Taxonomy Humans Chart
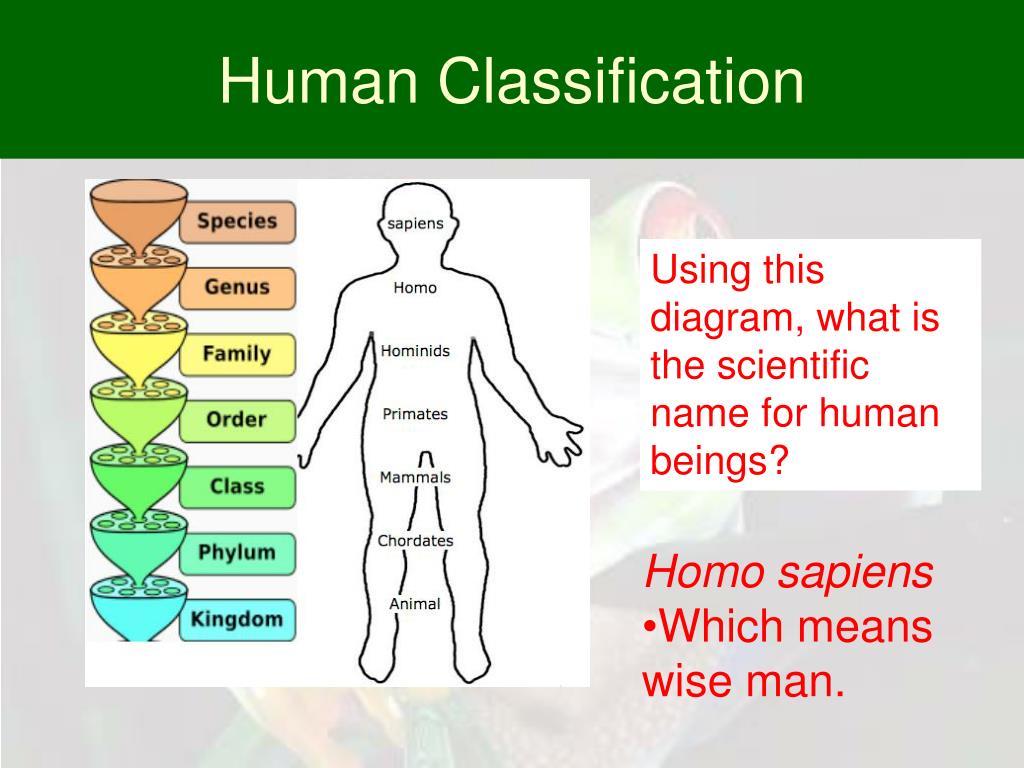
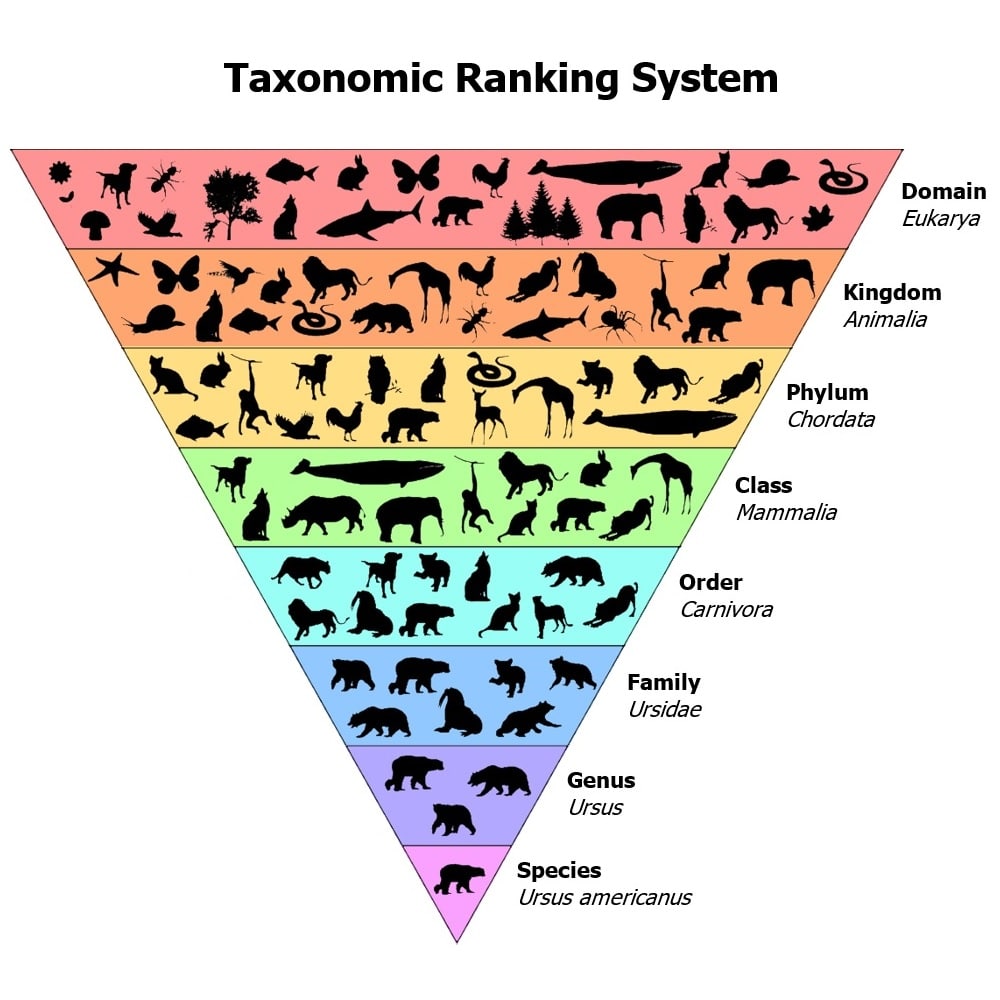
Taxonomy Humans Chart - Web the current taxonomic system now has eight levels in its hierarchy, from lowest to highest, they are: Web for example, the taxonomic classification of humans is: Species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. Species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. From the time of aristotle, scientists have been arranging living things in order to study and understand them. In the 18th century, carolus linnaeus suggested a classification process, and this taxonomy system is still used today. One large space is divided into departments, such as produce, dairy, and meats. It’s even more general than asking whether an organism is a plant or an animal. This practice is called taxonomy, or linnaean enterprise. Wise man) within zoological taxonomy. This practice is called taxonomy, or linnaean enterprise. Web taxonomy (which means “arrangement law”) is the science of classifying organisms to construct internationally shared classification systems with each organism placed into more and more inclusive groupings. One large space is divided into departments, such as produce, dairy, and. One large space is divided into departments, such as produce, dairy, and. Thus species are grouped within genera, genera are grouped within families, families are grouped within orders, and so on (figure 8). Web human taxonomy is the classification of the human species (systematic name homo sapiens, latin: It was developed by the swedish botanist carolus linnaeus, who lived during the 18 th century, and his system of classification is still used. This is because their cells all have a nucleus. Humans are also classified within this system, highlighting our connections. The systematic genus, homo, is designed to include both anatomically modern humans. Web the ncbi taxonomy database allows browsing of the taxonomy tree, which contains a classification of organisms. Web human taxonomy is the classification of the human species (systematic name. A taxonomy chart is the organized graphic practice and representation of things and concepts. It was developed by the swedish botanist carolus linnaeus, who lived during the 18 th century, and his system of classification is still used today. Wise man) within zoological taxonomy. For example, protists, fungi, plants, and animals are part of the eukarya domain. Web superclass gnathostomata. The systematic genus, homo, is designed to include both anatomically modern humans. Taxonomy is the branch of biology that classifies all living things. Web the current taxonomic system now has eight levels in its hierarchy, from lowest to highest, they are: Usually, the taxonomy chart is used in biology to classify all living things. Web linnaean classification of humans. The systematic genus, homo, is designed to include both anatomically modern humans. Web the ncbi taxonomy database allows browsing of the taxonomy tree, which contains a classification of organisms. A taxonomy chart is the organized graphic practice and representation of things and concepts. Web superclass gnathostomata jawed vertebrates. Usually, the taxonomy chart is used in biology to classify all living. Humans are also classified within this system, highlighting our connections. The systematic genus, homo, is designed to include both anatomically modern humans. This method of giving scientific names to animals is typically rooted in latin by combining the genus and species. This is because their cells all have a nucleus. Kingdom, phylum or division, class, order, family, genus, and species. Thus species are grouped within genera, genera are grouped within families, families are grouped within orders, and so on (figure 8). All of these categories are. The term is derived from the greek taxis (“arrangement”) and nomos (“law”). Web taxonomy (which means “arrangement law”) is the science of classifying organisms to construct internationally shared classification systems with each organism placed. Taxonomy is both an art and a science, with dna analysis now playing a significant role. The term is derived from the greek taxis (“arrangement”) and nomos (“law”). Web the current taxonomic system now has eight levels in its hierarchy, from lowest to highest, they are: Web swedish naturalist linnaeus developed a system for classifying plants and animals, based on. The term is derived from the greek taxis (“arrangement”) and nomos (“law”). Web the current taxonomic system now has eight levels in its hierarchy, from lowest to highest, they are: Kingdom, phylum or division, class, order, family, genus, and species. The science of classifying living things is called taxonomy. Thus species are grouped within genera, genera are grouped within families,. Web taxonomy (which means “arrangement law”) is the science of classifying organisms to construct internationally shared classification systems with each organism placed into more and more inclusive groupings. This is because their cells all have a nucleus. Web human taxonomy is the classification of the human species (systematic name homo sapiens, latin: Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, etc. In the 18th century, carolus linnaeus suggested a classification process, and this taxonomy system is still used today. Humans are also classified within this system, highlighting our connections. Web the classic linnaean taxonomy is basically part of your family tree without drawing in all the branches. Think about how a grocery store is organized. Web the current taxonomic system now has eight levels in its hierarchy, from lowest to highest, they are: Species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. Web for example, the taxonomic classification of humans is: Web taxonomy (which literally means “arrangement law”) is the science of classifying organisms to construct internationally shared classification systems with each organism placed into more and more inclusive groupings. From the time of aristotle, scientists have been arranging living things in order to study and understand them. Thus species are grouped within genera, genera are grouped within families, families are grouped within orders, and so on (figure 8). Linnaeus invented binomial nomenclature, the system of giving each type of organism a genus and species. Species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain.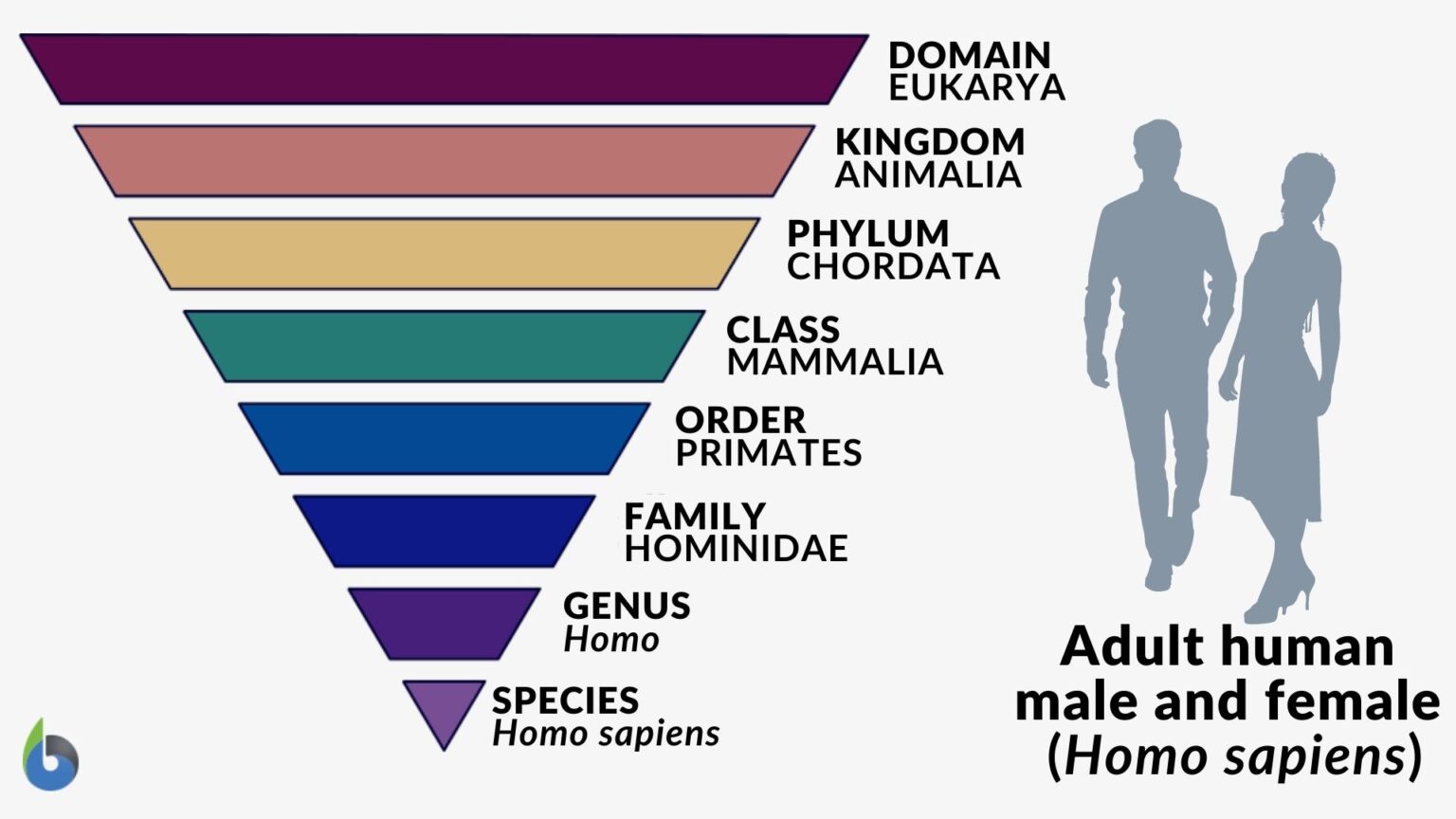
Taxonomy Definition, Examples, Classification Biology Online Dictionary
PPT Classifying Organisms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

gotbooks.miracosta.edu/oceans

How did humans begin to classify and name all of life on Earth? •

Human Taxonomy Chart

Human Taxonomy Chart

Human evolution VCE Biology Unit 4 LibGuides at St Albans Secondary
Human Taxonomy Chart EdrawMax Template bob娱乐网站
trees · Data Science Research in Biology Fall 2022
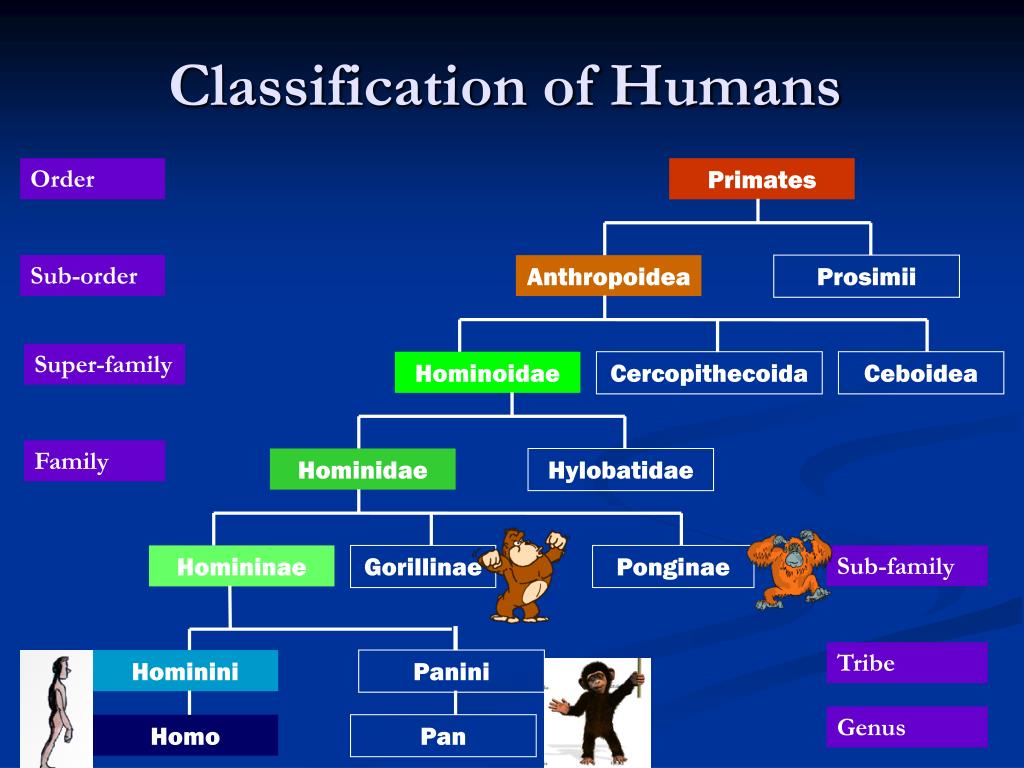
Human Taxonomy Classification Chart
Web Carl Linnaeus Was A Swedish Botanist Who Developed A New System Of Classification Of Living Organisms In 1758.
A Taxonomy Chart Is The Organized Graphic Practice And Representation Of Things And Concepts.
In A Classification, A Taxon Is A.
This Practice Is Called Taxonomy, Or Linnaean Enterprise.
Related Post: