Sleep Apnea Heart Rate Chart
Sleep Apnea Heart Rate Chart - Web obstructive sleep apnea (osa), a heterogeneous and multifactorial sleep related breathing disorder with high prevalence, is a recognized risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. The first stage is simply the act of transitioning from. Web obstructive sleep apnea (osa), characterized by cyclic collapse of the upper airway and partial or complete cessation of airflow during sleep, is highly prevalent with prevalence of 34% in men and 17% in women in the general population [ 1 ]. Another study determined that patients with both heart failure and sleep apnea died at twice the rate of those with just heart failure ^2. The main types of sleep apnea are: Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts. Our previous work demonstrated that shannon entropy of the degree distribution (e dd ), obtained from the network domain of heart rate variability (hrv), might be a potential indicator for cvd. Web the sleep profile of a patient with severe sleep apnea shows a reduced percentage of deep sleep (stages 3 and 4), an increased percentage of light sleep (stages 1 and 2), and a long. Patients with osa are at an increased risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Your brain tries to protect you by waking you up enough to breathe, but this prevents restful, healthy sleep. Untreated severe sleep apnea increases the risk for cardiovascular events. Web a normal heart rate while sleeping is often between 40 to 50 beats per minute (bpm), though there is variability between individuals. Web for most adults, a normal resting heart rate is considered to be between 60 and 100 beats per minute. 10 we set out to examine overnight. Consumer wearable heart rate (hr) sensors may be a means for passive hr monitoring in patients with af. Web during deep sleep, your breathing rate and heart rate slow down even more and your body wholly relaxes. Web previous studies have provided insight into heart rate periodicity changes at particular frequency ranges by examining individual apneic episodes, 12 individual sleep. The main types of sleep apnea are: 13 several earlier studies have demonstrated that this pattern can be used to detect osa and suggested that the. Apneas are periods when a person stops breathing and hypopneas are instances where airflow is blocked, causing shallow breathing. The first stage is simply the act of transitioning from. , susan redline 1 *. Paused breathing during your sleep raises your risk of heart disease, high blood pressure and stroke — We discuss what is considered a normal sleeping heart rate for each age range, as well as share signs to look out for that may indicate an underlying condition. Web a normal heart rate while sleeping is often between 40 to 50 beats. The main types of sleep apnea are: Web obstructive sleep apnea (osa), characterized by cyclic collapse of the upper airway and partial or complete cessation of airflow during sleep, is highly prevalent with prevalence of 34% in men and 17% in women in the general population [ 1 ]. Web one study found that 50 percent or more of cardiovascular. 10 we set out to examine overnight heart rate variability in osa using frequency‐domain analysis with special attention to high frequency a. Web obstructive sleep apnea (osa), a heterogeneous and multifactorial sleep related breathing disorder with high prevalence, is a recognized risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Web during deep sleep, your breathing rate and heart rate slow down. Web obstructive sleep apnea (osa), a heterogeneous and multifactorial sleep related breathing disorder with high prevalence, is a recognized risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Web patients with obstructive sleep apnea (osa) are at a higher risk for atrial fibrillation (af). Untreated severe sleep apnea increases the risk for cardiovascular events. Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder. Web previous studies have provided insight into heart rate periodicity changes at particular frequency ranges by examining individual apneic episodes, 12 individual sleep stages, 14 or very low frequency ranges. Light sleep is broken down into stages 1 and 2. Diurnal variations in blood pressure, heart rate, and cardiac events occur during normal sleep. Web episodes of osa are accompanied. Paused breathing during your sleep raises your risk of heart disease, high blood pressure and stroke — Autonomic dysfunction leads to adverse cardiovascular outcomes in diverse pathways. Consumer wearable heart rate (hr) sensors may be a means for passive hr monitoring in patients with af. Web during deep sleep, your breathing rate and heart rate slow down even more and. But children are very different because adult heart rates tend to slow as we get older. 13 several earlier studies have demonstrated that this pattern can be used to detect osa and suggested that the. If you snore loudly and feel tired even after a full night's sleep, you might have sleep apnea. Patients with osa are at an increased. Web episodes of osa are accompanied by a characteristic heart rate pattern, known as cyclic variation of heart rate (cvhr), which consists of bradycardia during apnea followed by abrupt tachycardia on its cessation. Patients with osa are at an increased risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Web the sleep profile of a patient with severe sleep apnea shows a reduced percentage of deep sleep (stages 3 and 4), an increased percentage of light sleep (stages 1 and 2), and a long. If you snore loudly and feel tired even after a full night's sleep, you might have sleep apnea. 4 despite its high prevalence in. Over time, this condition can cause serious complications. 13 several earlier studies have demonstrated that this pattern can be used to detect osa and suggested that the. Obstructive sleep apnea (osa) is a highly prevalent condition, resulting in recurrent hypoxic events, sleep arousal, and daytime sleepiness. Paused breathing during your sleep raises your risk of heart disease, high blood pressure and stroke — Osa is characterized by repeated intermittent hypoxia (ih), frequent arousals, and daytime drowsiness. Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts. Obstructive sleep apnea (osa), a highly prevalent sleep disorder, is closely related to cardiovascular disease (cvd). Web during deep sleep, your breathing rate and heart rate slow down even more and your body wholly relaxes. Web people with untreated sleep apnea are twice as likely to have a heart attack compared with those who don't have the disorder. Consumer wearable heart rate (hr) sensors may be a means for passive hr monitoring in patients with af. Web obstructive sleep apnea (osa), characterized by cyclic collapse of the upper airway and partial or complete cessation of airflow during sleep, is highly prevalent with prevalence of 34% in men and 17% in women in the general population [ 1 ].
Sleep apnea and the heart Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine
Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease Circulation Research

My PulseOx charts does this indicate sleep apnea? r/SleepApnea

Basics of Sleep Apnea and Heart Failure American College of Cardiology

Figure 1 from Instantaneous heart rate as a robust feature for sleep
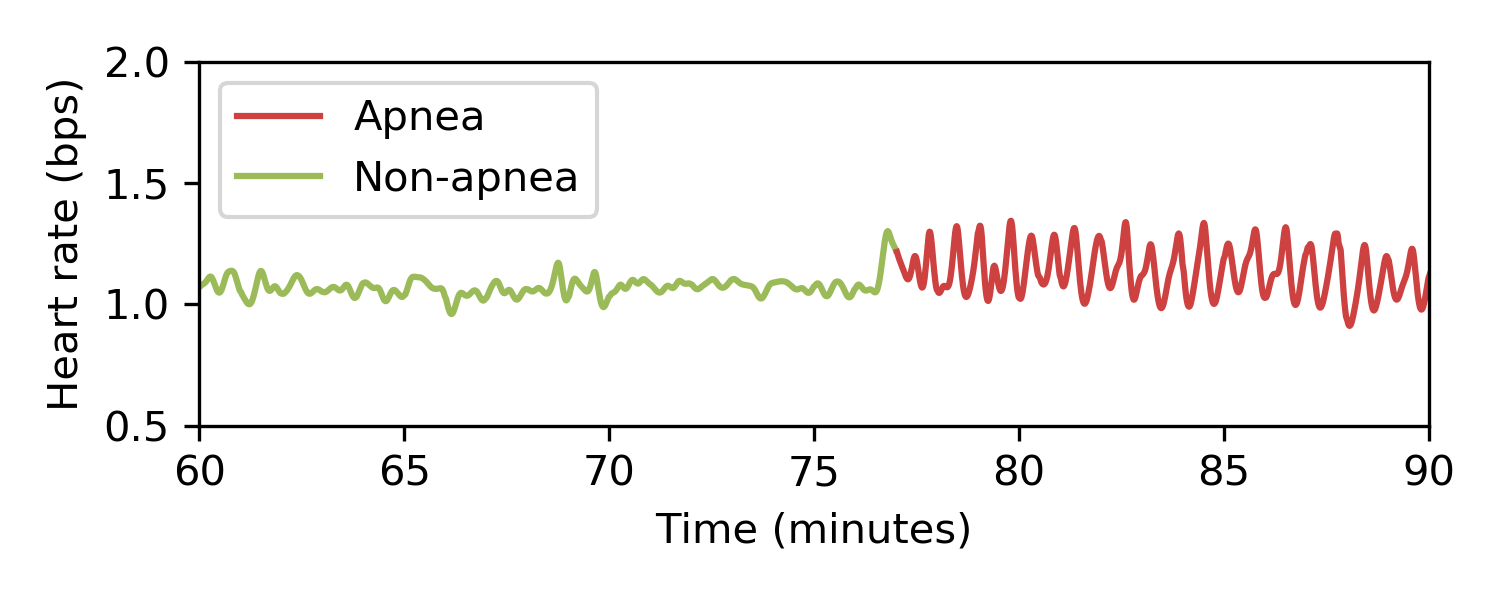
GitHub ChiQiao/ApneaECG Detect sleep apnea using heart rate data

Sleep‐disordered breathing in heart failure Pearse 2016 European

50 Shocking Statistics on Sleep Apnea 2024 Ultimate Guide
Original ("raw") heart rate time series from the two subjects (one

Nocturnal Arrhythmias and Heart‐Rate Swings in Patients With
One Way Doctors Assess The Likelihood Of Sleep Apnea Is A With The Stopbang Test, At Left.
Diurnal Variations In Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, And Cardiac Events Occur During Normal Sleep.
Untreated Severe Sleep Apnea Increases The Risk For Cardiovascular Events.
Web Obstructive Sleep Apnea Has Been Linked To Higher Rates Of Hypertension, Stroke, And Coronary Artery Disease.
Related Post: