymers vary widely, based on their monomers, structures, and additives. A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). *one of the most important biomolecules. *control rate of chemical reactions through enzymes. Web definition of macromolecules. A monomer is a type of molecule that has the ability to chemically bond with other molecules in a long chain; Each vinyl chloride monomer molecule contributes a ch 2 group joined to a chcl unit by a single bond. Examples of monomers and polymers.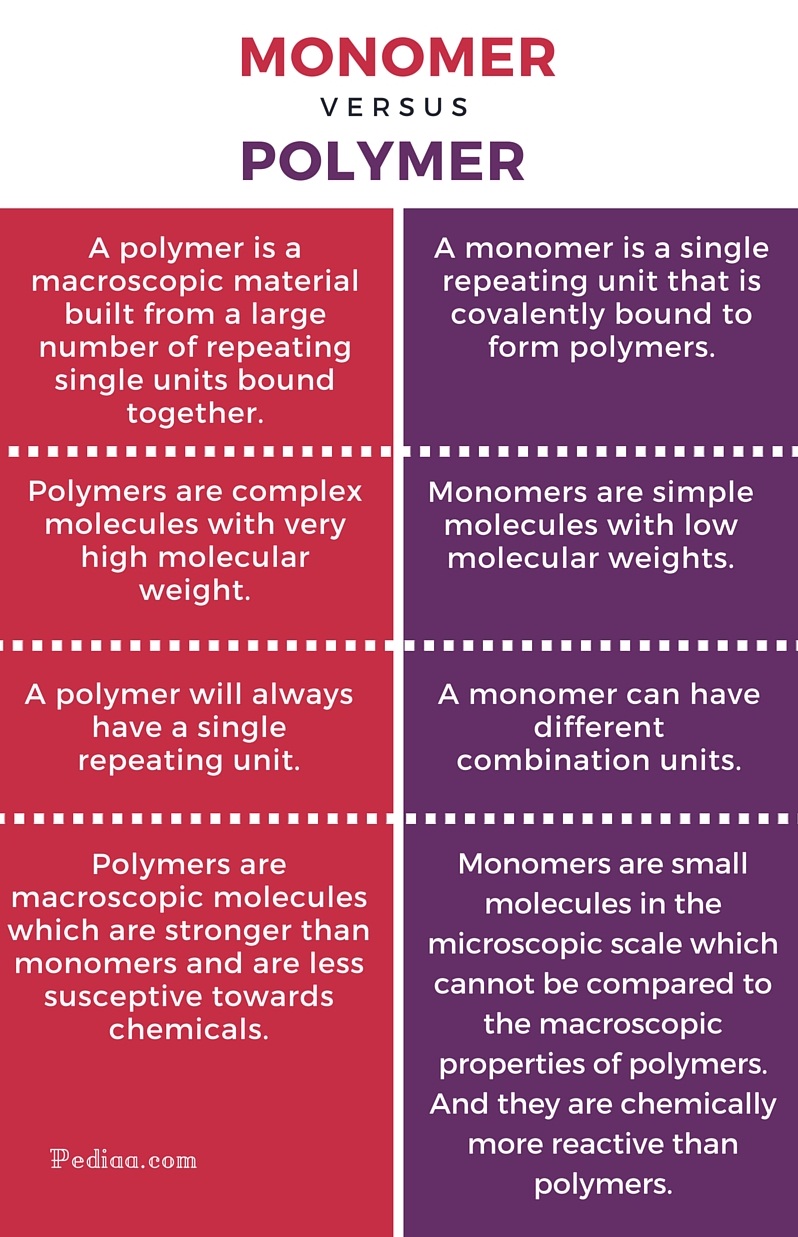
Difference Between Monomer and Polymer

16.7 Polymers Chemistry LibreTexts
Monomers vs. Polymers YouTube

Polymers Basicmedical Key

Image Gallery Monomers Chart

Quantum Science for standard 10 to 12, Innovative technique and
PPT CELL BIOLOGY (C) 2015 PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Polymers And Monomers Chart
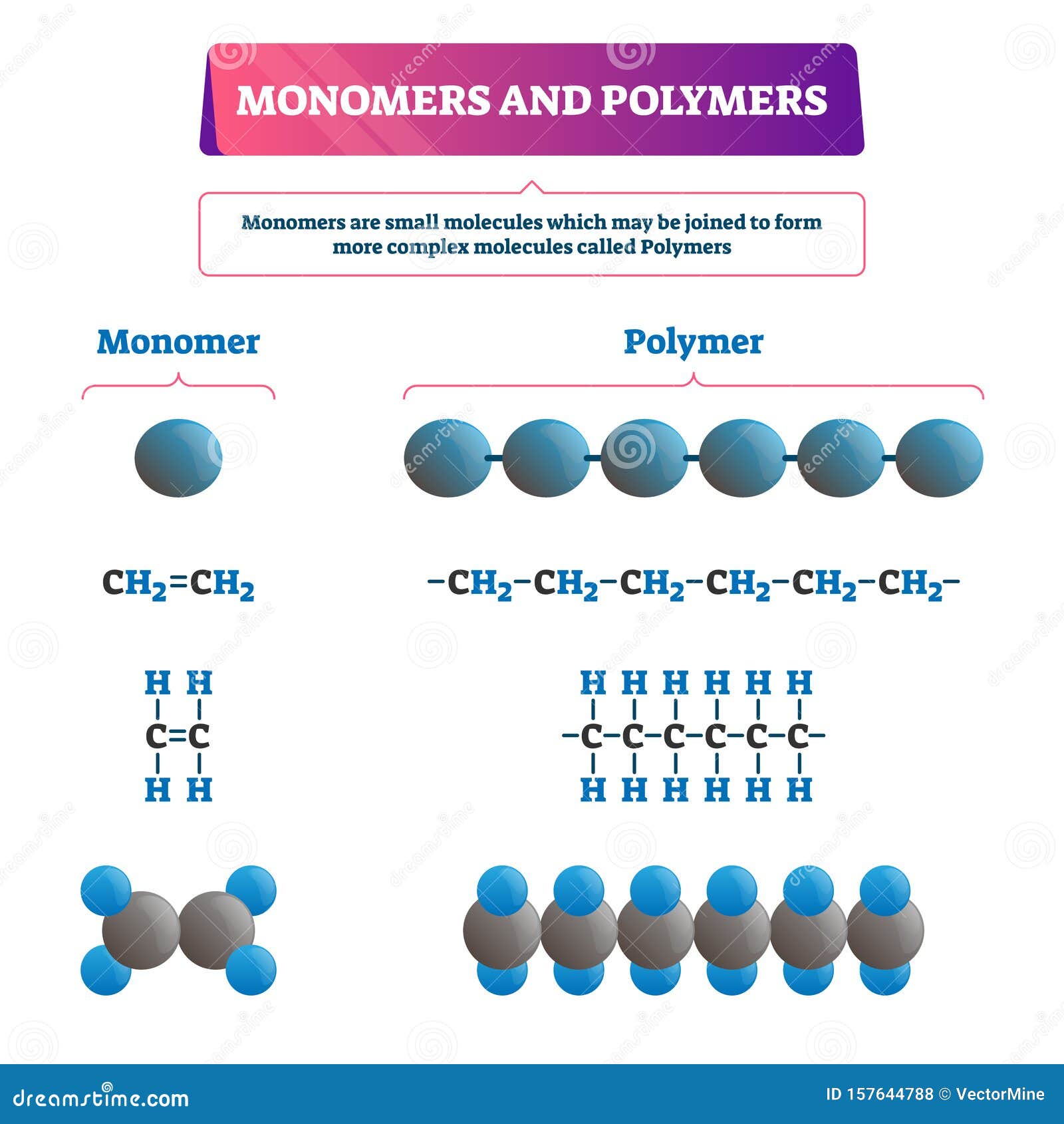
Polymers And Monomers Examples

What are the MONOMERS of each POLYMER? ppt download
The Monomers Combine With Each Other Using Covalent Bonds To Form Larger Molecules Known As Polymers.
Amino Acids Make Up Proteins.
How Those Smaller Units Are Arranged Within The Polymer Is An Issue We Haven't Addressed Very Closely Yet.
In Doing So, Monomers Release Water Molecules As Byproducts.
Related Post: