Serous Membrane Drawing
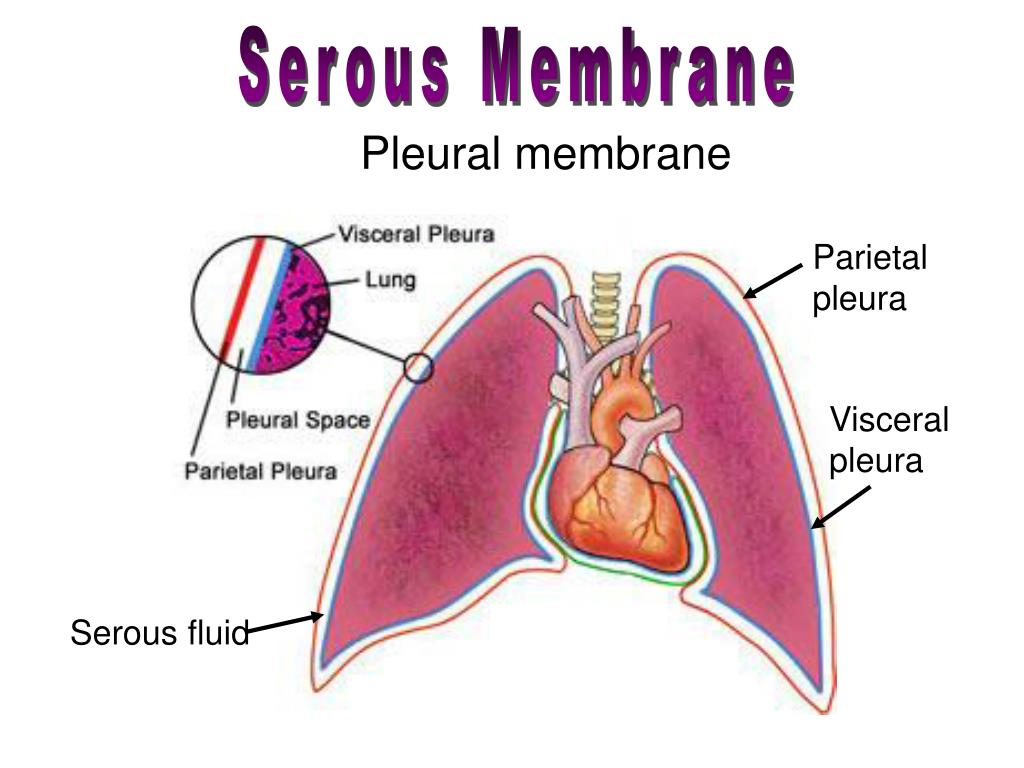
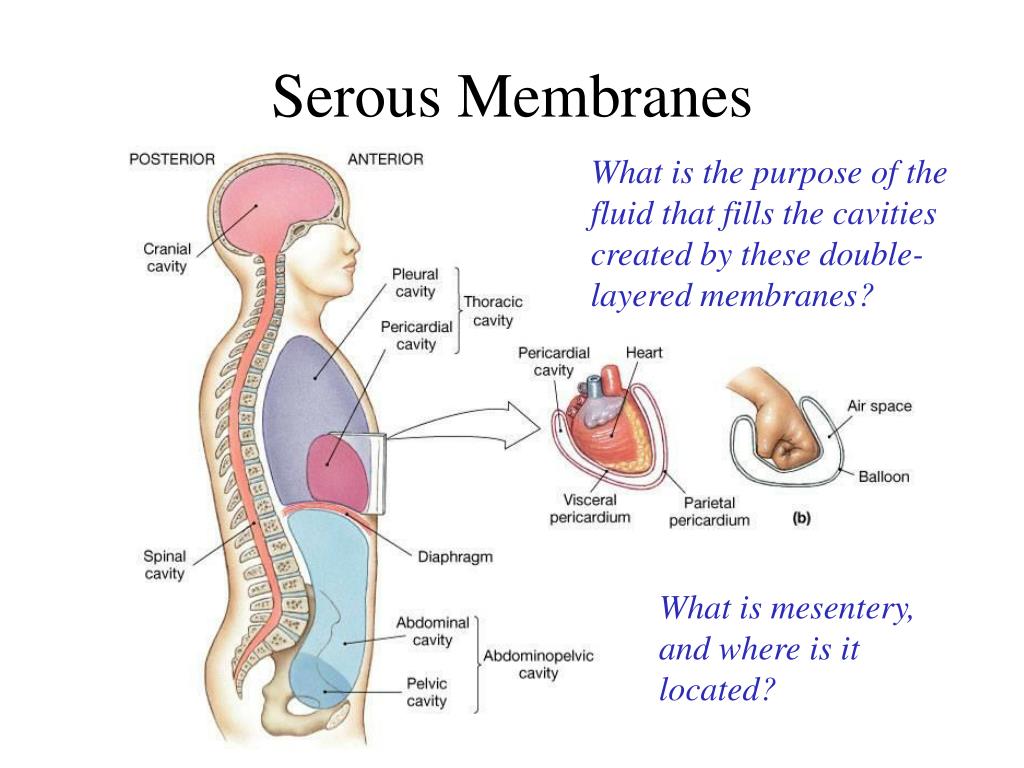
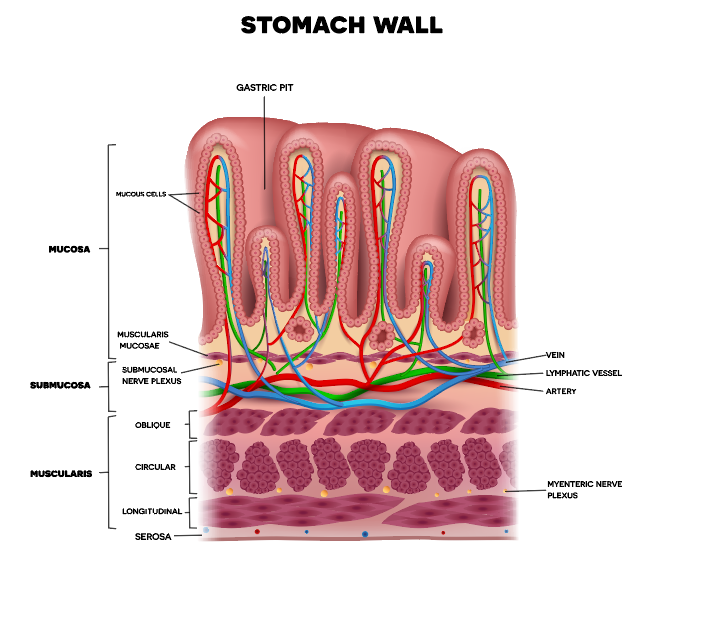
Serous Membrane Drawing - The two pleura that cover the lungs and the pericardium that covers the heart. This also explains the name 'serous membrane'. Body cavities and serous membranes. Three serous membranes line the thoracic cavity; Web the serosal mesothelium is a major source of smooth muscle cells of the gut vasculature. Each pleural cavity is lined by a serous membrane called the pleura. Web the ventral body cavities are enclosed inside serous membranes ( serosa) that line the cavities and the organs inside them and create fluids that lubricate cushion the cavities to protect the organs prevent friction during movement. Web anatomy physiology of body cavities, serous membranes, and their contents explained, drawn, defined. A serous membrane (also referred to as serosa) is an epithelial membrane composed of mesodermally derived epithelium called the mesothelium that is supported by connective tissue. The pleural cavity reduces friction. The largest part of the gut tube is ensheathed in peritoneum. Web anatomy physiology of body cavities, serous membranes, and their contents explained, drawn, defined. These two parts are continuous with each other at the hilum of each lung. The peritoneum provides support and protection for the abdominal organs, and is the. A fourth, the peritoneum, is the serous membrane. Web the serous membrane, or serosal membrane, is a thin membrane that lines the internal body cavities and organs such as the heart, lungs, and abdominal cavity. Web the serous membrane. The pleural cavity reduces friction. Web mesothelium is a simple squamous epithelium that forms the epithelial layer of serous membranes which line body cavities and internal organs.serous membranes, and. Serous membranes line and enclose several body cavities, known as serous cavities, where they secrete a lubricating fluid to reduce friction from. Web draw it video tutorial: Serous membranes consist of a single layer of epithelium, named mesothelium, attached to a supporting layer of connective tissue, with a small layer in between, the basal membrane (fig 1). A fourth, the. Web the ventral body cavities are enclosed inside serous membranes ( serosa) that line the cavities and the organs inside them and create fluids that lubricate cushion the cavities to protect the organs prevent friction during movement. A serous membrane consists of a single layer of flattened mesothelial cells applied to the The serous membrane allows for frictionless movement in. Web serous membrane cavities — are lined by serous membrane — are normally empty (except for microscopic cells and a film of fluid) — function to preclude adhesions among organs, thereby allowing organs to move freely relative to one another. Serous membranes consist of a single layer of epithelium, named mesothelium, attached to a supporting layer of connective tissue, with. Web the serous membrane. The pleural cavity reduces friction. Histologically, this can be seen as a layer on the outside of the gut. Resident progenitors, not exogenous migratory cells, generate the majority of visceral mesothelium in organogenesis. The peritoneum provides support and protection for the abdominal organs, and is the. Web serous membrane cavities — are lined by serous membrane — are normally empty (except for microscopic cells and a film of fluid) — function to preclude adhesions among organs, thereby allowing organs to move freely relative to one another. In histology this layer is called serosa after serous membrane. Resident progenitors, not exogenous migratory cells, generate the majority of. A fourth, the peritoneum, is the serous membrane in the abdominal cavity that covers abdominal organs and forms double sheets of mesenteries that suspend many of the. Web serous membranes are identified according locations. These two parts are continuous with each other at the hilum of each lung. Parietal serosa line the body cavities and visceral serosa line the outer. The largest part of the gut tube is ensheathed in peritoneum. Serous membranes line and enclose several body cavities, known as serous cavities, where they secrete a lubricating fluid to reduce friction from. Web the serous membrane. The serous membrane allows for frictionless movement in a number of vital organs. The thin membrane is made up of mesothelium tissue which. The peritoneum provides support and protection for the abdominal organs, and is the. The pleural cavity reduces friction. Web the ventral body cavities are enclosed inside serous membranes ( serosa) that line the cavities and the organs inside them and create fluids that lubricate cushion the cavities to protect the organs prevent friction during movement. Web the serosal mesothelium is. A fourth, the peritoneum, is the serous membrane in the abdominal cavity that covers abdominal organs and forms double sheets of mesenteries that suspend many of the. Web the ventral body cavities are enclosed inside serous membranes ( serosa) that line the cavities and the organs inside them and create fluids that lubricate cushion the cavities to protect the organs prevent friction during movement. Three serous membranes line the thoracic cavity; Web the serous membrane, or serosal membrane, is a thin membrane that lines the internal body cavities and organs such as the heart, lungs, and abdominal cavity. Web the peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom. Web mesothelium is a simple squamous epithelium that forms the epithelial layer of serous membranes which line body cavities and internal organs.serous membranes, and therefore mesothelium, line the pericardial, pleural and peritoneal cavities. Web membranes of the anterior (ventral) body cavity. The pleural cavity reduces friction. Web anatomy physiology of body cavities, serous membranes, and their contents explained, drawn, defined. Web the serosa, also known as the serous membrane, is a single layer of simple squamous epithelium called mesothelium.it is supported by a thin underlying layer of loose connective tissue, abundant in blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves and adipose tissue.it lines closed body cavities including the pericardial, peritoneal and pleural. Web the serous membrane in the drawing above is composed of epithelium which is always simple squamous epithelium attached to a thin layer of connective tissue, which is always areolar connective tissue. Web draw it video tutorial: A fourth, the peritoneum, is the serous membrane in the abdominal cavity that covers abdominal organs and forms double sheets of mesenteries that suspend many of the. This also explains the name 'serous membrane'. Mesothelium is composed of specialized mesothelial cells which produce serous fluid, a thin, watery. Web serous membranes are identified according locations.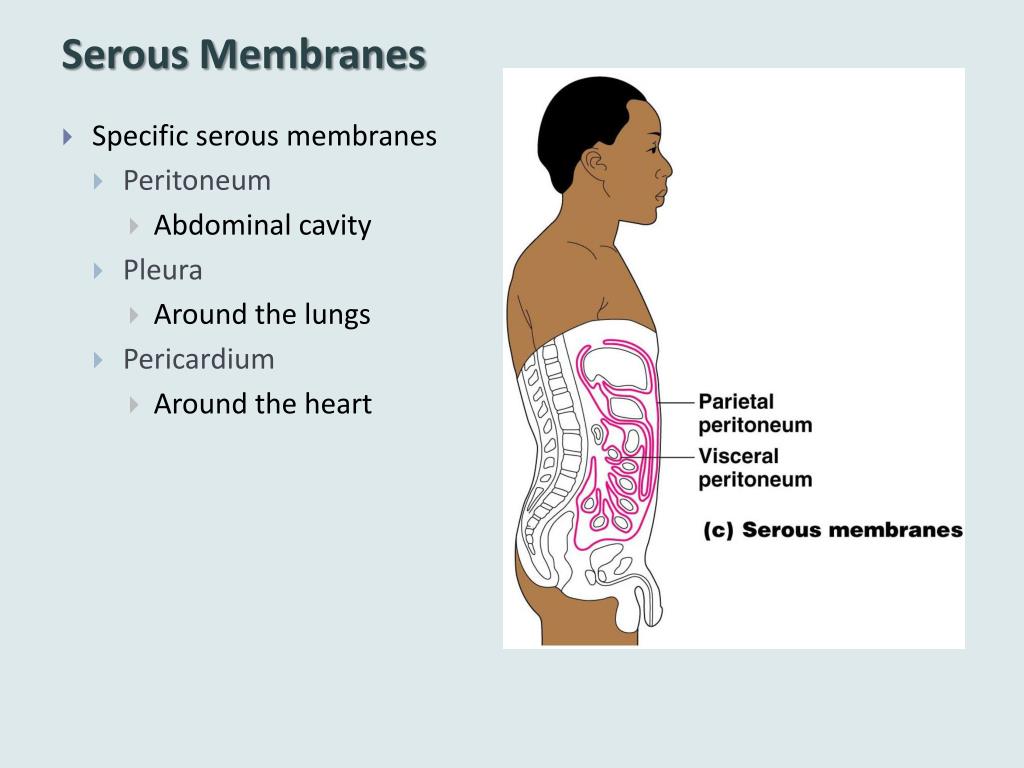
PPT Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Anatomy Body Cavities & Serous Membranes YouTube

Serous Membrane Definition, Function and Structure Biology Dictionary

serous membranes of thoracic Cavity (part 1) Diagram Quizlet

Serous Membrane, Vintage Illustration Stock Vector Illustration of
PPT The Human Body PowerPoint Presentation ID640744
PPT The Tissue Level of Organization PowerPoint Presentation, free
Body Cavities and Membranes SCIENTIST CINDY

Body Membranes Types Of Membranes In The Body Serous Membranes

Chapter 1I Serous Membranes YouTube
The Two Pleura That Cover The Lungs And The Pericardium That Covers The Heart.
Web The Pleural Fluid Helps Lubricate The Membranes Lining The Pleural Cavity And Lungs When Breathing In And Out.
This Also Explains The Name 'Serous Membrane'.
The Pleural Fluid Is Located In The Pleural Cavity, Also Known As The Pleural Space, Which Is The Potential Space Between The Lungs And Chest Wall Shown In Yellow.
Related Post: