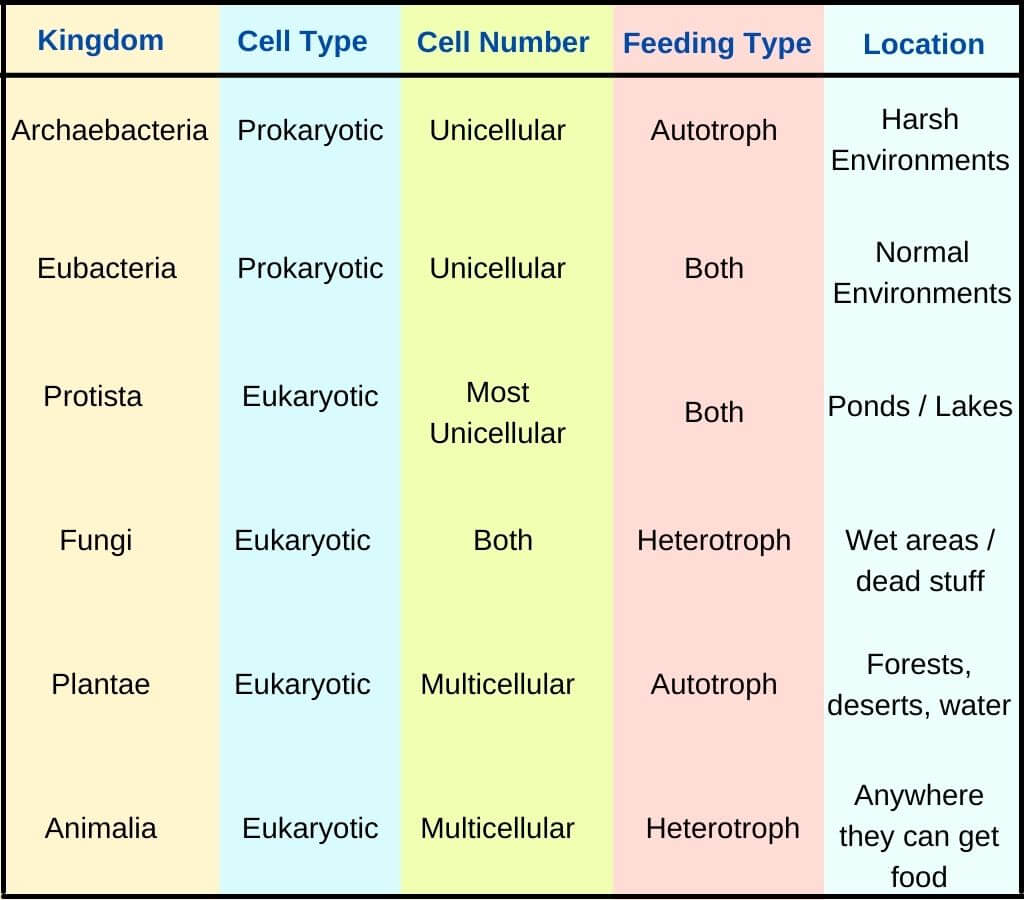
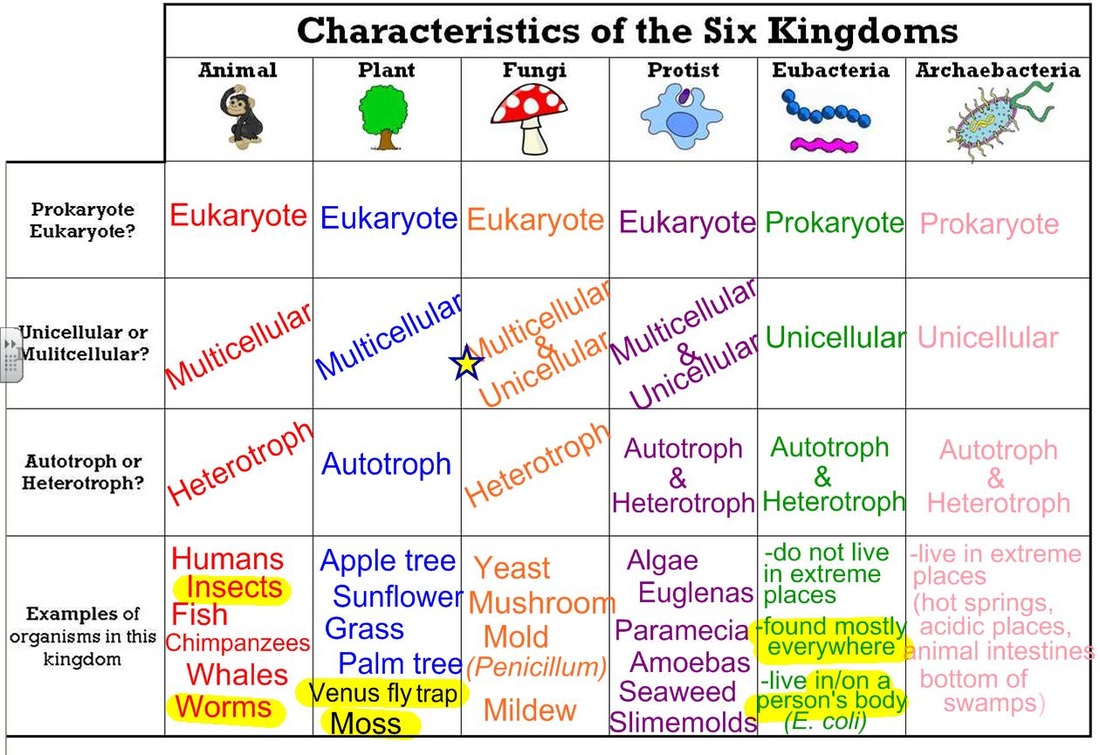
Six Kingdoms Characteristics Chart
Six Kingdoms Characteristics Chart - No organized nucleus, no internal membranes, peptidoglycan cell wall, have ribosomes (small), bacteria and bluegreen algae b. Web the six kingdoms are grouped according to five major categories in addition to other major characteristics. How do the three domains of life differ from each other? Photos courtesy of noaa, usfws, usda, nih. Web the six kingdoms are grouped according to five major categories in addition to other major characteristics. Born in 1707, carl linnaeus will long be remembered for his work in classifying plants and animals. Web understanding the main characteristics of the six kingdoms provides insight into the incredible diversity of life on earth. Web the six kingdoms of life. Web 6 kingdoms of life, from simplest to most complex, are as follows: Who couldnt find any good study material so decided to make her own. Web the six kingdoms are grouped according to five major categories in addition to other major characteristics. They are made of cells. Web there are specific characteristics that scientists use to categorize all organisms into six kingdoms. Web 6 kingdoms of life, from simplest to most complex, are as follows: Web the 6 kingdoms of life include animalia, plantae, fungi,. Each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. They grow, develop, and die. Web the six kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi and protista. This is called a taxonomic rank and the last two names, genus and species, form the biological nomenclature. Previously, eubacteria and archaebacteria were lumped together in the kingdom of monera. Web the six kingdoms of life. Each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. A breakdown of kingdom biology. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Once you know about the six kingdoms of life, you’ll be a classification king… or queen! A breakdown of kingdom biology. 1 classification of living things and naming of organisms. Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like. Web discover which kingdom you belong to and what characteristics you’d have if you fell into one of the other five kingdoms. Web 6 kingdoms of life, complete your thinking map by putting the title of the kingdom and some illustrated examples of organisms that belong to that kingdom in each box. 6 classification of living things practice questions. They. Web discover which kingdom you belong to and what characteristics you’d have if you fell into one of the other five kingdoms. How are organisms classified into kingdoms? Web the six kingdoms are grouped according to five major categories in addition to other major characteristics. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. Web the six kingdoms of life are animalia,. They adapt to their environment. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Living things all have these characteristics: From the ancient archaea thriving in extreme environments to the complex multicellular organisms in the animal kingdom, each kingdom contributes uniquely to the tapestry of life. This isn't as easy as it. How are organisms classified into kingdoms? They adapt to their environment. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. 6 classification of living things practice questions. How are organisms classified into kingdoms? This isn't as easy as it seemed at first! Web the six kingdoms are grouped according to five major categories in addition to other major characteristics. Born in 1707, carl linnaeus will long be remembered for his work in classifying plants and animals. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista,. Web there are now six commonly accepted kingdoms. 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) 5.) 6.) 1 classification of living things and naming of organisms. They grow, develop, and die. Web 6 kingdoms of life, complete your thinking map by putting the title of the kingdom and some illustrated examples of organisms that belong to that kingdom in each box. Here are some key points to remember about the six kingdoms of life: Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. A breakdown of kingdom biology. What is the difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote? Classification attempts to impose a hierarchy on the complex and dynamic variety of life on earth by describing how different species group together and how they are related to one. Web the six kingdoms are grouped according to five major categories in addition to other major characteristics. Who couldnt find any good study material so decided to make her own. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. How do the three domains of life differ from each other? Organisms in the same kingdom share certain fundamental similarities. Difficulty level 3 (developing to mastery) type of assignment individual or group. In 1977, carl woese and colleagues proposed the fundamental subdivision of the prokaryotes into the eubacteria (later called the bacteria) and archaebacteria (later called the archaea), based on ribosomal rna structure; Web the 6 kingdoms of life include animalia, plantae, fungi, prostista, eubacteria and archaebacteria. From the ancient archaea thriving in extreme environments to the complex multicellular organisms in the animal kingdom, each kingdom contributes uniquely to the tapestry of life. Each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. 5 phylogeny, cladistics, and cladograms.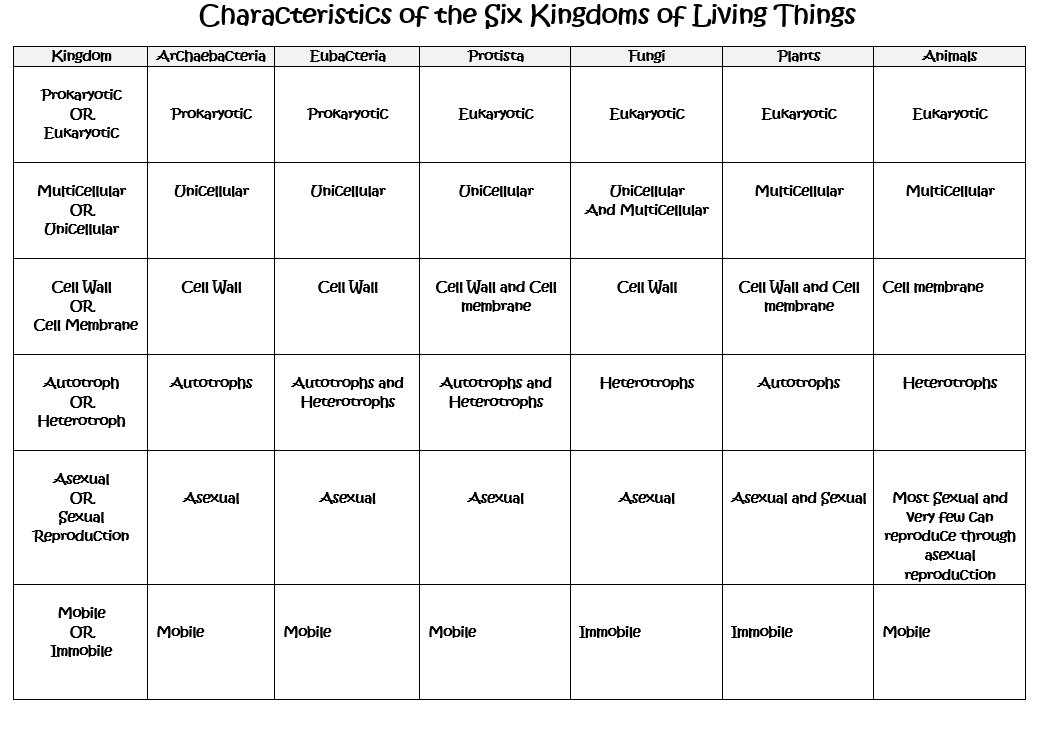
Blog Archives Mr. Shaw Life Science
A Simple Explanation of the 6 Kingdoms of Life

The 6 Kingdoms of Life Simple Explanation for Kids WeHaveKids
Classification of Organisms Rumney Marsh Academy Science Revere

Montessori Materials The Six Kingdoms Chart with Cards

SOLUTION The Six Kingdoms of Life Characteristic Chart Studypool

Characteristics of the 6 Kingdoms Taxonomy, Prokaryotes, Eubacteria
Science poster of six kingdoms of life 2906732 Vector Art at Vecteezy
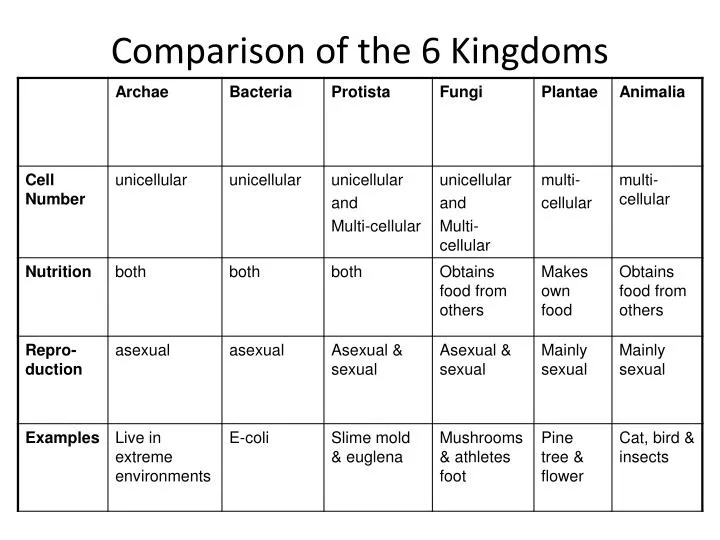
PPT Comparison of the 6 Kingdoms PowerPoint Presentation, free
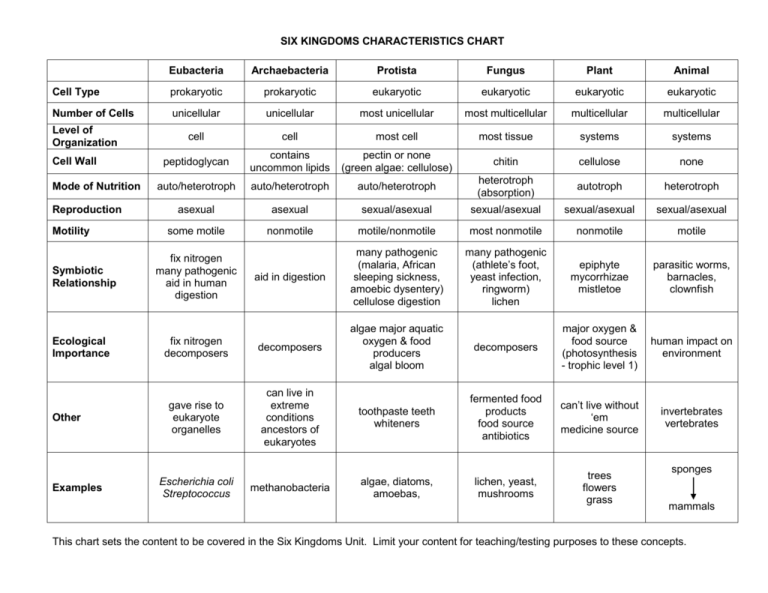
SIX KINGDOMS CHARACTERISTICS CHART
What Is The Difference Between An Autotroph And A Heterotroph?
Born In 1707, Carl Linnaeus Will Long Be Remembered For His Work In Classifying Plants And Animals.
This Is Called A Taxonomic Rank And The Last Two Names, Genus And Species, Form The Biological Nomenclature.
Web 6 Kingdoms Of Life, Complete Your Thinking Map By Putting The Title Of The Kingdom And Some Illustrated Examples Of Organisms That Belong To That Kingdom In Each Box.
Related Post: