Polymers And Monomers Chart
Polymers And Monomers Chart - A polymer is a chain of an unspecified number of monomers. This type of reaction is known as dehydration synthesis, which means “to put together while losing water.” figure 1. The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. A molecule that is a building block for larger molecules (polymers). Hdpe is composed of macromolecules in which n ranges from 10,000 to 100,000 (molecular weight 2*10 5 to 3 *10 6). For example, an amino acid acts as the building blocks for proteins. For example, a carbohydrate is a polymer that is made of repeating monosaccharides. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. Web there are two general types of polymerization reactions: In condensation polymerization, each step of the process is accompanied by the formation of a molecule of some simple compound, often water. Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. Typically, the building blocks are organic molecules held together via covalent bonds. Web polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Two classes of polymerization usually are distinguished. A polymer is a molecule of high molecular weight, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low molecular weight. What other kinds of building blocks are. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Web polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Web a monomer is a type of molecule that has the ability to. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Ethylene molecules are joined together in long chains. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. This type of reaction is dehydration synthesis, which means “to put together while losing water.” A polymer is analogous to a necklace made from many small beads (monomers). A polymer is a molecule of high molecular weight, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low molecular weight. This type of reaction is known as dehydration synthesis, which means “to put together while losing water.” figure 1. In addition polymerization, the monomers add to one another in such. A molecule that is a building block for larger molecules (polymers). In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. Polymers make up many of the materials in living organisms, including, for example, proteins, cellulose, and nucleic acids. Web functional groups in monomers and polymers. Web polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large. Web polymers are long molecules composed of chains of units called monomers. Web most large biological molecules are polymers, long chains made up of repeating molecular subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. What are monomers and polymers? Amino acids make up proteins. What other kinds of building blocks are available? Web the monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Amino acids make up proteins. A molecule that is a building block for larger molecules (polymers). Web a monomer is a type of molecule that has the ability to chemically bond with other molecules in a long chain; This type of reaction is. Ethylene molecules are joined together in long chains. Monosaccharides such as glucose make up polysaccharides like starches. Web polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called monomers. A polysaccharide (carbohydrate) is a polymer. Essentially, monomers are the building blocks of polymers, which are. Web there are two general types of polymerization reactions: Amino acids make up proteins. The monomers are a dicarboxylic acid (terephthalic acid) and a dialcohol, also called a diol (ethylene glycol). In condensation polymerization, each step of the process is accompanied by the formation of a molecule of some simple compound, often water. Examples of monomers and polymers. Web most large biological molecules are polymers, long chains made up of repeating molecular subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Web a monomer is the smallest unit of a polymer. · 1 · mar 25 2018. Web functional groups in monomers and polymers. In condensation polymerization, each step of the process is accompanied by the formation of a molecule of some simple compound, often water. The monomers are a dicarboxylic acid (terephthalic acid) and a dialcohol, also called a diol (ethylene glycol). Typically, the building blocks are organic molecules held together via covalent bonds. A molecule that is a building block for larger molecules (polymers). Web polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. Monosaccharides such as glucose make up polysaccharides like starches. Amino acids make up proteins. Essentially, monomers are the building blocks of polymers, which are more complex type of molecules. This type of reaction is dehydration synthesis, which means “to put together while losing water.” Examples of monomers and polymers. A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). This type of reaction is known as dehydration synthesis, which means “to put together while losing water.” figure 1.
Image Gallery Monomers Chart
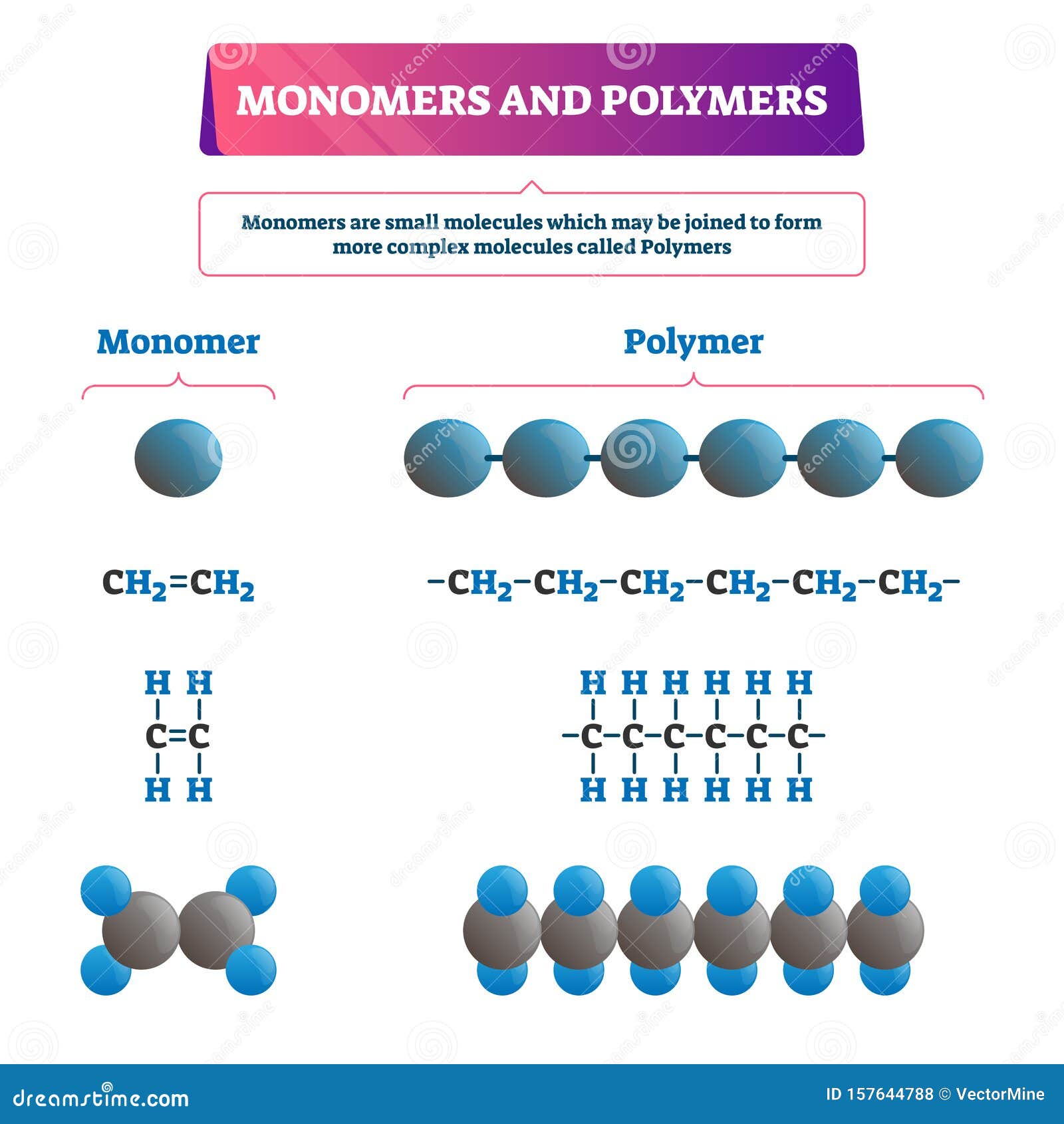
Polymers And Monomers Examples

Quantum Science for standard 10 to 12, Innovative technique and
PPT CELL BIOLOGY (C) 2015 PowerPoint Presentation, free download
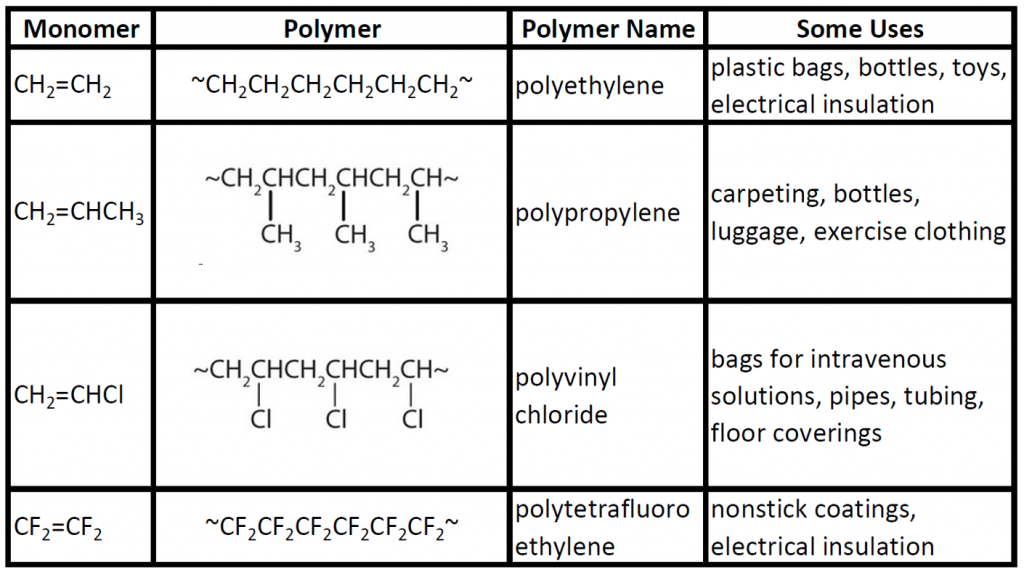
Polymers And Monomers Chart

16.7 Polymers Chemistry LibreTexts
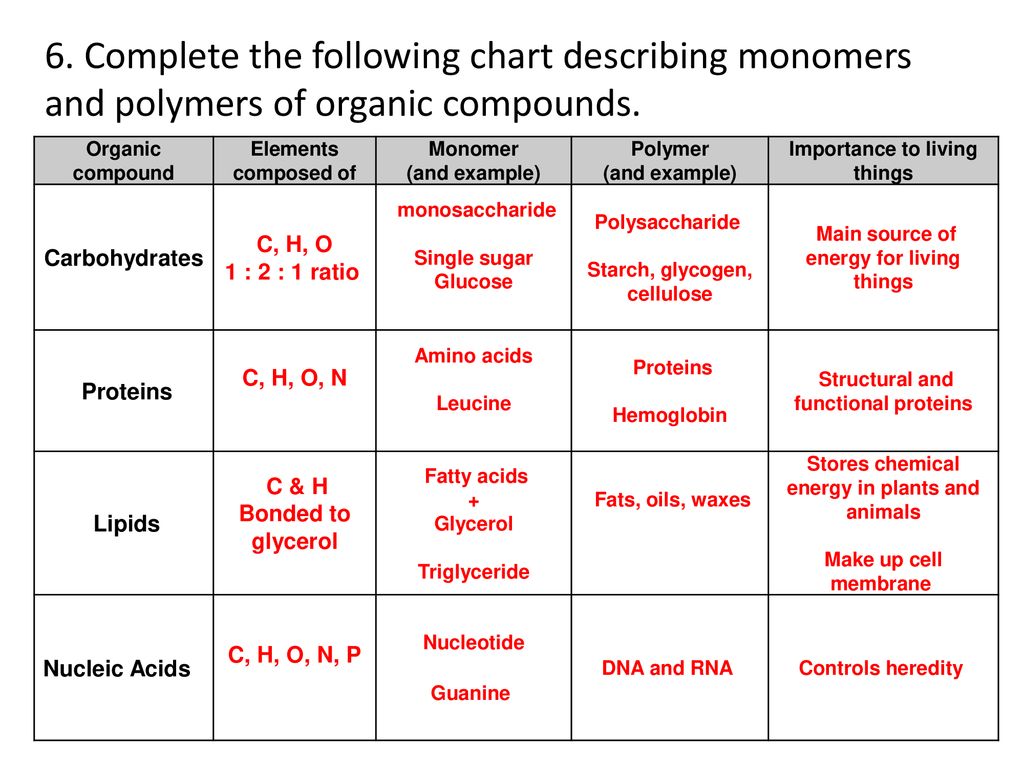
Polymers And Monomers Chart

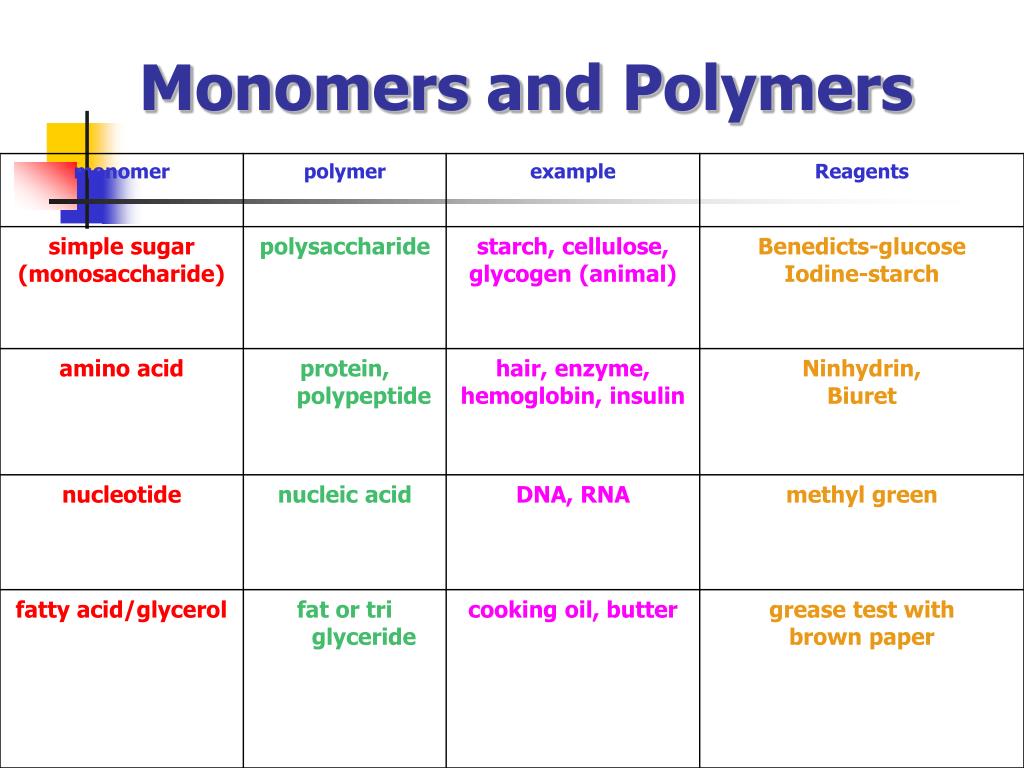
What are the MONOMERS of each POLYMER? ppt download
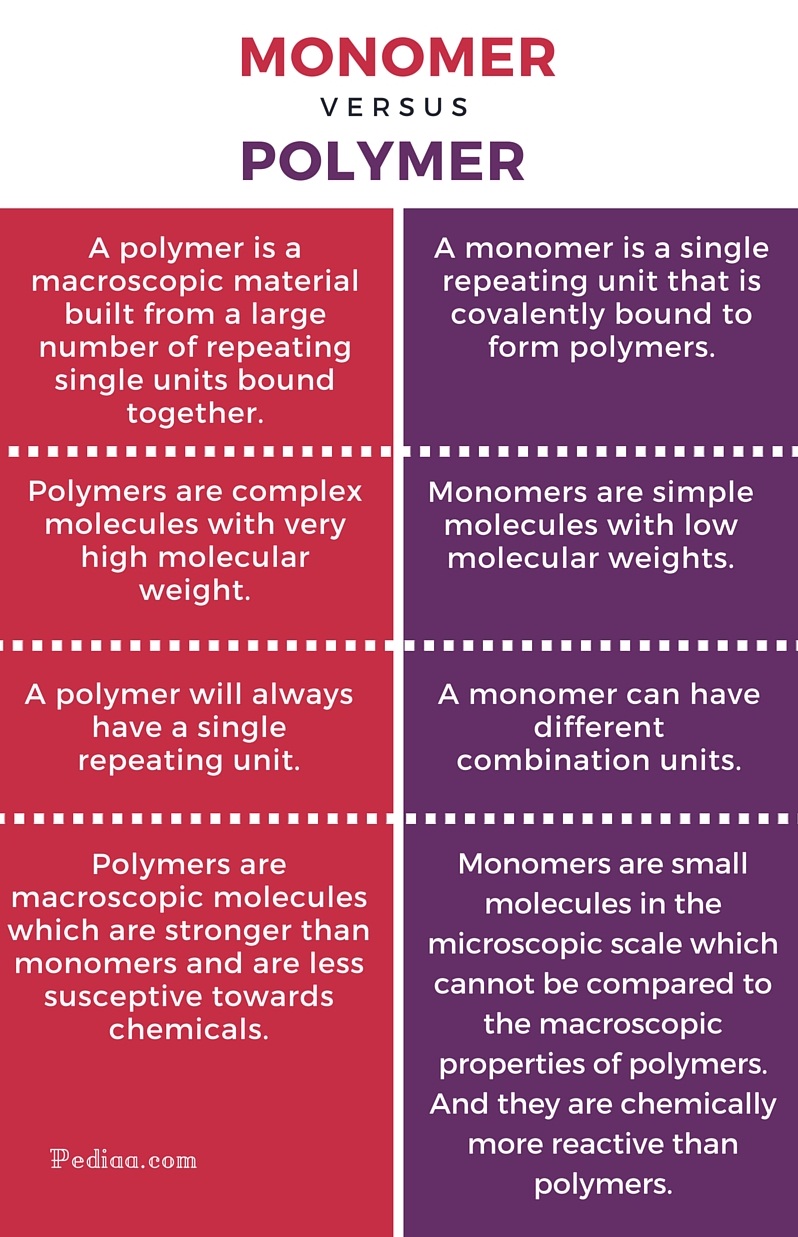
Difference Between Monomer and Polymer
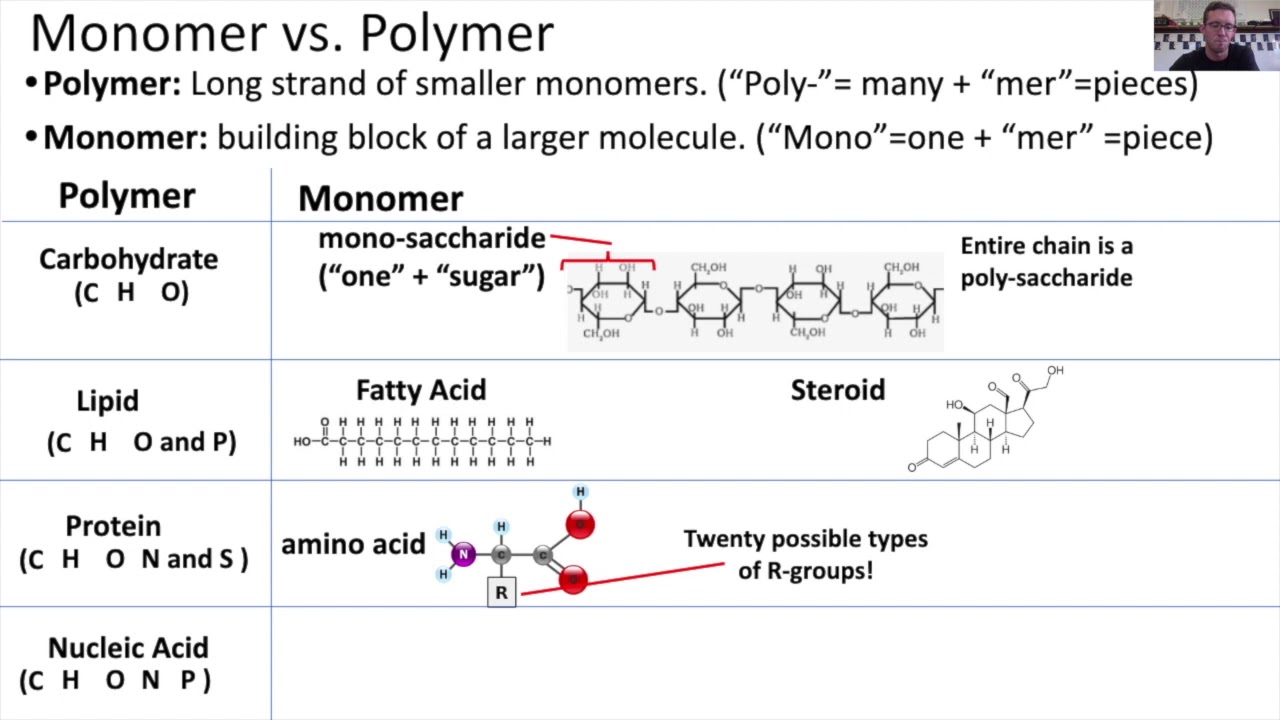
Monomers vs. Polymers YouTube
Download Reference Work Entry Pdf.
A Monosaccharide Is The Monomer That Makes Up A Polysaccharide.
In Doing So, Monomers Release Water Molecules As Byproducts.
Web In Biology, Macromolecules Refer To Large Organic Molecules That Form By Polymerization, A Process That Joins Smaller Units Called Monomers Via Covalent Bonds.
Related Post: