Posterior And Anterior Drawer Test
Posterior And Anterior Drawer Test - Web anterior and posterior drawer test: Whereas excessive posterior displacement of the tibia may indicate injury of the posterior. The examiner sits on the both feet of the subject and places his hands around the upper tibia of one leg. The test is performed with the patient in the supine position and the knee in about 30 degrees of. Web the anterior drawer test for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) stability is a special test for your knee. Web the anterior drawer test is used to identify acl tears or compromised integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament. Some older studies note a lower sensitivity (accuracy) level for detecting acl injuries — as low as 61 percent. A lachman test is a variation of the anterior drawer test. Patella fracture (usually postop during rehab), patellar tendon rupture. Healthcare provider often perform a posterior drawer test to assess the function of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl)—one of the four ligaments of the knee. The anterior drawer test shows sensitivity and specificity, however there was heterogeneity in the studies included: Neutral and at 30° of internal and external rotation. The test is performed with the patient in a relaxed supine position with knees bent to approximately 90 degrees. It is designed to help you or your healthcare provider determine if you have sprained or. The test simply involves your practitioner. The most commonly used test for acl and pcl evaluation, they are easy to perform, but require some attention to avoid mistakes and for correct interpretation. Patella fracture (usually postop during rehab), patellar tendon rupture. A positive result in either test indicates ligament laxity or injury, with the degree of movement and lack of. Whereas excessive posterior displacement of the tibia may indicate injury of the posterior. Frost and hanson 7 described the posterior drawer test using the same patient and clinician positioning as that used for the anterior drawer test. A positive result in either test indicates ligament laxity or injury, with the degree of movement and lack of end, feel in the. The examiner should sit on the foot of the patient's leg. To perform the anterior drawer test, the patient should be positioned in supine with the hip flexed to 45 degrees and knee flexed to 90 degrees. Web the lachman test is the most accurate test for detecting acl injury, followed by the anterior drawer test and the pivot shift. The test is performed with the patient in the supine position and the knee in about 30 degrees of. Web anterior and posterior drawer test: Web anterior drawer test* with the patient supine on the examining table, flex the hip to 45° and the knee to 90°. The anterior drawer test shows sensitivity and specificity, however there was heterogeneity in. Web the posterior drawer test and the lachman test were positive, while the front drawer test was negative, and no laxity of the collateral ligament was found. The test simply involves your practitioner. The lachman test is the most sensitive in assessing acl rupture, with 95% sensitivity and 94% specificity. Web multiple provocative maneuvers can be employed to assess the. The examiner sits on the both feet of the subject and places his hands around the upper tibia of one leg. Instead of holding your thigh at 45 degrees like you would for an anterior drawer test, your provider will hold your thigh at 20 or 30 degrees. Have the patient flex the hip and knees to 90°, feet. The. Web the posterior drawer test and the lachman test were positive, while the front drawer test was negative, and no laxity of the collateral ligament was found. Web the anterior drawer test pulls the tibia forward to evaluate the acl, while the posterior drawer test pushes the tibia backward to assess the pcl. The most commonly used test for acl. Maximum load to failure is 2600 newtons (intact acl is 1725 newtons) complications. The test simply involves your practitioner. It is designed to help you or your healthcare provider determine if you have sprained or torn your acl. The test is performed with the patient in a relaxed supine position with knees bent to approximately 90 degrees. The terms ligament. Web multiple provocative maneuvers can be employed to assess the acl, including the anterior drawer, pivot shift, and lachman tests. Observe if the tibia slides forward (like a drawer) from under the femur. The patient’s foot should be flat on the table and further stabilized by the. Have the patient flex the hip and knees to 90°, feet. Web results. Web posterior drawer test. Associated with age < 20 years and graft size < 8mm. Web the posterior drawer test is a common orthopedic test to assess for posterior cruciate ligament tears. Instead of holding your thigh at 45 degrees like you would for an anterior drawer test, your provider will hold your thigh at 20 or 30 degrees. A positive result in either test indicates ligament laxity or injury, with the degree of movement and lack of end, feel in the tibia determining the severity of the injury. The most commonly used test for acl and pcl evaluation, they are easy to perform, but require some attention to avoid mistakes and for correct interpretation. Web the drawer test is used in the initial clinical assessment of suspected rupture of the. Web the anterior drawer test pulls the tibia forward to evaluate the acl, while the posterior drawer test pushes the tibia backward to assess the pcl. Web budoff and nirschl agree that the posterior drawer is the best test to determine pcl integrity, but conclude that grading is the most important as this will determine the course of treatment. Web the lachman test is the most accurate test for detecting acl injury, followed by the anterior drawer test and the pivot shift test. The examiner should sit on the foot of the patient's leg. Healthcare provider often perform a posterior drawer test to assess the function of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl)—one of the four ligaments of the knee. Web anterior drawer test* with the patient supine on the examining table, flex the hip to 45° and the knee to 90°. To perform the anterior drawer test, the patient should be positioned in supine with the hip flexed to 45 degrees and knee flexed to 90 degrees. Place a hand along each side of the patient's knee, while palpating the joint line. Some older studies note a lower sensitivity (accuracy) level for detecting acl injuries — as low as 61 percent.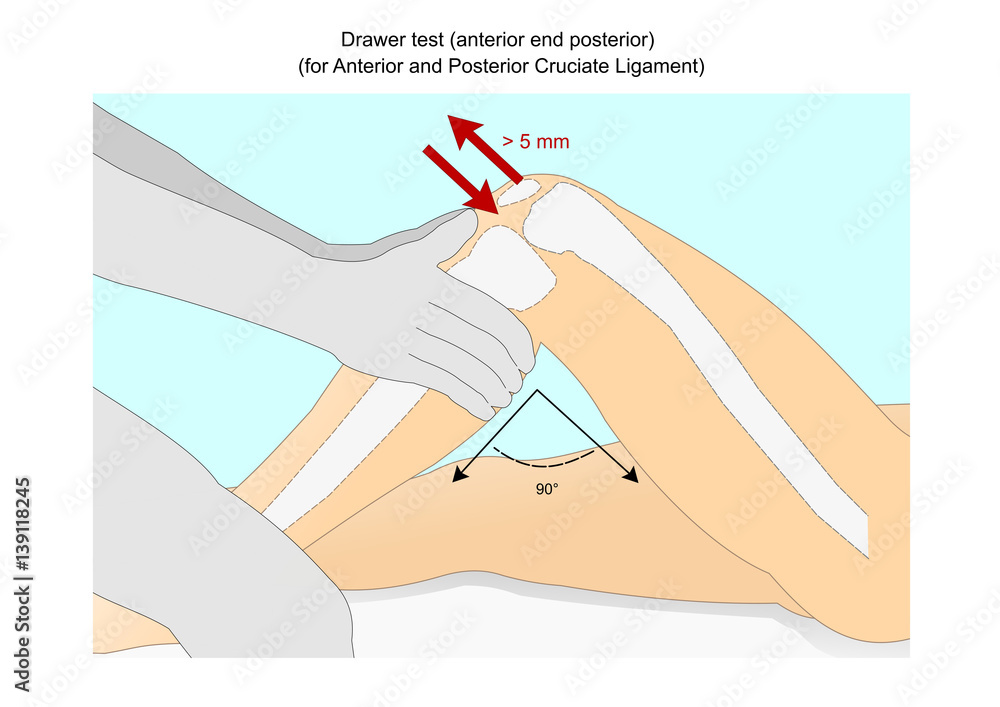
Drawer test to check the integrity of the anterior and posterior

Drawer Test for ACL and PCL in the Knee Pilates Therapy

Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament YouTube

Knee Anterior Posterior Drawer Test YouTube

Knee Tests The Knee Resource

Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injury Knee

Anterior Drawer Test⎟Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture YouTube

Anterior/Posterior drawer test of the Knee YouTube

Drawer Test for ACL and PCL in the Knee Pilates Therapy

Posterior Drawer Test Of The Knee • Easy Explained OrthoFixar 2022 in
Like The Anterior Drawer Test, The Test Is Conducted In Supine Lying Position With The Hip Flexed To 45° And The Knee Flexed To 90°.
Whereas Excessive Posterior Displacement Of The Tibia May Indicate Injury Of The Posterior.
Maximum Load To Failure Is 2600 Newtons (Intact Acl Is 1725 Newtons) Complications.
It Is Designed To Help You Or Your Healthcare Provider Determine If You Have Sprained Or Torn Your Acl.
Related Post: