Stainless Steel Bolt Torque Chart
Stainless Steel Bolt Torque Chart - = clamp load for j429 grade 5 and 8, fnl grade 9, a574, class 4.6, 8.8, 10.9 and 12.9, the clamp loads are listed at 75% of the proof loads specified by the standard. To construct a securely assembled joint using bolts or machine screws, the fasteners must be tightened to develop the proper amount of clamping force. Different lengths of thread engagement were analyzed This applies to ‘grades’ a1, a2, a3, a4 and a5. Web if lubrication has been applied to the bolt and/or the nut (other than the normal protective oil film), multiply the recommended torque by the appropriate factor shown in the table. The below estimated torque calculations are only offered as a guide. Bolt and nut are both phosphated; This table is offered as the suggested maximum torque values for threaded products and is only a guide. Web the following data tables are designed to be used as general guidance when installing stainless steel fasteners. Web values given represent the torque required to induce a tension in the bolt corresponding to approximately 65% of its proof load. = clamp load for j429 grade 5 and 8, fnl grade 9, a574, class 4.6, 8.8, 10.9 and 12.9, the clamp loads are listed at 75% of the proof loads specified by the standard. For a307 grade a, 75% of 36,000 psi is utilized. The risk of galling or thread seizing can be reduced by: Stainless steel fasteners tend to. Web bolt torque chart reference guides include grade 2, b7, a307, a325, grade 8, a490, and grade 5. Stainless steel fasteners tend to gall, especially with long run downs, prevailing torque fasteners, impact drivers, and lack of lubrication. This applies to ‘grades’ a1, a2, a3, a4 and a5. The risk of galling or thread seizing can be reduced by: Stainless. 5)stainless steel fasteners tend to gall while being tightened. Web values given represent the torque required to induce a tension in the bolt corresponding to approximately 65% of its proof load. Web if lubrication has been applied to the bolt and/or the nut (other than the normal protective oil film), multiply the recommended torque by the appropriate factor shown in. While all care has been taken with its preparation, no responsibility is accepted for the The above data is based on a dry installation and should not be used for a lubricated installation. While fastenal has used reliable sources and testing to determine these values, there are many variables that will effect the results and the use of this information. Web values given represent the torque required to induce a tension in the bolt corresponding to approximately 65% of its proof load. Bolt and nut are both phosphated; All material included in this chart is advisory only, and its use by anyone. The lubricated values were calculated at 90% of the dry condition test results. Around 640 torque tables were. Stainless steel fasteners tend to gall, especially with long run downs, prevailing torque fasteners, impact drivers, and lack of lubrication. Torque values are calculated giving way to preliminary data tables. The following torque values are suggested maximums based upon actual lab testing on clean and dry or near dry fasteners. The below estimated torque calculations are only offered as a. This shows torque values in nm for property classes 50, 70 and 80 as shown in the table below. Web remember, you may need to vary these numbers somewhat based on the individual joint or the amount of fastener lubrication. To construct a securely assembled joint using bolts or machine screws, the fasteners must be tightened to develop the proper. Recommended bolt torque values for stainless steel and nonferrous fasteners (inch series). Around 640 torque tables were developed for unc, unf, and m fasteners. Required torque = torque recommended x 0.75. While fastenal has used reliable sources and testing to determine these values, there are many variables that will effect the results and the use of this information is at. All material included in this chart is advisory only, and its use by anyone. Stainless steel fasteners tend to gall, especially with long run downs, prevailing torque fasteners, impact drivers, and lack of lubrication. Around 640 torque tables were developed for unc, unf, and m fasteners. * this table is recommended for use as a guide only. For a307 grade. Stainless steel fasteners tend to gall, especially with long run downs, prevailing torque fasteners, impact drivers, and lack of lubrication. To construct a securely assembled joint using bolts or machine screws, the fasteners must be tightened to develop the proper amount of clamping force. The below estimated torque calculations are only offered as a guide. Testing is done to various. This applies to ‘grades’ a1, a2, a3, a4 and a5. To construct a securely assembled joint using bolts or machine screws, the fasteners must be tightened to develop the proper amount of clamping force. All material included in this chart is advisory only, and its use by anyone. Recommended bolt torque values for stainless steel and nonferrous fasteners (inch series). Different lengths of thread engagement were analyzed Stainless steel fasteners tend to gall, especially with long run downs, prevailing torque fasteners, impact drivers, and lack of lubrication. Stainless steel fasteners tend to gall, especially with long run downs, prevailing torque fasteners, impact drivers, and lack of lubrication. This table is offered as the suggested maximum torque values for threaded products and is only a guide. The following torque values are suggested maximums based upon actual lab testing on clean and dry or near dry fasteners. The lubricated values were calculated at 90% of the dry condition test results. While all care has been taken with its preparation, no responsibility is accepted for the Web check bolt torque chart online, view bolt torque chart stainless steel and m30 stainless steel bolt torque. Therefore, using the correct installation torque is. Web torque and pullout load. * this table is recommended for use as a guide only. Web if lubrication has been applied to the bolt and/or the nut (other than the normal protective oil film), multiply the recommended torque by the appropriate factor shown in the table.
Stainless Steel 316 Bolts and A4 S31600 Stud/ Hex Bolt/ Nuts/ Fasteners

304 Stainless Steel Metric Bolt Torque Chart A Visual Reference of
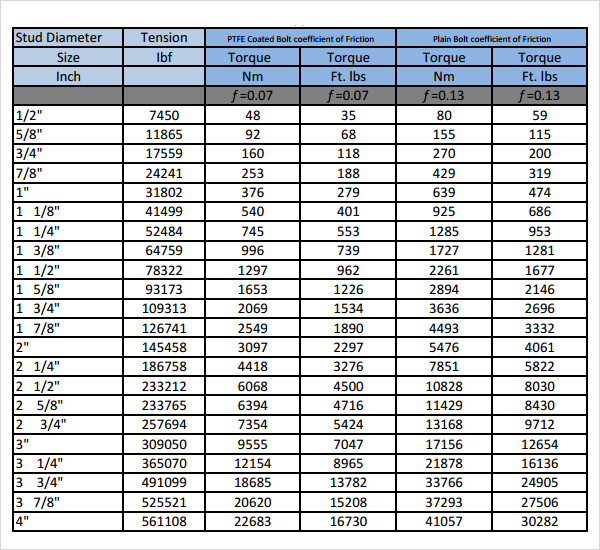
FREE 7+ Sample Bolt Torque Chart Templates in PDF MS Word

A270 Stainless Steel Hex Head Bolt A2 70 Bolt Torque & Size Chart

Stainless Steel Torque Chart Website of julisalt!
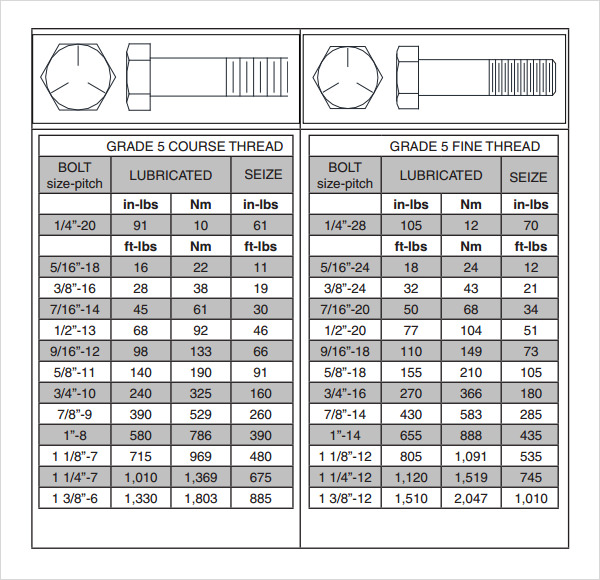
FREE 7+ Sample Bolt Torque Chart Templates in PDF MS Word

Metric Stainless Bolt Torque Chart
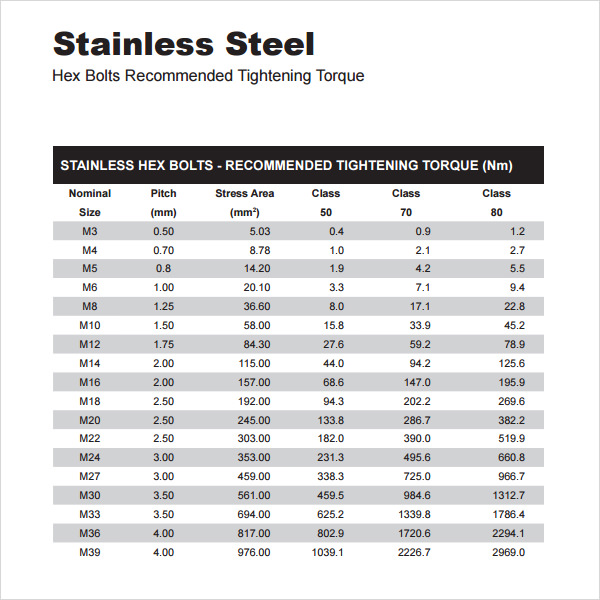
FREE 7+ Sample Bolt Torque Chart Templates in PDF MS Word
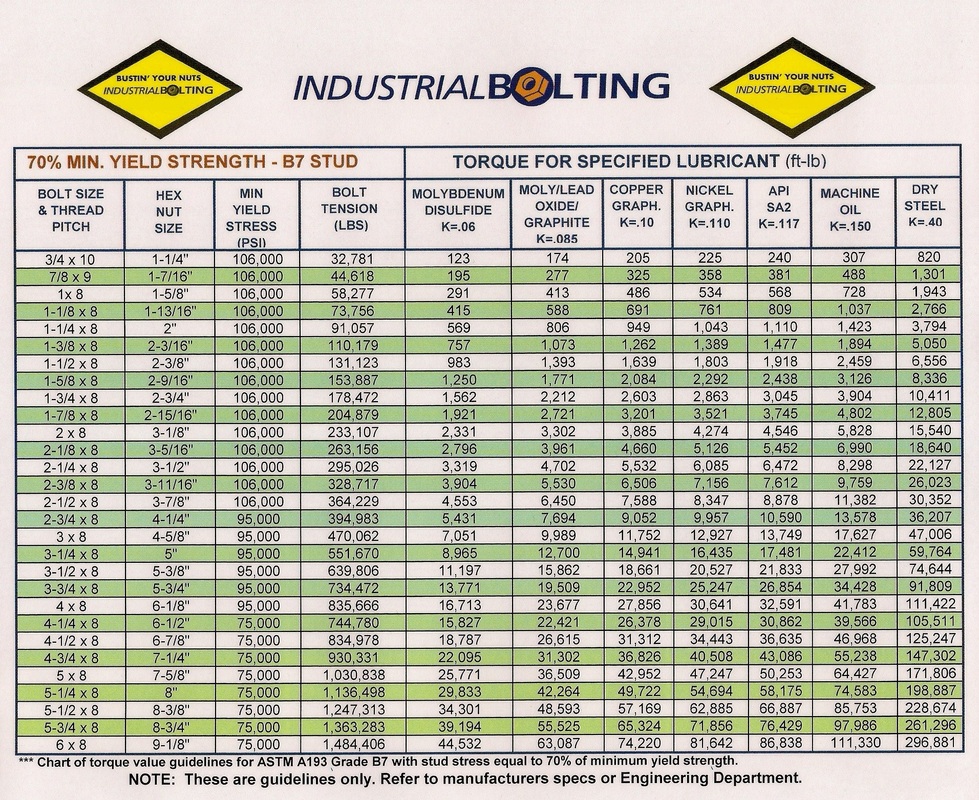
Torque Charts Industrial Torque Tools
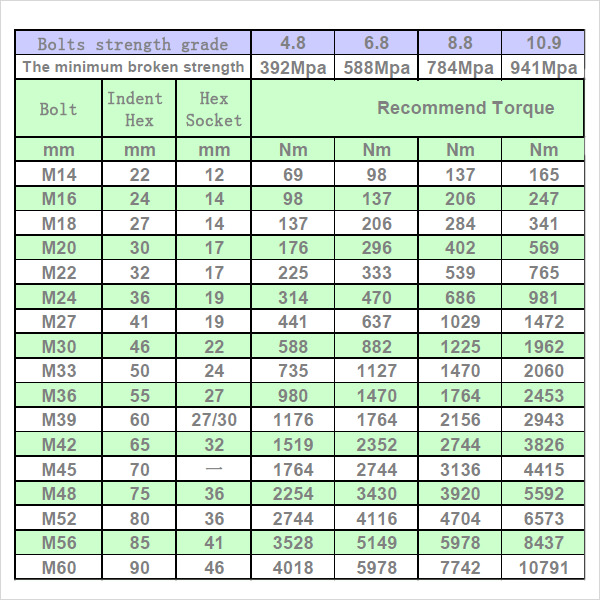
FREE 7+ Sample Bolt Torque Chart Templates in PDF MS Word
Testing Is Done To Various Bolts And Metal Plates, Torqueing Them Until The Point Of Failure.
Web Bolt Torque Chart Reference Guides Include Grade 2, B7, A307, A325, Grade 8, A490, And Grade 5.
The Below Estimated Torque Calculations Are Only Offered As A Guide.
In Developing This Information, Fastenal Has Made A Determined Effort.
Related Post: