Ice Formation Temperature Chart
Ice Formation Temperature Chart - Web online calculator, figures and tables with melting points of ice to water at pressures ranging from 0 to 29000 psia (0 to 2000 bara). At temperatures below 0 °c (32 °f), water vapour develops into frost at ground level and snowflakes (each of which consists of a single ice crystal) in clouds. Ice forms when the surface water temperature drops to the freezing point. Lakes since 1840 as indicators of climate change. However, drop size, drop dis tribution, and aerodynamic effects of the aircraft influence ice formation. Web to see a corresponding daily sea ice concentration image, click on a line in the chart. Web basically, all clouds at subfreezing temperatures have icing potential. Web these graphs are of most practical use to determine how much an ice sheet is likely to grow in a day or two of fairly constant temperatures. It does not provide a chart of ice formation temperature or a direct answer to the query. In this section we will examine the process of ice formation, the different types of ice that are found in the ocean, and the impacts of climate change on global ice cover. Web online calculator, figures and tables with melting points of ice to water at pressures ranging from 0 to 29000 psia (0 to 2000 bara). Regional ice regimes and influences. Web ice, solid substance produced by the freezing of water vapour or liquid water. Web heat loss through the ice takes place by conduction; Web an ice (initial, change, equilibrium). Sea ice formation because of the salt content, seawater begins to freeze at. Web online calculator, figures and tables with melting points of ice to water at pressures ranging from 0 to 29000 psia (0 to 2000 bara). Ice may not form even though the potential exists. As long as the ice is thin, it may be broken by strong. Sea ice extent is derived from sea ice concentration. Ice may not form even though the potential exists. Lakes since 1840 as indicators of climate change. The warmer the air temperature, the more likely the super cooled droplet will hit the leading edge of an aircraft surface and freeze as it flows back forming clear and glaze icing. Web the. As long as the ice is thin, it may be broken by strong winds. Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° c, 32 ° f, or 273.15 k. Web this document tracks the first and last freeze and thaw dates of selected u.s. However, drop size, drop dis. This stage is referred to as grease ice (figure \(\pageindex{2. These are more hazardous as they are extremely disruptive to airflow around a surface. When reusing charctic images or data, please credit “national snow and ice data center.” Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° c, 32 °. In this section we will examine the process of ice formation, the different types of ice that are found in the ocean, and the impacts of climate change on global ice cover. It does not provide a chart of ice formation temperature or a direct answer to the query. Limitations in measuring infrared radiation from space include the following: Ice. Web a glaciation (or ice age) occurs when the earth’s climate is cold enough that large ice sheets grow on continents. Below the same temperature, liquid water forms a solid, as, A small lake becomes ice covered overnight. For example if you have bare ice that 2 thick and it is going to average 10 degrees for the next two. Web the properties of ice vary substantially with temperature, purity and other factors. This oval and the coding associated with it, are referred to as the egg code. Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° c, 32 ° f, or 273.15 k. Lakes since 1840 as indicators of. Web this document tracks the first and last freeze and thaw dates of selected u.s. Web an ice (initial, change, equilibrium) table is simple matrix formalism that used to simplify the calculations in reversible equilibrium reactions (e.g., weak acids and weak bases or complex ion formation). Limitations in measuring infrared radiation from space include the following: Ice may not form. Temperature given as °c, °f, k and °r. It occurs naturally on earth, on. Ice may not form even though the potential exists. Sea ice formation because of the salt content, seawater begins to freeze at. 2.1 statistics by historical date. Web ice, solid substance produced by the freezing of water vapour or liquid water. A maximum of three ice types is described within the oval. Temperature given as °c, °f, k and °r. Web a glaciation (or ice age) occurs when the earth’s climate is cold enough that large ice sheets grow on continents. This oval and the coding associated with it, are referred to as the egg code. Web the properties of ice vary substantially with temperature, purity and other factors. Web these graphs are of most practical use to determine how much an ice sheet is likely to grow in a day or two of fairly constant temperatures. For example if you have bare ice that 2 thick and it is going to average 10 degrees for the next two full days, the ice will. It occurs naturally on earth, on. When reusing charctic images or data, please credit “national snow and ice data center.” Web basically, all clouds at subfreezing temperatures have icing potential. It does not provide a chart of ice formation temperature or a direct answer to the query. Ice may not form even though the potential exists. Images are not available for the average or standard deviation. Web to see a corresponding daily sea ice concentration image, click on a line in the chart. Limitations in measuring infrared radiation from space include the following:Lake Ice Ice growth
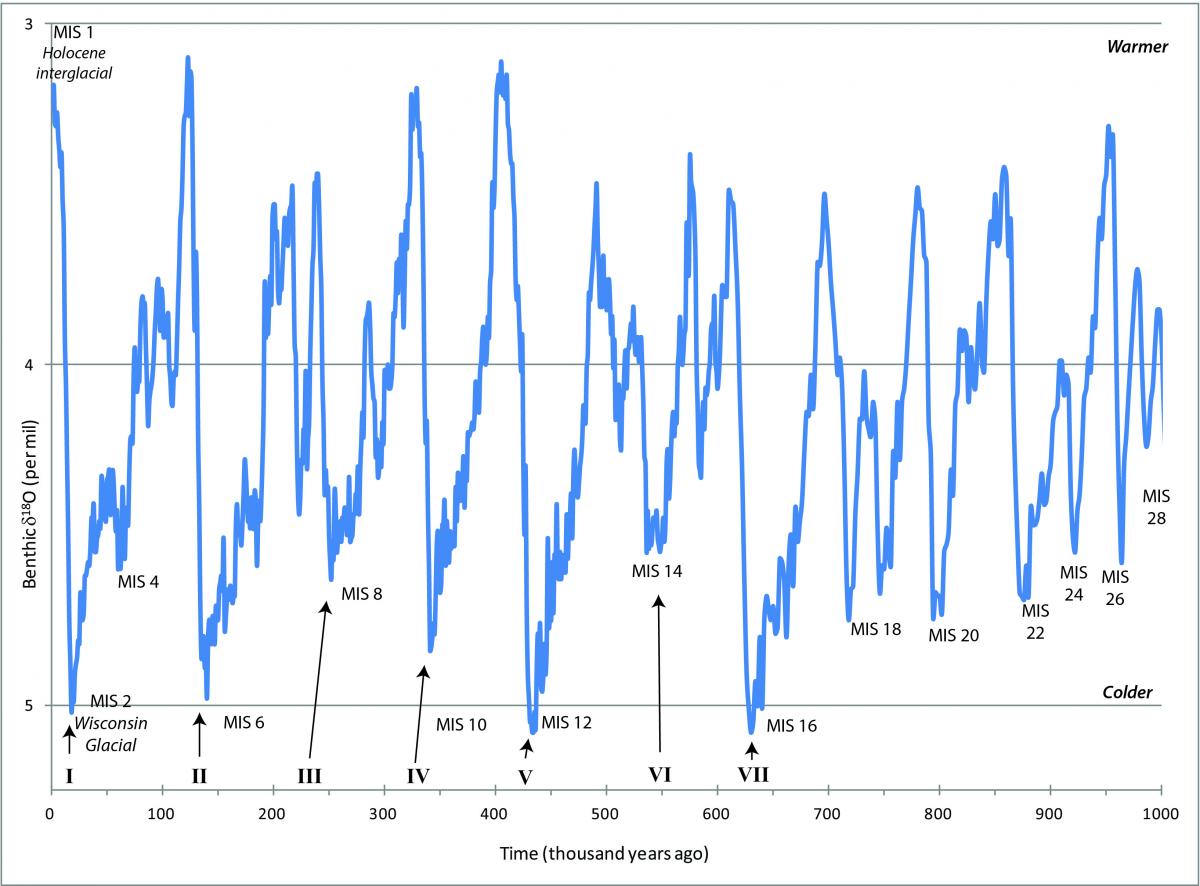
When have ice ages occurred? Explore the Ice Age Midwest

Ice crystal shape as a function of formation temperature and
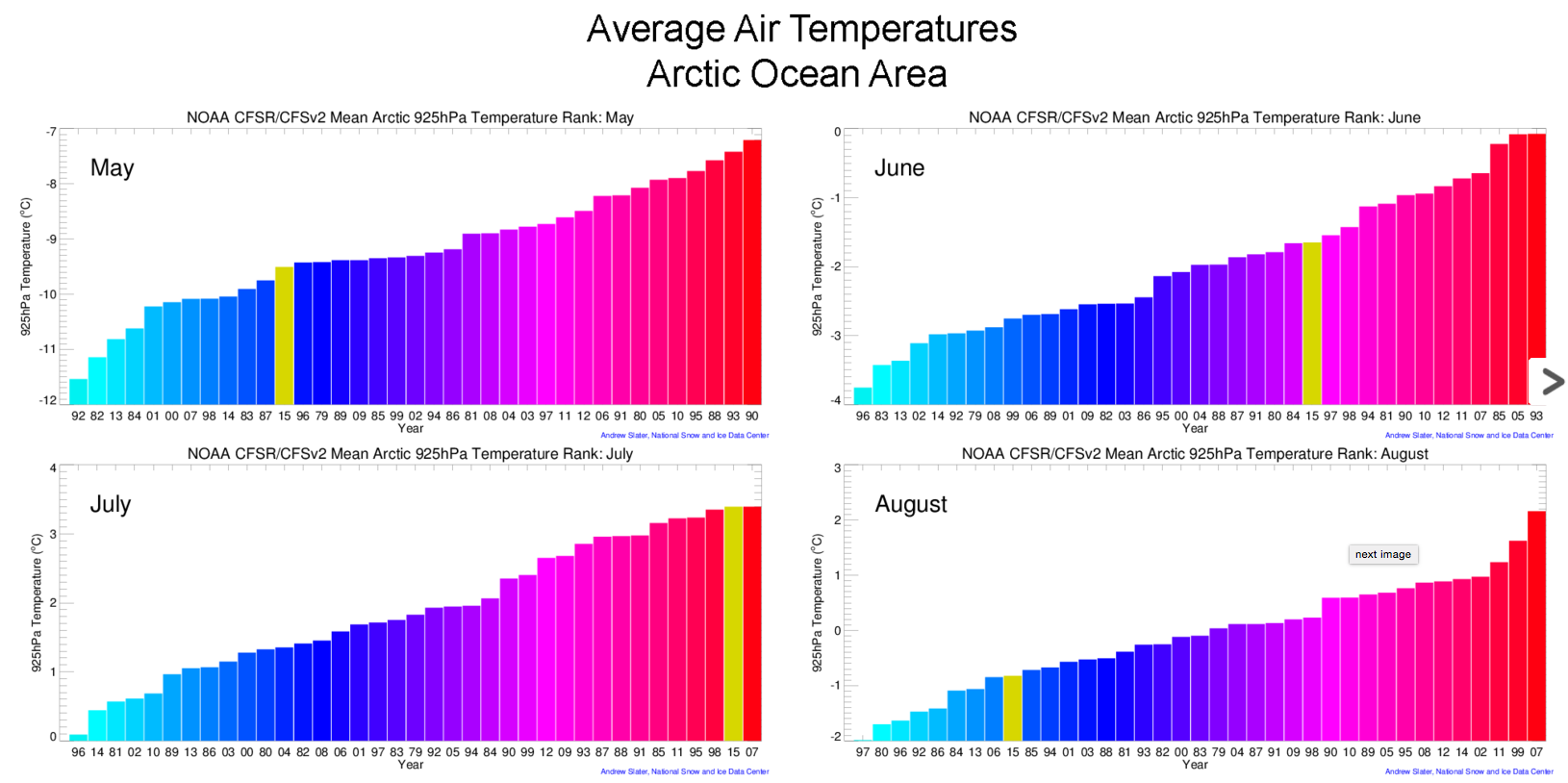
Five charts that show how Arctic and Antarctic sea ice is faring in 2015

Creating a Sustainable Future Arctic Sea Ice Charts
Lake Ice Ice growth
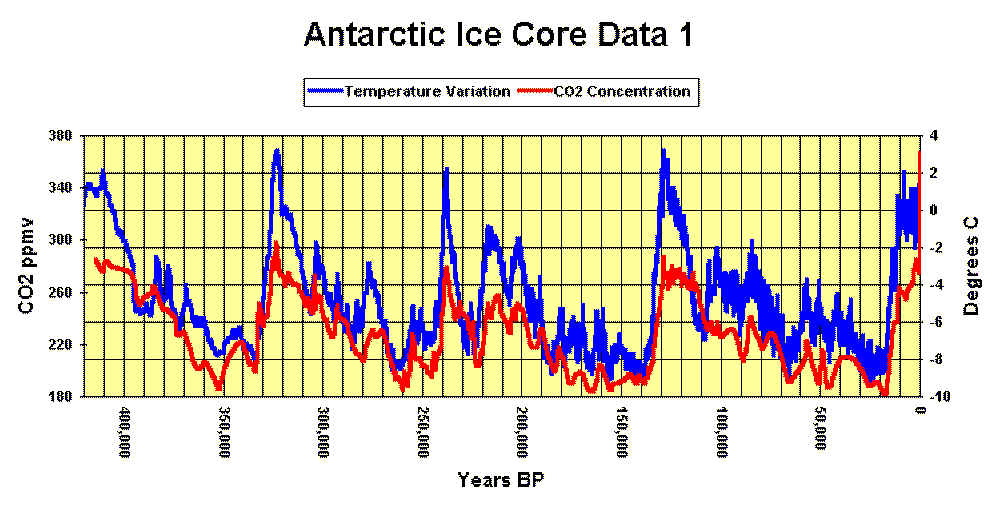
What causes ice ages? From charts and graphs a pattern emerges.

Explaining Climate Change
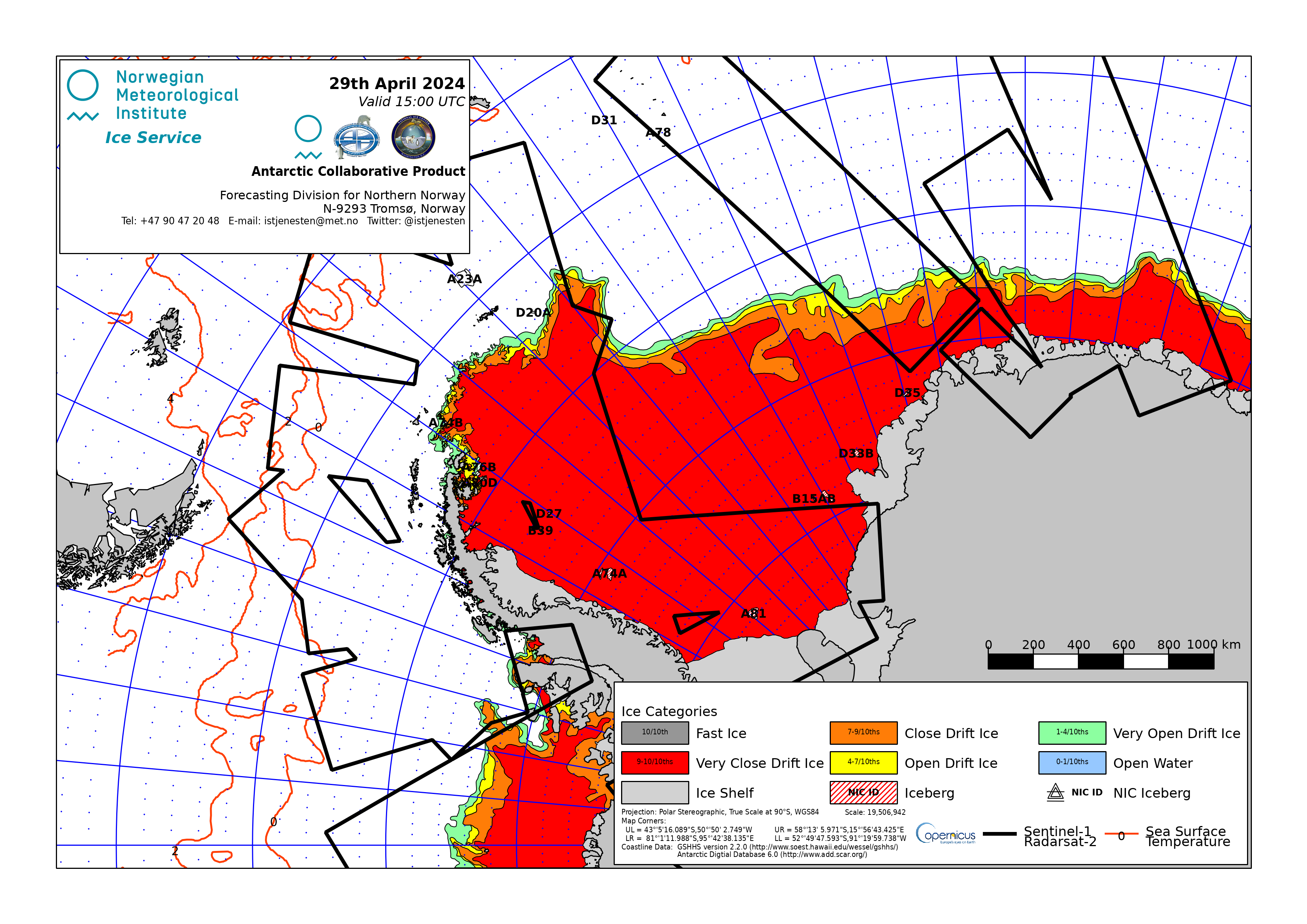
Ice Service charts cryo.met.no
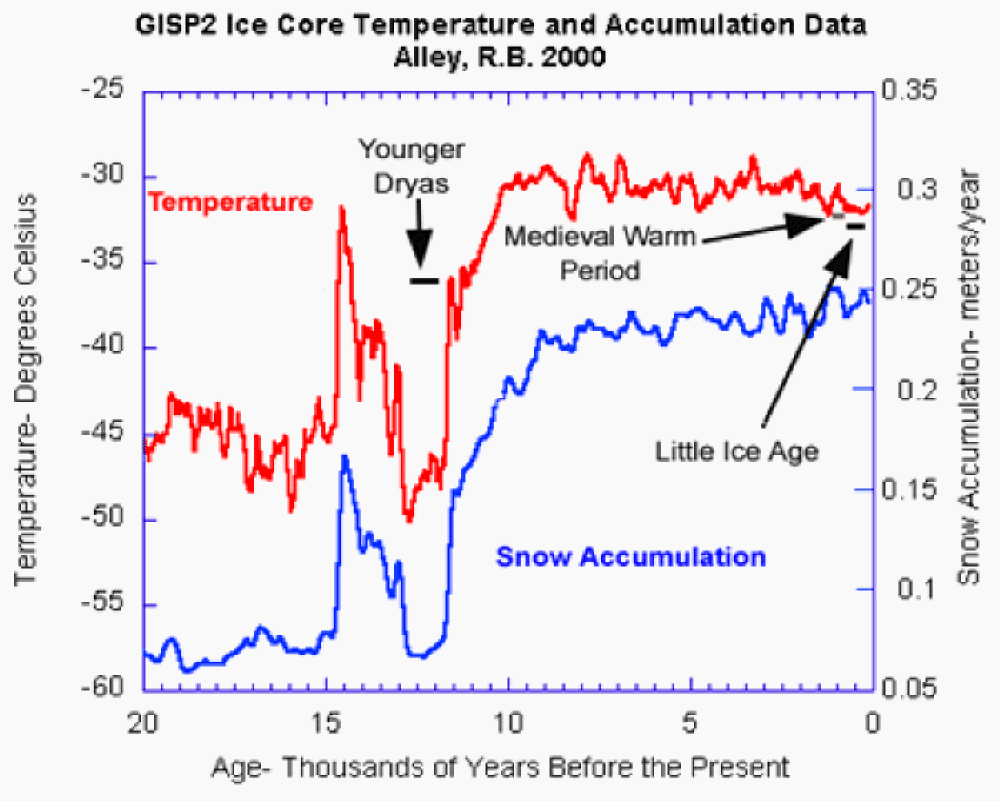
What causes ice ages? From charts and graphs a pattern emerges.
As Long As The Ice Is Thin, It May Be Broken By Strong Winds.
Formation Energies Of Different Ice Surface Phases As A Function Of Order Parameter S.
Ice Is Water That Is Frozen Into A Solid State, Typically Forming At Or Below Temperatures Of 0 ° C, 32 ° F, Or 273.15 K.
Web Infrared Sensors Can Detect Sea Ice Because Its Temperature Is Generally Much Colder Than The Surrounding Ocean.
Related Post: