Sedimentary Rocks Identification Chart
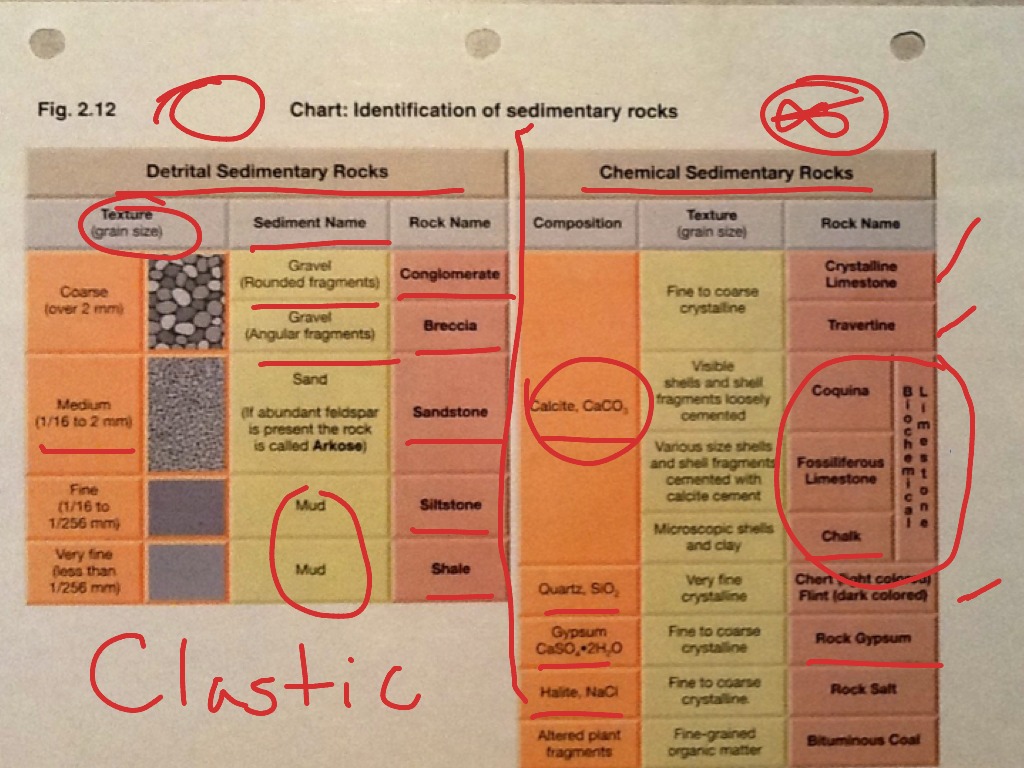
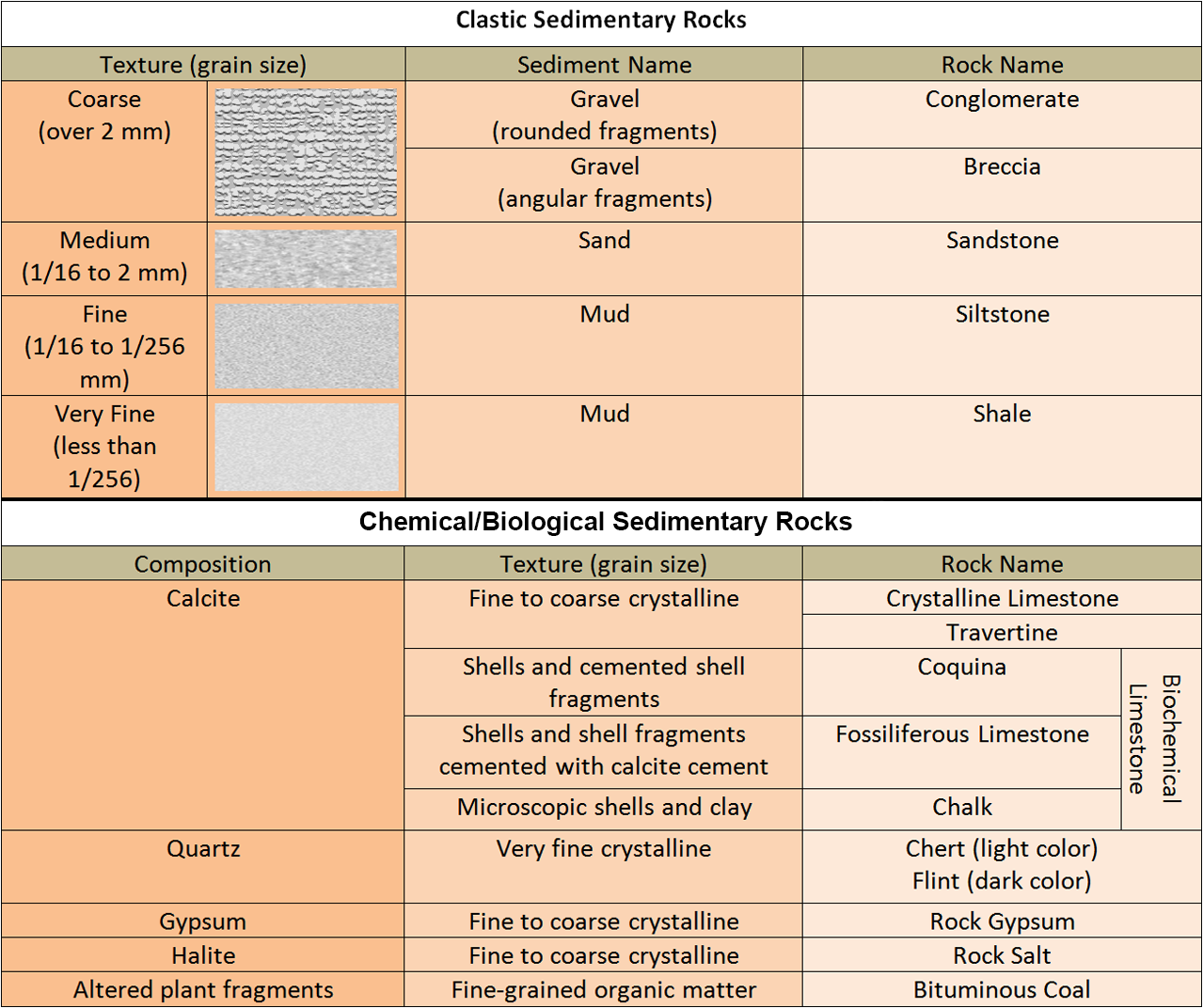
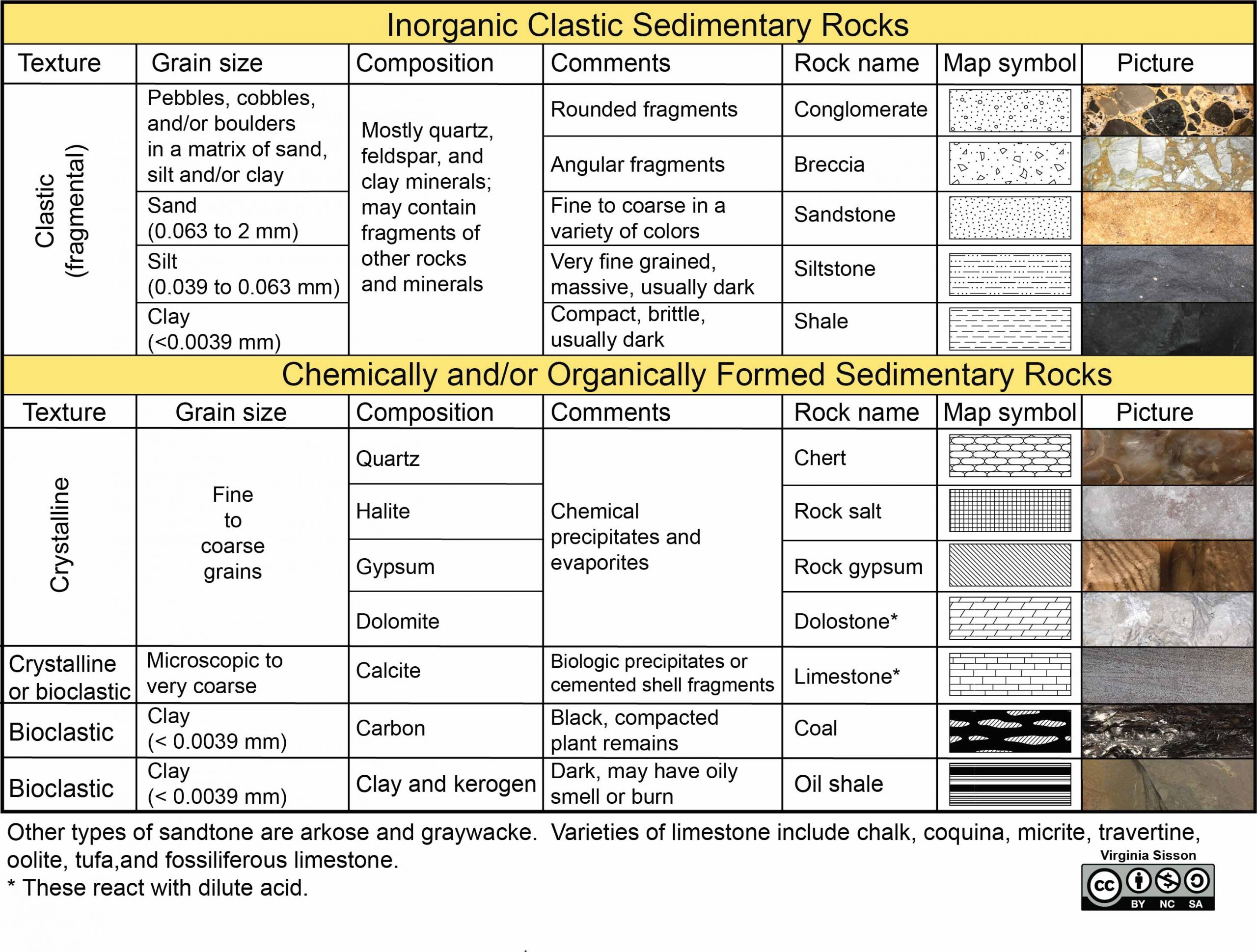
Sedimentary Rocks Identification Chart - Clastic rocks may also include chemically weathered sediment. Web drag the rock name to the correct rock. If it is clastic, examine the sizes and shapes of the fragments to determine the rock type. Web key properties include: Web the size, shape, and composition of the clasts varies widely based upon the source rock and the length of time the sediment has been moving through the system. Web sedimentary rocks form by the accumulation and cementation of mineral or organic particles on the earth’s surface, often in water bodies. The biggest division in types of sedimentary rocks types is based on the primary type of weathering that leads to. We’re not talking about comparing the refractive index of emerald simulants or sussing out the origin of a stone based on microscopic inclusions in this case. Photos and brief descriptions of some common sedimentary rock types are shown on this page. Most sedimentary rocks exhibit visible layers or beds, a result of different periods or conditions of sediment deposition. Web drag the rock name to the correct rock. Photos and facts about clastic, chemical and organic sedimentary rocks. Web to identify your rock, first take note of its physical properties like color, luster, banding, layering, and grain size. Web clay and silt are less than 1/16 mm. The texture is the appearance of the crystals. Sand is clasts between 1/16 and 2 mm in size, and gravel is greater than 2 mm. If it is organic or chemical, determine the rock’s composition and look for unique characteristics to arrive at an identification. The texture is the appearance of the crystals. The rock is sedimentary (siltstone, sandstone or conglomerate). Chemical sedimentary rocks are identified by identifying. They are formed on or near the earth’s surface from the compression of ocean sediments or other processes. The biggest division in types of sedimentary rocks types is based on the primary type of weathering that leads to. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Web to identify a sedimentary rock, first determine if it is clastic,. The rock is sedimentary (siltstone, sandstone or conglomerate). Web sedimentary rock is classified into two main categories: Web here's how to identify 44 of the most common igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rock types with a handy rock identification chart. These rocks usually have layers that hold important clues to earth’s history. Sand is between 1/16 millimeter and 2 mm. Sand is clasts between 1/16 and 2 mm in size, and gravel is greater than 2 mm. If it is organic or chemical, determine the rock’s composition and look for unique characteristics to arrive at an identification. Please note that you can expand this image to fill the screen by clicking on the blue arrows on the right side of. Clastic rocks are classified by The rock is sedimentary (limestone) or metamorphic (marble). Mud is anything smaller than sand and includes the silt and clay size grades of the wentworth. Web sedimentary rocks are derived from pre‑existing rocks by weathering and erosion. Web sedimentary rock, rock formed at or near earth’s surface by the accumulation and lithification of sediment (detrital. Mud is anything smaller than sand and includes the silt and clay size grades of the wentworth. Web sedimentary rock is classified into two main categories: Clastic rocks are classified by Clastic rocks may also include chemically weathered sediment. If it is clastic, examine the sizes and shapes of the fragments to determine the rock type. We just want to know, roughly, what our rock is. Clastic rocks are classified by Web the classification of sedimentary rocks is largely based on differentiating the processes that lead to their formation. They are formed on or near the earth’s surface from the compression of ocean sediments or other processes. The texture is the appearance of the crystals. Grains feel gritty and are silt, sand, or pebble size. Web clay and silt are less than 1/16 mm. If it is clastic, examine the sizes and shapes of the fragments to determine the rock type. The rock is sedimentary (siltstone, sandstone or conglomerate). Web organic sedimentary rocks form from the accumulation of plant or animal debris. Web to identify a sedimentary rock, first determine if it is clastic, organic, or chemical. Sedimentary rocks are one of three main types of rocks, along with igneous and metamorphic. We just want to know, roughly, what our rock is. Clastic rocks may also include chemically weathered sediment. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Chemical sedimentary rocks are identified by identifying the mineral from which they are composed. Clastic or detrital sedimentary rocks are made from pieces of bedrock, sediment, derived primarily by mechanical weathering. Clastic rocks may also include chemically weathered sediment. Web the solid particles and dissolved ions (charged atoms and molecules) freed by this action are transported by water, wind, gravity, and glaciers from their source (that is, the original rock) to depositional basins (the places where sediment accumulates). The classification and description of the various clastic sedimentary rock types appears in the top section of the chart below. The rock is sedimentary (limestone) or metamorphic (marble). If it is clastic, examine the sizes and shapes of the fragments to determine the rock type. Write the name of the rock on each flashcard. Please note that you can expand this image to fill the screen by clicking on the blue arrows on the right side of the diagram. Web here's how to identify 44 of the most common igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rock types with a handy rock identification chart. Web sedimentary rock is classified into two main categories: Web sedimentary rocks are derived from pre‑existing rocks by weathering and erosion. Sand is clasts between 1/16 and 2 mm in size, and gravel is greater than 2 mm. Sand is between 1/16 millimeter and 2 mm. Only three grades are used: These are not visible to the unaided eye.
American Educational Identifying Sedimentary Rock Chart Amazon.in
Sedimentary rock classification Science, Geology ShowMe
Types of sedimentary rocks The Society

Overview of Sedimentary Rocks Laboratory Manual for Earth Science
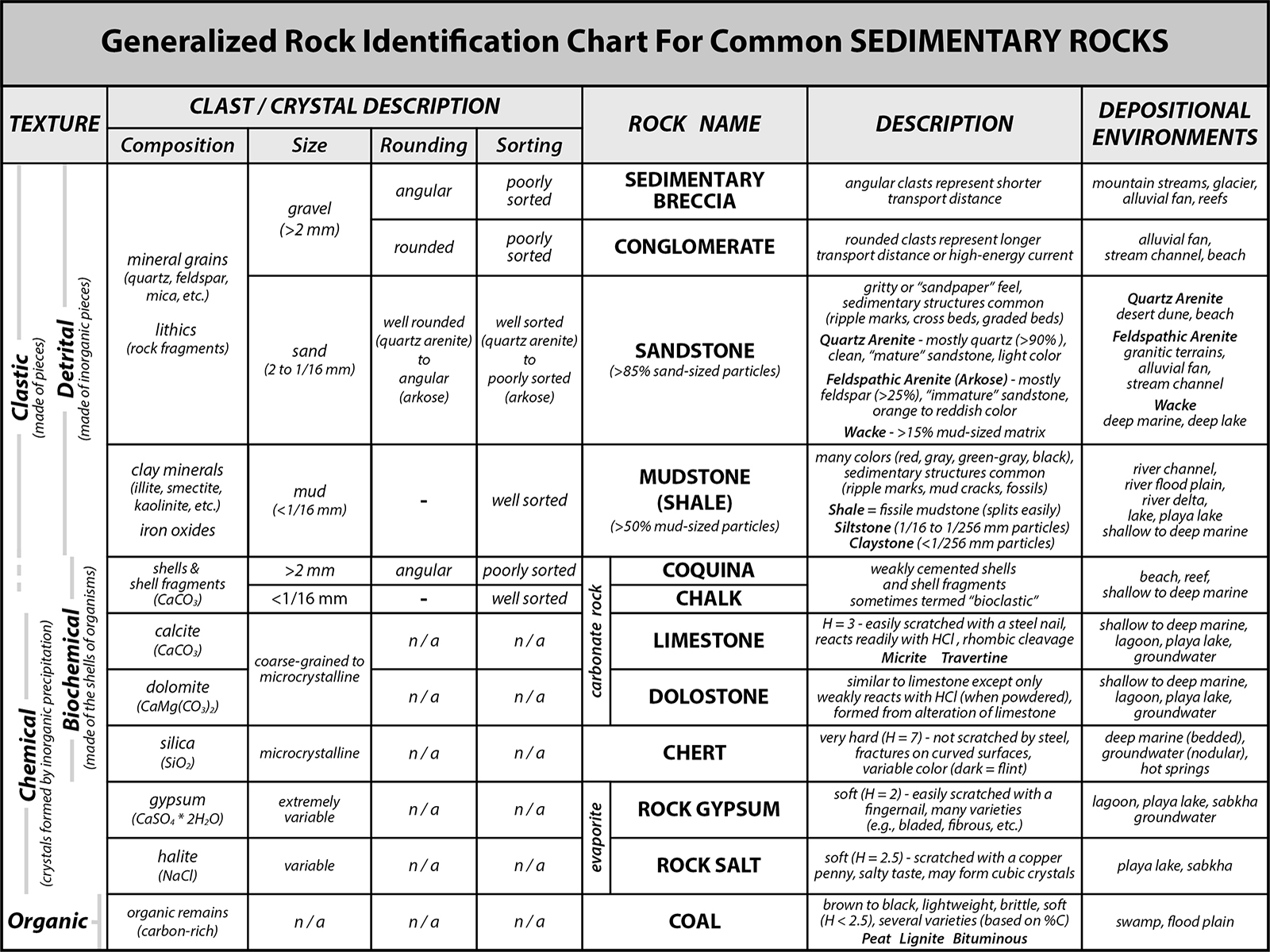
Part B
Chapter 2 Earth Materials The Story of Earth An Observational Guide

Chapter 9 Sedimentary Rocks Physical Geology

Buy Rock Collection and ID Chart 18 Rocks Igneous, Metamorphic
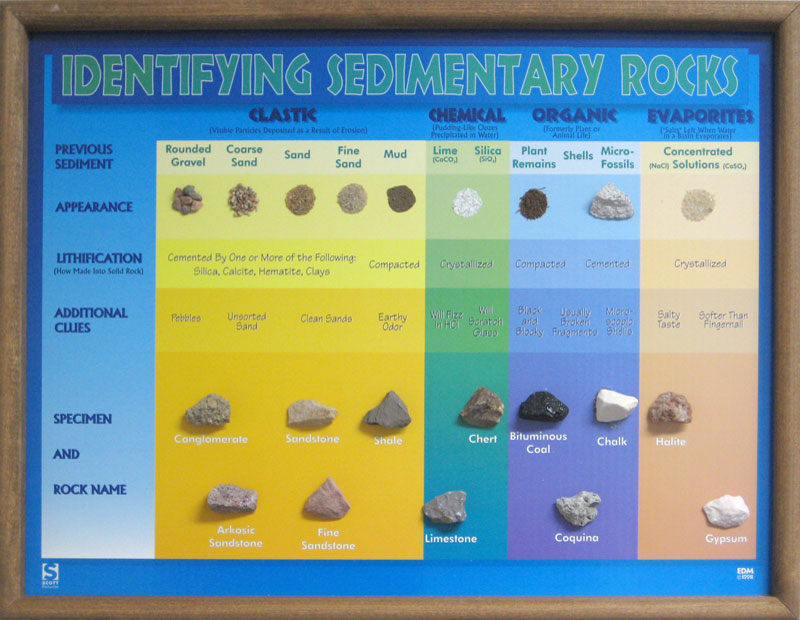
Scott Resources & Hubbard Scientific Identifying Sedimentary Rocks
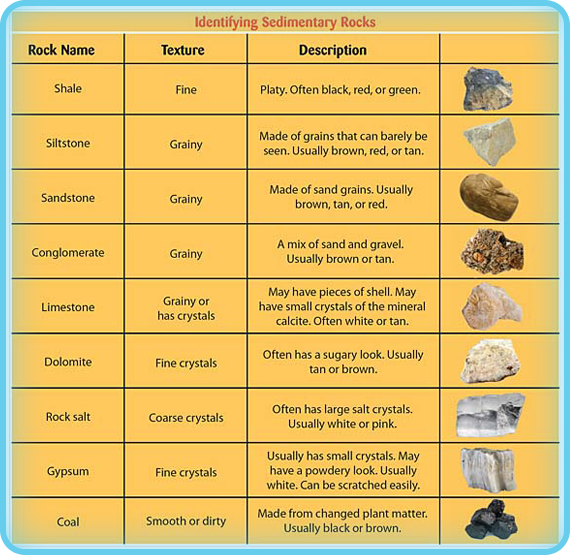
Studying Rocks PowerKnowledge Earth & Space Science
Web Sedimentary Rocks Form By The Accumulation And Cementation Of Mineral Or Organic Particles On The Earth’s Surface, Often In Water Bodies.
The Texture Is The Appearance Of The Crystals.
Web Sedimentary Rock, Rock Formed At Or Near Earth’s Surface By The Accumulation And Lithification Of Sediment (Detrital Rock) Or By The Precipitation From Solution At Normal Surface Temperatures (Chemical Rock).
Web To Identify A Sedimentary Rock, First Determine If It Is Clastic, Organic, Or Chemical.
Related Post: