Terrestrial Biomes Chart
Terrestrial Biomes Chart - In turn, the vegetation influences what types of animals can inhabit the area. Avg winter 5°c or below. Many places on earth share similar climatic conditions despite being found in geographically different areas. Divided into two main categories, marine and freshwater, they are characterized by salinity, temperature, oxygen levels, nutrient levels. Some additional trees emerge through this closed upper canopy. Tropical wet forests, savannas, subtropical deserts, chaparral, temperate grasslands, temperate forests, boreal forests, and arctic tundra. Web terrestrial biomes are based on land, while aquatic biomes include both ocean and freshwater biomes. Web terrestrial biomes are any biomes that exist on land. Web review your understanding of the taiga, tropical rainforest, temperate forest, shrubland, grassland, savanna, desert, and tundra biomes in this free article aligned to ap standards. Aquatic biomes are biomes that are characterized by the presence of water. The same biome can occur in different. Web review your understanding of the taiga, tropical rainforest, temperate forest, shrubland, grassland, savanna, desert, and tundra biomes in this free article aligned to ap standards. Biomes contain many ecosystems within the same area. Web figure 8.1 shows a map of the distribution of the most extensive terrestrial biomes. The eight major terrestrial. Web the earth has terrestrial biomes and aquatic biomes. Divided into two main categories, marine and freshwater, they are characterized by salinity, temperature, oxygen levels, nutrient levels. Web there are eight major terrestrial biomes: Web a layer of trees rises above this understory and is topped by a closed upper canopy —the uppermost overhead layer of branches and leaves. There. Web characteristics of the earth's terrestrial biomes. Dominated by trees and other woody vegetation, can be classified according to numerous characteristics, with seasonality being the most widely used. Web there are eight major terrestrial biomes: Tropical rainforests, savannas, subtropical deserts, chaparral, temperate grasslands, temperate forests, boreal forests, and arctic tundra. Web there are eight major terrestrial biomes: Annual totals and fluctuations of precipitation affect the kinds of vegetation that can exist in each region. Taiga/boreal forest, temperate rainforest, temperate seasonal/deciduous forest, tropical rainforest, shrubland/chaparral, temperate grassland, savanna, desert and tundra. Web terrestrial biomes are any biomes that exist on land. Moisture and temperature are usually the most important environmental influences on the distribution of terrestrial biomes (figure. Biomes contain many ecosystems within the same area. Tropical wet forests, savannas, subtropical deserts, chaparral, temperate grasslands, temperate forests, boreal forests, and arctic tundra. Tropical wet forests, savannas, subtropical deserts, chaparral, temperate grasslands, temperate forests, boreal forests, and arctic tundra. The distribution of biomes is determined by environmental conditions, which must be appropriate to support the dominant species. Aquatic biomes. Web terrestrial biomes are based on land, while aquatic biomes include both ocean and freshwater biomes. The eight major terrestrial biomes on earth are each distinguished by characteristic temperatures and amount of precipitation. Scientists call these major ecosystem types biomes. Web terrestrial biomes are any biomes that exist on land. Web a biome refers to a major type of terrestrial. Dominated by trees and other woody vegetation, can be classified according to numerous characteristics, with seasonality being the most widely used. Biomes contain many ecosystems within the same area. Web the terrestrial biomes on earth are each distinguished by characteristic temperatures and amount of precipitation. Web a layer of trees rises above this understory and is topped by a closed. There are eight major terrestrial biomes: Web terrestrial biomes are any biomes that exist on land. Temperature and precipitation, and variations in both, are key abiotic factors that shape the composition of animal and plant communities in terrestrial biomes. Annual totals and fluctuations of precipitation affect the kinds of vegetation and animal life that can exist in broad geographical regions.. Dominated by trees and other woody vegetation, can be classified according to numerous characteristics, with seasonality being the most widely used. As you read about each biome, think about how its biodiversity and types of plants and animals relate to its climate. Web this map shows the locations of earth’s major terrestrial biomes. Web there are eight major terrestrial biomes:. In turn, the vegetation influences what types of animals can inhabit the area. The same biome can occur in different. The distribution of biomes is determined by environmental conditions, which must be appropriate to support the dominant species. Web use this chart and slide presentation for the essentials of 9 biomes: Temperature and precipitation, and variations in both, are key. Moisture and temperature are usually the most important environmental influences on the distribution of terrestrial biomes (figure 8.2). Web the eight major terrestrial biomes on earth are each distinguished by characteristic temperatures and amount of precipitation. Divided into two main categories, marine and freshwater, they are characterized by salinity, temperature, oxygen levels, nutrient levels. Tropical rainforests, savannas, deserts, chaparral, temperate grasslands, temperate forests, taiga (boreal forests), and arctic tundra. The following figures summarize the basic features of major terrestrial biomes. In turn, the vegetation influences what types of animals can inhabit the area. Many places on earth share similar climatic conditions despite being found in geographically different areas. The eight major terrestrial biomes on earth are each distinguished by characteristic temperatures and amount of precipitation. Web there are eight major terrestrial biomes: Temperature and precipitation, and variations in both, are key abiotic factors that shape the composition of animal and plant communities in terrestrial biomes. Web figure 8.1 shows a map of the distribution of the most extensive terrestrial biomes. Annual totals and fluctuations of precipitation affect the kinds of vegetation and animal life that can exist in broad geographical regions. Web terrestrial biomes are any biomes that exist on land. Web there are eight major terrestrial biomes: Annual totals and fluctuations of precipitation affect the kinds of vegetation that can exist in each region. Biomes contain many ecosystems within the same area.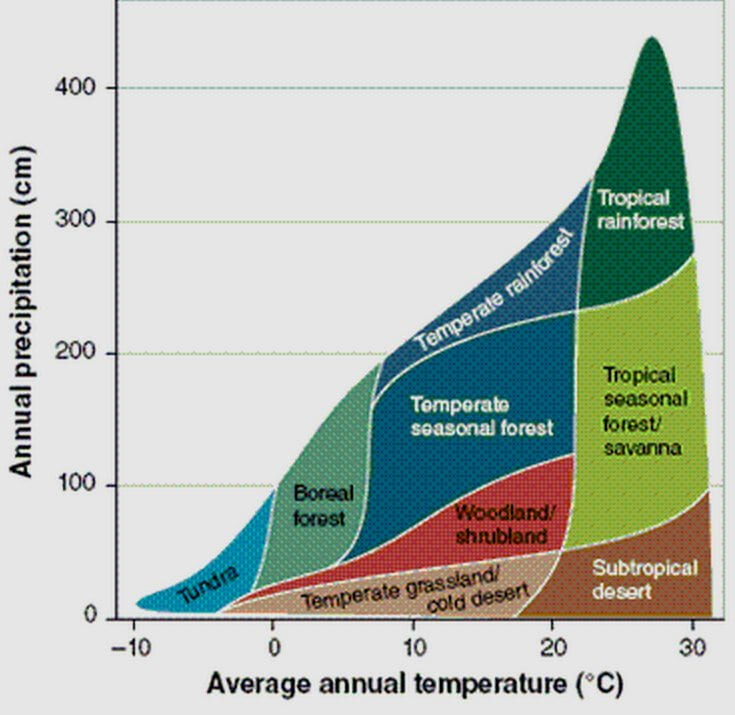
Introduction to Ecology; Major patterns in Earth’s climate Biological
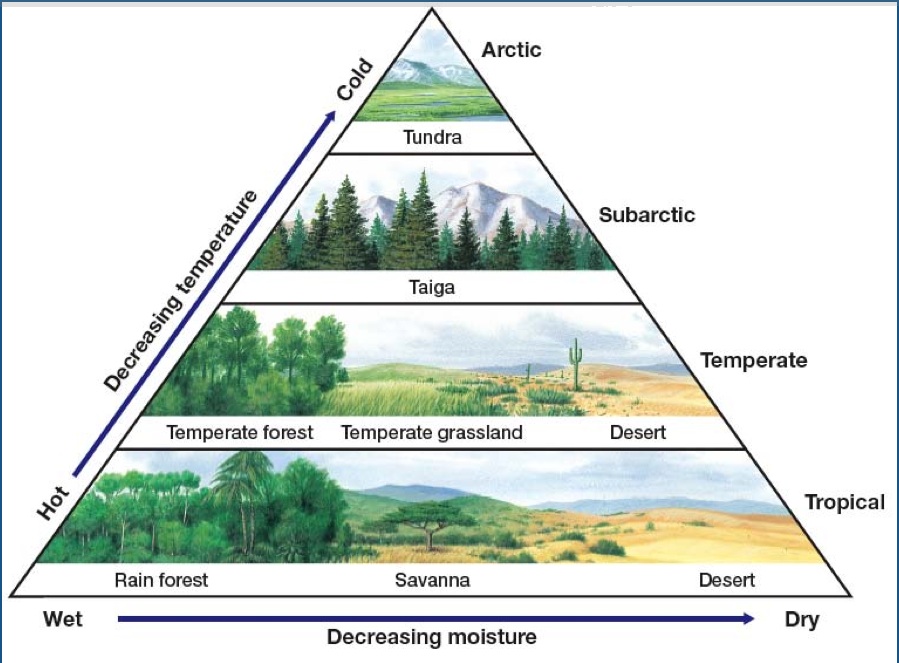
Terrestrial biomes
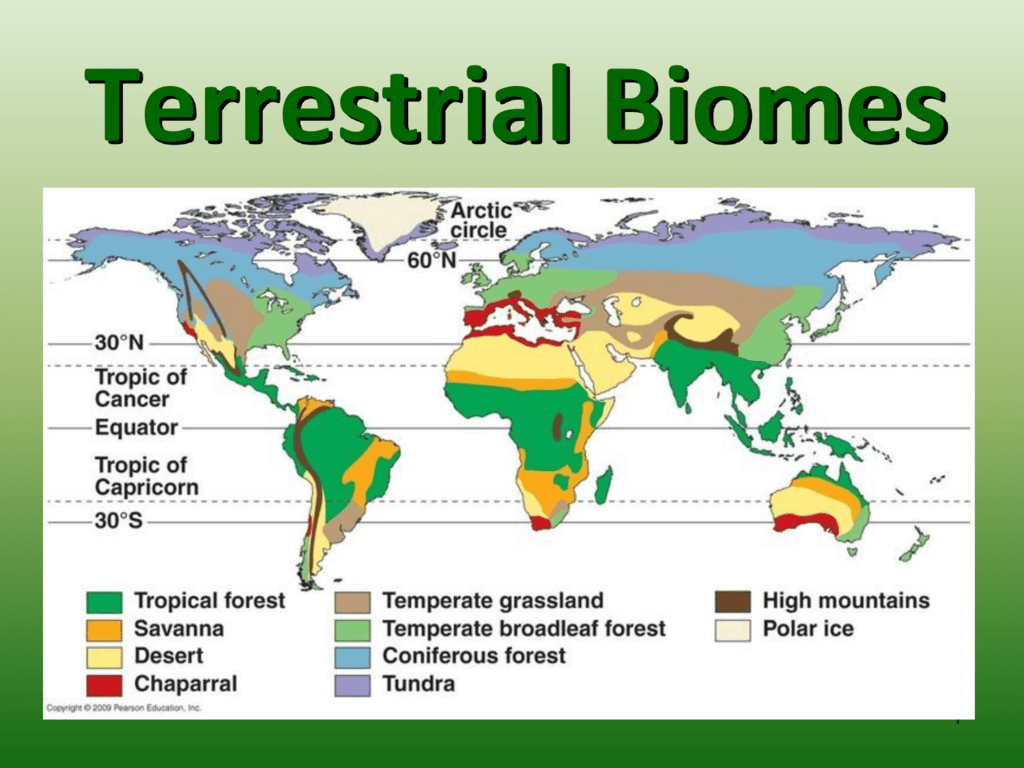
Major Terrestrial Biomes

Exploring Earth's Beautiful Biomes Centre of Excellence
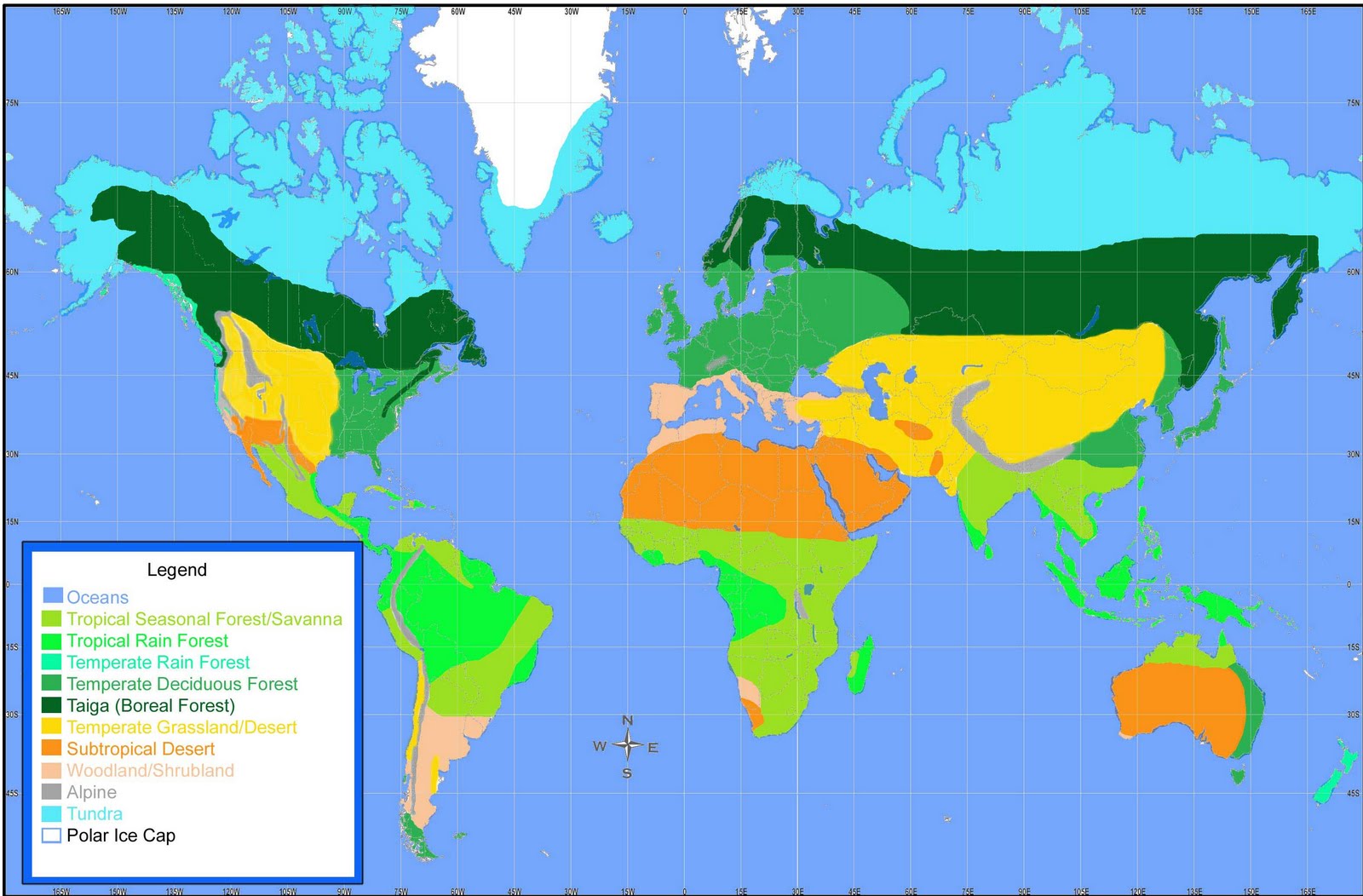
Biomes of the World Info
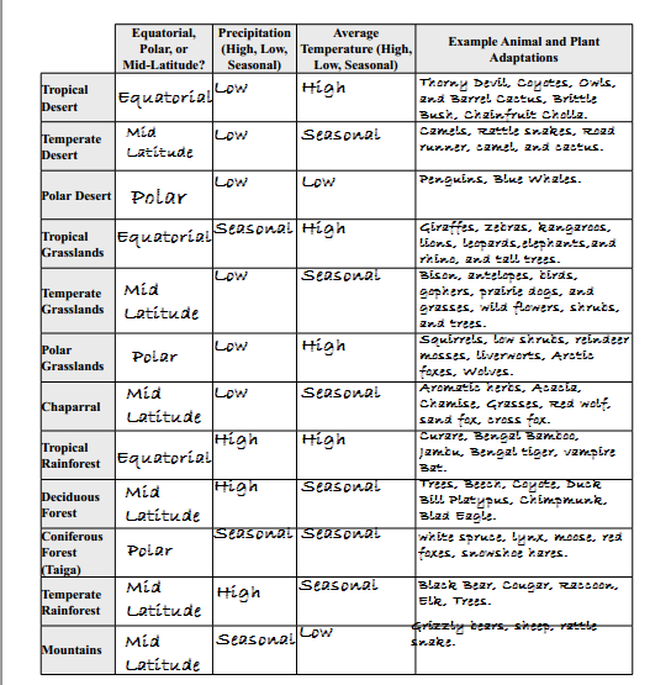
Terrestrial Biomes Study Guide! AP Environmental Science!

Earth's different biomes Infographics

Exploring Beautiful Biomes of the World Centre of Excellence
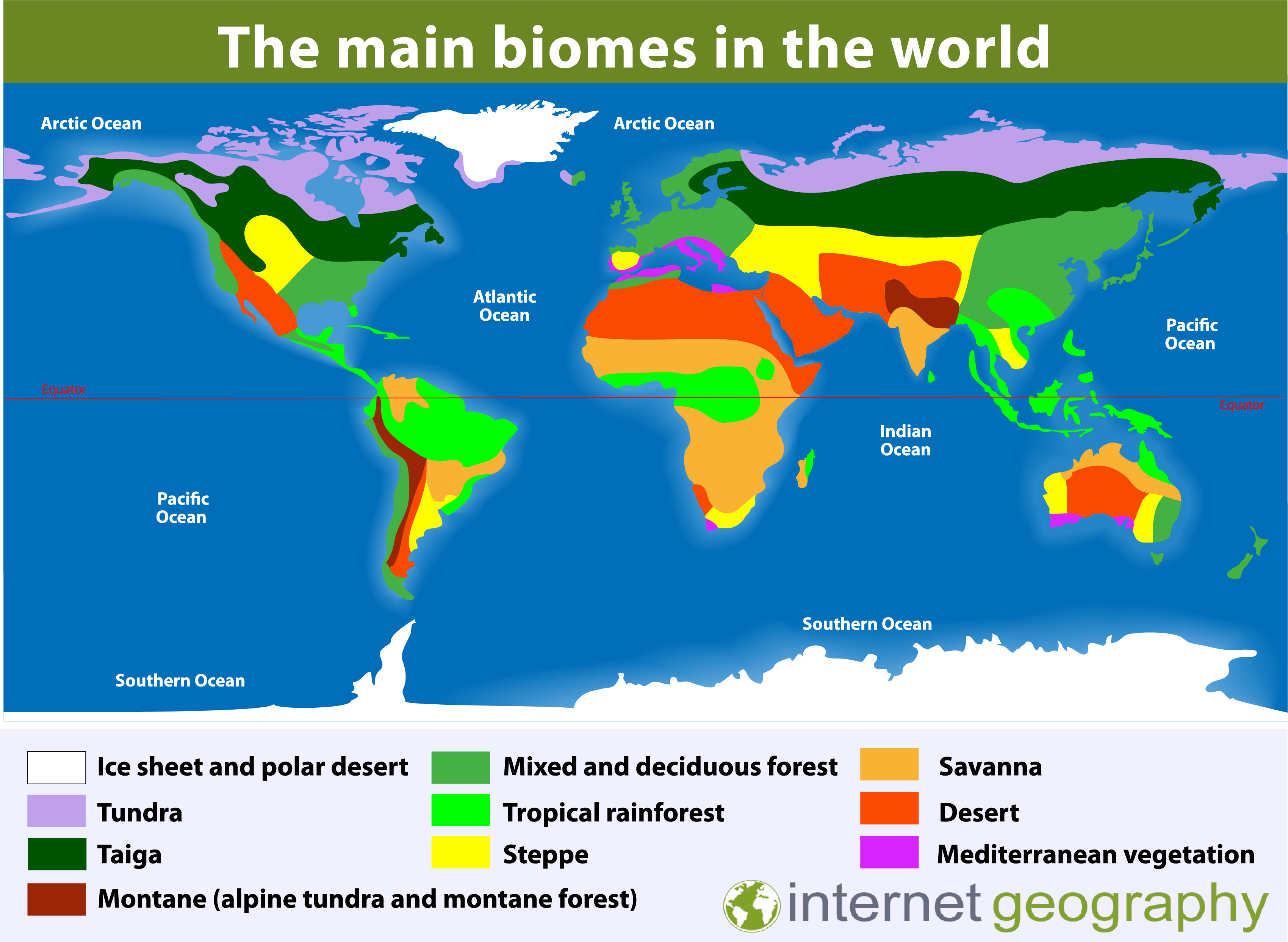
Global Biomes GEOGRAPHY FOR 2024 & BEYOND

LABORATORY 9 CLIMATE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF BIOMES AND SOILS
Web A Layer Of Trees Rises Above This Understory And Is Topped By A Closed Upper Canopy —The Uppermost Overhead Layer Of Branches And Leaves.
These Layers Provide Diverse And Complex Habitats For The Variety Of Plants, Animals, And Other Organisms Within The Tropical Wet Forests.
The Same Biome Can Occur In Different.
Web The Earth Has Terrestrial Biomes And Aquatic Biomes.
Related Post: