Acei Arb Equivalency Chart
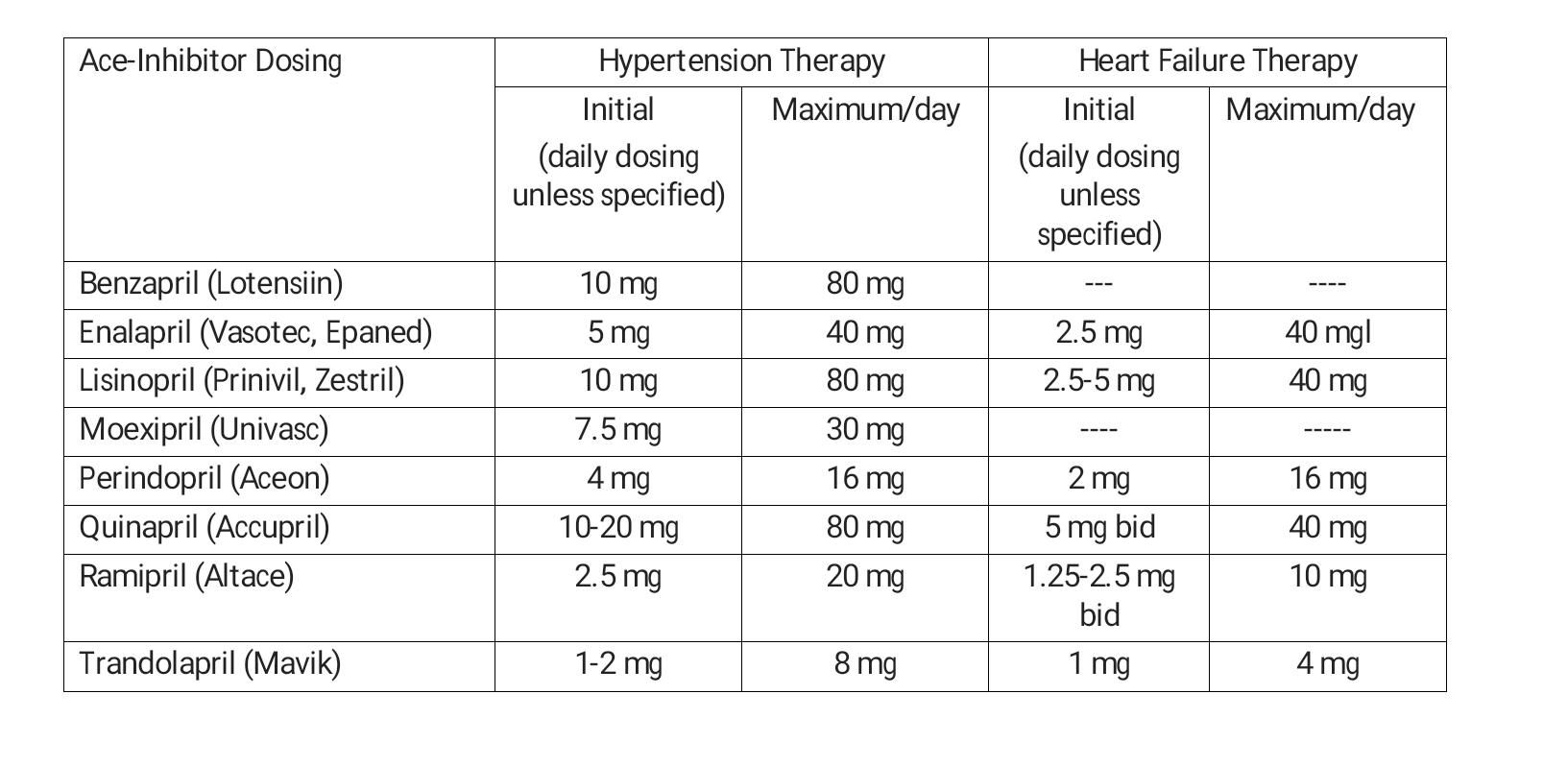
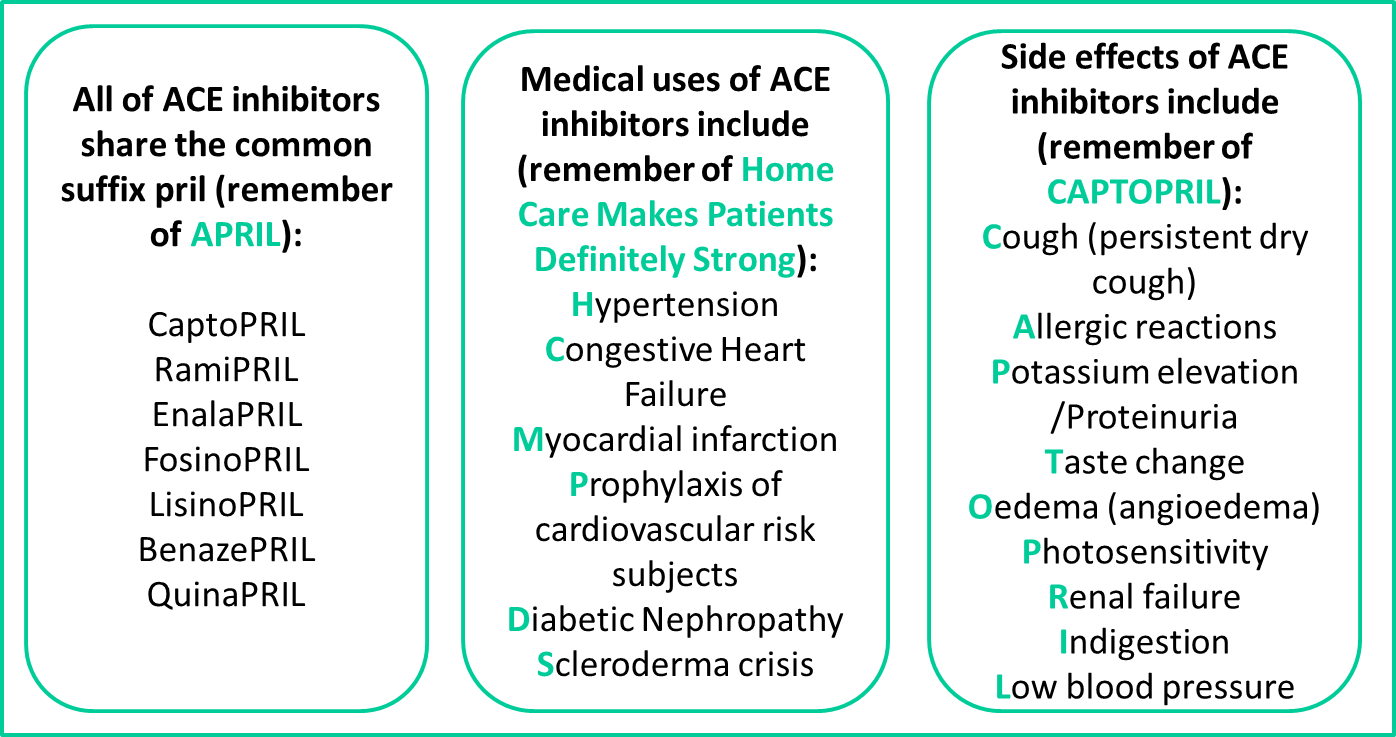
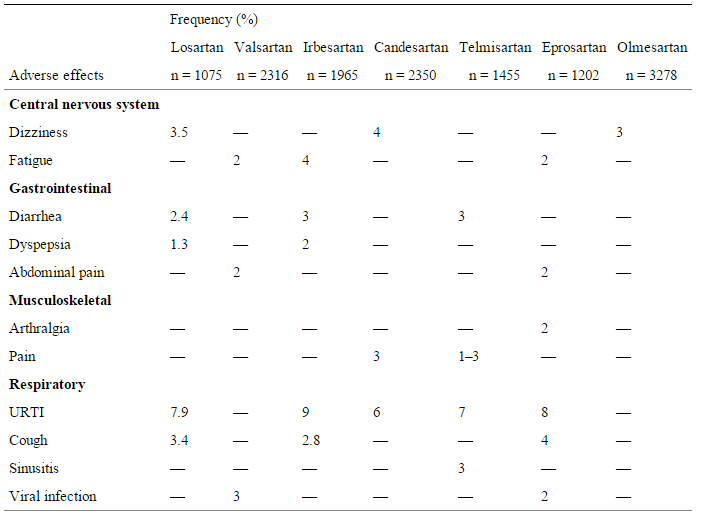
Acei Arb Equivalency Chart - Web 18 rows ace inhibitors and arbs act by blocking raas with beneficial. The table below indicates dosing of arbs based on outcome data. Benazepril (lotensin) captopril (capoten) enalapril (vasotec) fosinopril (monopril) 10 mg daily. Web various angiotensin receptor ii blockers (arbs) have been periodically shorted. Switch the patient to the fully covered acei at a therapeutically appropriate dose as shown below. Angiotensin receptor blocker (arb) antihypertensive dose comparison. Drug comparisons based on potency 4 mg, 8 mg, 16 mg, 32 mg. Web ace inhibitors and arbs are two types of oral (taken by mouth) prescription medicines commonly recommended for people with kidney disease. 4 to 32 mg once daily. Switch the patient to the fully covered acei at a therapeutically appropriate dose as shown below. The information provided is intended to help. The table below indicates dosing of arbs based on outcome data. 4 mg, 8 mg, 16 mg, 32 mg. Web ace inhibitors and arbs are two types of oral (taken by mouth) prescription medicines commonly recommended for. Web 10 mg once daily. Benazepril (lotensin) captopril (capoten) enalapril (vasotec) fosinopril (monopril) 10 mg daily. When outcomes were compared with arb use, ace inhibitor use was associated with similar risk of acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, hemorrhagic. Web angiotensin ii receptor antagonist (arb) dosing: Switch the patient to the fully covered acei at a therapeutically appropriate dose as shown. Web angiotensin ii receptor antagonist (arb) dosing: 160mg (160mg bid evaluated in heart failure studies) the table helps convert. Arbs still currently available as of jan 26, 2020: Switch the patient to the fully covered acei at a therapeutically appropriate dose as shown below. Web patients can switch at the next fill of their prescription. Web patients can switch at the next fill of their prescription. Benazepril (lotensin) captopril (capoten) enalapril (vasotec) fosinopril (monopril) 10 mg daily. Switch the patient to the fully covered acei at a therapeutically appropriate dose as shown below. Web 18 rows ace inhibitors and arbs act by blocking raas with beneficial. When outcomes were compared with arb use, ace inhibitor. Arbs still currently available as of jan 26, 2020: When outcomes were compared with arb use, ace inhibitor use was associated with similar risk of acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, hemorrhagic. 4 to 32 mg once daily. The table below indicates dosing of arbs based on outcome data. The information provided is intended to help. Web angiotensin ii receptor antagonist (arb) dosing: Web 10 mg once daily. Switch the patient to the fully covered acei at a therapeutically appropriate dose as shown below. 12 july 2022 updated evidence in the section on deciding between an ace. Web various angiotensin receptor ii blockers (arbs) have been periodically shorted. Web an estimation of equivalent doses between arbs and aceis. Tool for switching between agents in canada. Benazepril (lotensin) captopril (capoten) enalapril (vasotec) fosinopril (monopril) 10 mg daily. Lisinopril (prinivil, zestril) 2.5 mg once daily. Web 10 mg once daily. Web 25 november 2022 ramipril added to table 1 and a dose equivalency table added. Web patients can switch at the next fill of their prescription. Web 3 pharmacist’s letter/prescriber’s letter. Web ace inhibitors and arbs are two types of oral (taken by mouth) prescription medicines commonly recommended for people with kidney disease. Web an estimation of equivalent doses between. Web angiotensin ii receptor antagonist (arb) dosing: Arbs still currently available as of jan 26, 2020: Web various angiotensin receptor ii blockers (arbs) have been periodically shorted. When outcomes were compared with arb use, ace inhibitor use was associated with similar risk of acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, hemorrhagic. Lisinopril 2.5 mg once daily. 12 july 2022 updated evidence in the section on deciding between an ace. Drug comparisons based on potency Web various angiotensin receptor ii blockers (arbs) have been periodically shorted. Web ace inhibitors and arbs are two types of oral (taken by mouth) prescription medicines commonly recommended for people with kidney disease. The table below indicates dosing of arbs based on. Web angiotensin ii receptor antagonist (arb) dosing: The table below indicates dosing of arbs based on outcome data. 4 mg, 8 mg, 16 mg, 32 mg. Drug comparisons based on potency 12 july 2022 updated evidence in the section on deciding between an ace. Benazepril (lotensin) captopril (capoten) enalapril (vasotec) fosinopril (monopril) 10 mg daily. Lisinopril 2.5 mg once daily. The information provided is intended to help. Angiotensin receptor blocker (arb) antihypertensive dose comparison. 160mg (160mg bid evaluated in heart failure studies) the table helps convert. Web 10 mg once daily. Tool for switching between agents in canada. Web various angiotensin receptor ii blockers (arbs) have been periodically shorted. Web patients can switch at the next fill of their prescription. Arbs still currently available as of jan 26, 2020: Web 25 november 2022 ramipril added to table 1 and a dose equivalency table added.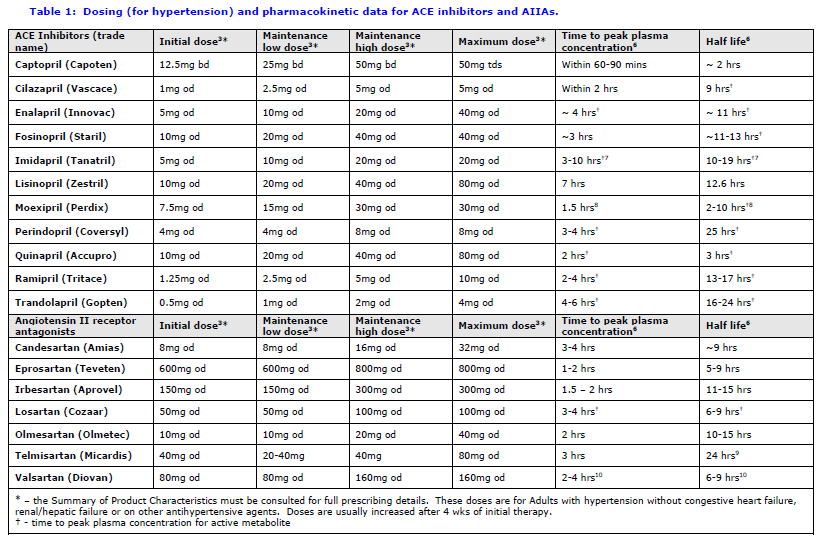
ASK DIS Dose Equivalence ACEi and ARB

Ace To Arb Conversion Chart
Ace Inhibitor To Arb Conversion Chart
Equivalency Ace Inhibitor To Arb Conversion Chart

Ace And ARB Conversion Chart
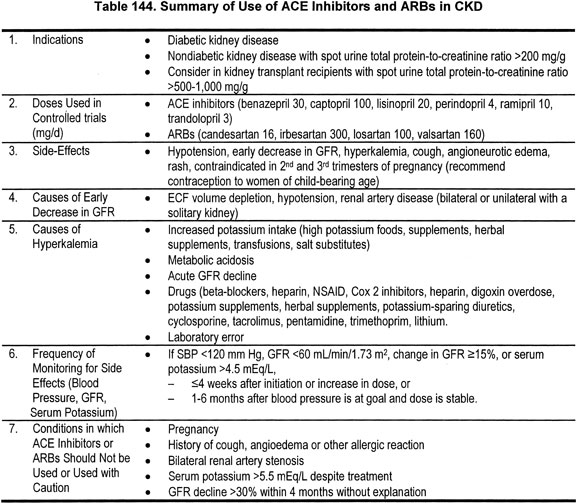
Ace Arb Conversion Chart

Acei Conversion Chart Pharmacist Letter LETTER RTS

ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST (ARB) DOSING TOOL GrepMed

From ACE Inhibitors/ARBs to ARNIs in Coronary Artery Disease and Heart
Acei Conversion Chart Pharmacist Letter
When Outcomes Were Compared With Arb Use, Ace Inhibitor Use Was Associated With Similar Risk Of Acute Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, Hemorrhagic.
The Table Below Indicates Dosing Of Arbs Based On Outcome Data.
Aug 2009 (Full Update Feb 2012);
Web Ace Inhibitors And Arbs Are Two Types Of Oral (Taken By Mouth) Prescription Medicines Commonly Recommended For People With Kidney Disease.
Related Post: