Rocks And Minerals Chart
Rocks And Minerals Chart - They contain a variety of minerals, including quartz, feldspar, mica, and olivine. Includes about 30 unlabeled minerals, fossils, gemstones, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Observing these characteristics underlies the initial steps of identification. This chart shows the relative abundance of the common rock forming minerals in some of earth's most abundant rock types. Terminology can be referenced in the illustrated glossary of terms that is located at the end of the descriptive information. Web to identify your rock, first take note of its physical properties like color, luster, banding, layering, and grain size. Web to identify a mineral, first observe its physical characteristics like hardness, color, streak, luster, cleavage, and specific gravity. Note that glassy igneous rocks pumice and obsidian are not included on this diagram. These charts include many rocks and minerals and will help you identify the samples in your mini me geology kits and those commonly found in nature. Web to identify minerals and rocks, it's essential to grasp their physical properties. Their color ranges from light (in rocks with high silica content) to dark (in rocks with low silica content). Web photographs and information for a large collection of igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Additionally, you can use identification resources like books and flow charts. Web complete with photos and information. Additionally, you can use identification resources like books and flow charts. In this guide, we’ll learn that rocks and minerals are formed and changed through some really fascinating processes on earth. Their color ranges from light (in rocks with high silica content) to dark (in rocks with low silica content). Includes about 30 unlabeled minerals, fossils, gemstones, igneous, sedimentary, and. In this guide, we’ll learn that rocks and minerals are formed and changed through some really fascinating processes on earth. Web welcome to the wondrous world of rocks and minerals! Such aggregates constitute the basic unit of which the solid earth is composed and typically form recognizable and mappable volumes. Rocks are generally made of two or more minerals. Web. Web to identify a mineral, first observe its physical characteristics like hardness, color, streak, luster, cleavage, and specific gravity. *click on each state to see the full guide* you can also click on the links below to see the rock and mineral guide for each state. In this guide, we’ll learn that rocks and minerals are formed and changed through. Web flow charts or, dichotomous keys, are a great tool for identifying rocks and minerals when you are learning about the different sample properties. Web complete with photos and information about each rock’s distinguishing characteristics, this rock identification guide has been designed to assist you in identifying the rocks provided in the deeper and deeper and mining matters ii kits.. Web to identify a mineral, first observe its physical characteristics like hardness, color, streak, luster, cleavage, and specific gravity. These charts include many rocks and minerals and will help you identify the samples in your mini me geology kits and those commonly found in nature. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Web to identify minerals and. Additionally, you can use identification resources like books and flow charts. Their color ranges from light (in rocks with high silica content) to dark (in rocks with low silica content). These include color, hardness, cleavage, fracture, luster, and specific gravity. We cover a lot of examples that can be helpful when you’re trying to narrow down the rock you’ve found. Web an interactive reference guide to rocks, minerals, and gemstones. Additionally, you can use identification resources like books and flow charts. Web flow charts or, dichotomous keys, are a great tool for identifying rocks and minerals when you are learning about the different sample properties. Their color ranges from light (in rocks with high silica content) to dark (in rocks. These include color, hardness, cleavage, fracture, luster, and specific gravity. Their color ranges from light (in rocks with high silica content) to dark (in rocks with low silica content). Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Web to identify a mineral, first observe its physical characteristics like hardness, color, streak, luster, cleavage, and specific gravity. Petrology is. These include color, hardness, cleavage, fracture, luster, and specific gravity. Their color ranges from light (in rocks with high silica content) to dark (in rocks with low silica content). Observing these characteristics underlies the initial steps of identification. Web on the following pages are descriptions of the properties and uses of the rocks and minerals in the teachers‘ kit. The. In this guide, we’ll learn that rocks and minerals are formed and changed through some really fascinating processes on earth. Write these traits down, then compare the mineral’s traits to those of known mineral types. Observing these characteristics underlies the initial steps of identification. Main types of igneous rocks. Web to identify minerals and rocks, it's essential to grasp their physical properties. Note that glassy igneous rocks pumice and obsidian are not included on this diagram. Web here's how to identify 44 of the most common igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rock types with a handy rock identification chart. Petrology is the scientific study of rocks while the the study of minerals is called mineralogy. The main classification of igneous rocks is by their formation: Includes about 30 unlabeled minerals, fossils, gemstones, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. This chart shows the relative abundance of the common rock forming minerals in some of earth's most abundant rock types. Web rock, in geology, naturally occurring and coherent aggregate of one or more minerals. Web a basic guide to common uk rock types, detailing igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Web complete with photos and information about each rock’s distinguishing characteristics, this rock identification guide has been designed to assist you in identifying the rocks provided in the deeper and deeper and mining matters ii kits. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Web to identify your rock, first take note of its physical properties like color, luster, banding, layering, and grain size.
Spectrum Educational Charts Chart 534 Mineral Wealth of India 1

rocks and minerals pictures free Minerals, Minerals and gemstones

Vintage Geology Wall Chart Rocks & Minerals Etsy

Why Buy From Us? Gemstones chart, Crystal healing stones, Crystals

Rocks And Minerals Chart

Rock And Minerals, Minerals Crystals Rocks, Minerals And Gemstones

16 best Mineral charts images on Pinterest Gemstones, Crystals and
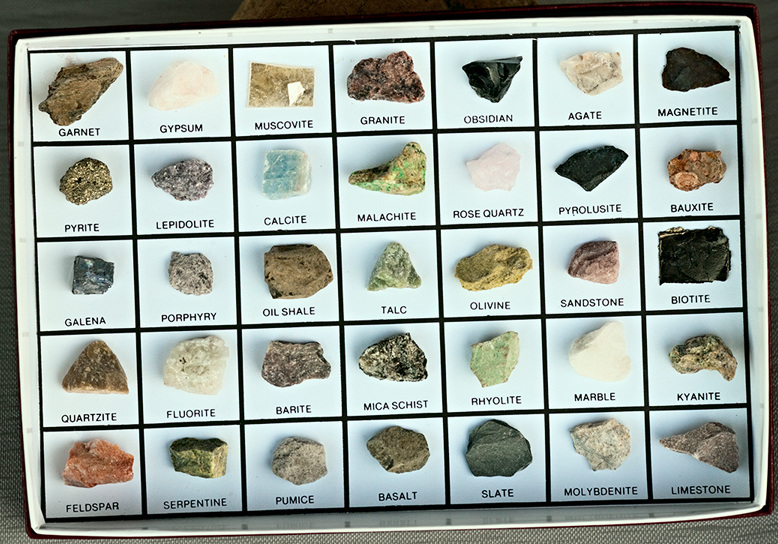
Rocks and Minerals Information on the earth

Knowledge Tree Carson Dellosa Education Rocks + Minerals Science Chart

Minerals poster by Chart Media Chart Media Minerals, Minerals and
Web On The Following Pages Are Descriptions Of The Properties And Uses Of The Rocks And Minerals In The Teachers‘ Kit.
Web To Identify A Mineral, First Observe Its Physical Characteristics Like Hardness, Color, Streak, Luster, Cleavage, And Specific Gravity.
But There Are Certain Things You Can Do To Help Identify Your Rock.
These Include Color, Hardness, Cleavage, Fracture, Luster, And Specific Gravity.
Related Post: