Vsepr Chart With Hybridization
Vsepr Chart With Hybridization - For example, i learned in physical inorganic chemistry that in a nitrogen molecule, each p orbital of one atom hybridizes with a p orbital of the other atom to form a bonding orbital and an antibonding orbital, neither of which belongs distinctly to one atom. Web the valence shell electron pair repulsion model is often abbreviated as vsepr (pronounced vesper) and is a model to predict the geometry of molecules. Web the complete table of hybridization and geometry. The central atom in polyatomic molecules is surrounded by several other atoms. The concept of hybridization helps us understand the bonding in organic molecules. Web sih4 lewis structure. Web what is the relationship between hybridization, vsepr, and molecular polarity? Hybridisation follows geometry, not the other way around. In multiatom molecules, you have hybridized orbitals of the whole molecule. Web summary vsepr and hybridization table. In the vsepr model, the molecule. Use the positions of atoms to establish the resulting molecular geometry. The total number of valence shell electron pairs determines the molecular shape. 4 bonding pairs around c, but trigonal planar instead of tetrahedral. Web sih4 lewis structure. These electron pairs include both bonding and nonbonding pairs. In the vsepr model, the molecule. Use the positions of atoms to establish the resulting molecular geometry. Thus, electron pairs will spread themselves as far from each other as possible to minimize repulsion. Web the valence shell electron pair repulsion model is often abbreviated as vsepr (pronounced vesper) and is a. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. Web vsepr theory (molecular shapes) a = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a. Generic formula picture bonded atoms lone pairs molecular shape electron geometry. For example, i learned in physical inorganic chemistry that in a nitrogen. This important canadian innovation is found worldwide in any intro chem course. These electron pairs include both bonding and nonbonding pairs. Web the valence shell electron pair repulsion model is often abbreviated as vsepr (pronounced vesper) and is a model to predict the geometry of molecules. Use the positions of atoms to establish the resulting molecular geometry. The concept of. The concept of hybridization helps us understand the bonding in organic molecules. Thus, electron pairs will spread themselves as far from each other as possible to minimize repulsion. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. • vsepr theory has four assumptions 1. Web number of electron domains (or "number of electron pairs") = (number. This whole thing assumes, by the way, that you know how to draw lewis structures. Web number of electron domains (or "number of electron pairs") = (number of other atoms something is bonded to) + (number of lone pairs) hybrid orbitals are used to form ã bonds and to hold lone pairs of electrons. Web rather, one determines the geometry. Predicted bond angle(s) hybridization of central atom. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. For example, i learned in physical inorganic chemistry that in a nitrogen molecule, each p orbital of one atom hybridizes with a p orbital of the other atom to form a bonding orbital and an antibonding orbital, neither of which. 4 bonding pairs around c, but trigonal planar instead of tetrahedral. Thus, electron pairs will spread themselves as far from each other as possible to minimize repulsion. Line, dash, and w edge. The concept of hybridization helps us understand the bonding in organic molecules. Web the valence shell electron pair repulsion model is often abbreviated as vsepr (pronounced vesper) and. Web rather, one determines the geometry by an independent mean (e.g. Web the complete table of hybridization and geometry. Web what is the relationship between hybridization, vsepr, and molecular polarity? Hybridization is the concept that explains the formation of hybrid orbitals in molecules by combining atomic orbitals from the same atom. Web vsepr theory (molecular shapes) a = the central. Web learn about vsepr theory and how to easily classify molecules in this tutorial. Predicted bond angle(s) hybridization of central atom. The valence shell electron pair repulsion (vsepr) theory is a simple and useful way to predict and rationalize the shapes of molecules. Unhybridized p orbitals are used to form ã. This whole thing assumes, by the way, that you. The total number of valence shell electron pairs determines the molecular shape. 4 bonding pairs around c, but trigonal planar instead of tetrahedral. Web we can use the vsepr model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing only on the number of electron pairs around the central atom, ignoring all other valence electrons present. Web ap vsepr and polarity reference sheet. Web number of electron domains (or "number of electron pairs") = (number of other atoms something is bonded to) + (number of lone pairs) hybrid orbitals are used to form ã bonds and to hold lone pairs of electrons. • vsepr theory has four assumptions 1. Web the complete table of hybridization and geometry. The concept of hybridization helps us understand the bonding in organic molecules. Generic formula picture bonded atoms lone pairs molecular shape electron geometry. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. Web the valence shell electron pair repulsion model is often abbreviated as vsepr (pronounced vesper) and is a model to predict the geometry of molecules. In the vsepr model, the molecule. In multiatom molecules, you have hybridized orbitals of the whole molecule. Specifically, vsepr models look at the bonding and molecular geometry of organic molecules and polyatomic ions. Web the vsepr theory helps us to predict the 3d shapes of the molecules. Thus, electron pairs will spread themselves as far from each other as possible to minimize repulsion.
IF5 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Polarity, and Molecular Shape

Samantha's Notes AP Chemistry VSEPR Theory Chart

9.2 Valence Bond Theory Chemistry LibreTexts
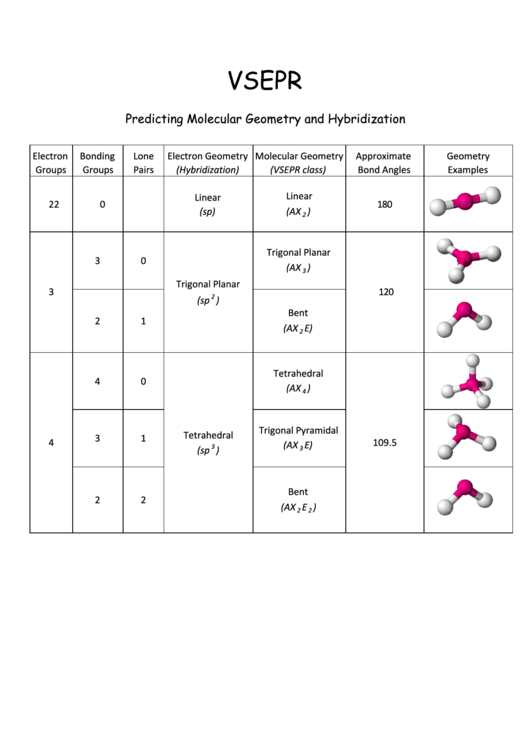
Vsepr Predicting Molecular Geometry And Hybridization Chart printable

Vsepr Chart With Angles

C2H4 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and MO Diagram

SOLUTION 05 chem nanotech vsepr theory hybridization Studypool
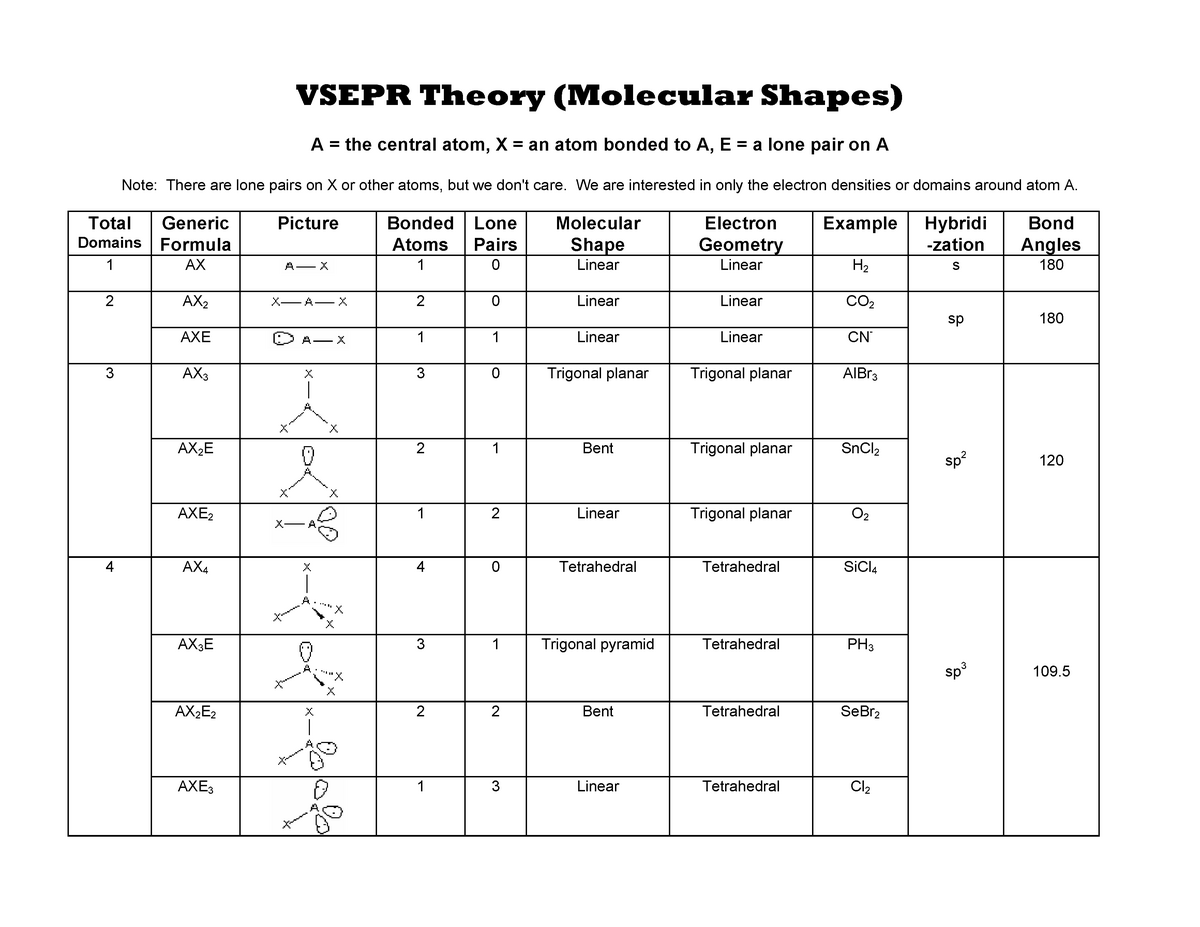
Main vseprtheorymolecularshapeschart Chem 1A03 McMaster Studocu
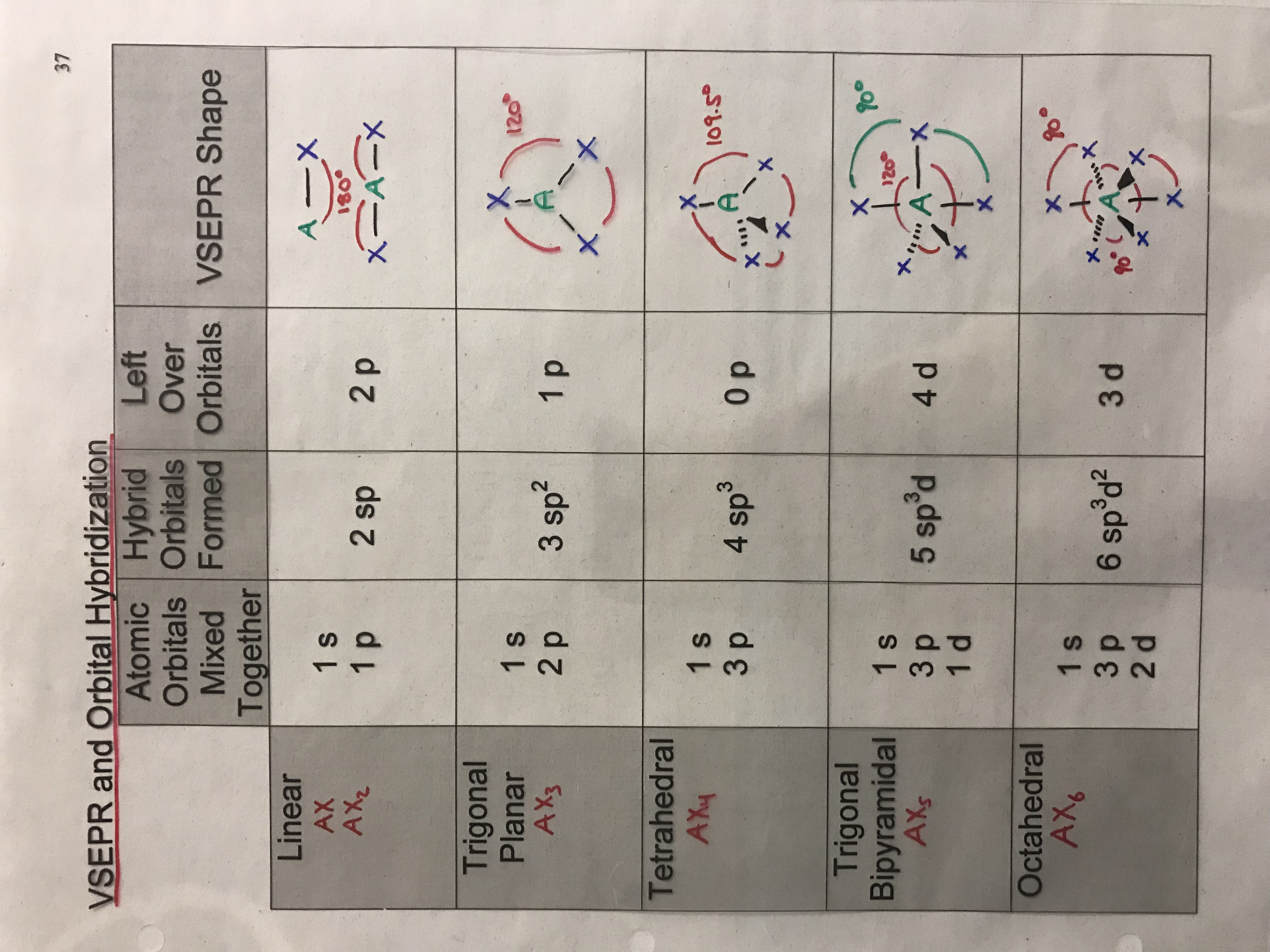
VSEPR Theory Table

SO42 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and Polarity
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (Vsepr) Theory Is A Simple And Useful Way To Predict And Rationalize The Shapes Of Molecules.
Multiple Bonds And Molecular Geometry.
Web Find Out The Appropriate Vsepr Geometry For The Specified Number Of Electron Pairs, Both Bonding And Lone Pairs.
Use The Positions Of Atoms To Establish The Resulting Molecular Geometry.
Related Post: